Ann Lab Med.
2021 May;41(3):323-327. 10.3343/alm.2021.41.3.323.
A Novel Species of the Genus Arsenicicoccus Isolated From Human Blood Using Whole-Genome Sequencing
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Daejeon Eulji Medical Center, Eulji University, Daejeon, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Urology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Integrative Biology and Physiology, University of California, Los Angeles, USA
- KMID: 2512691
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2021.41.3.323
Abstract
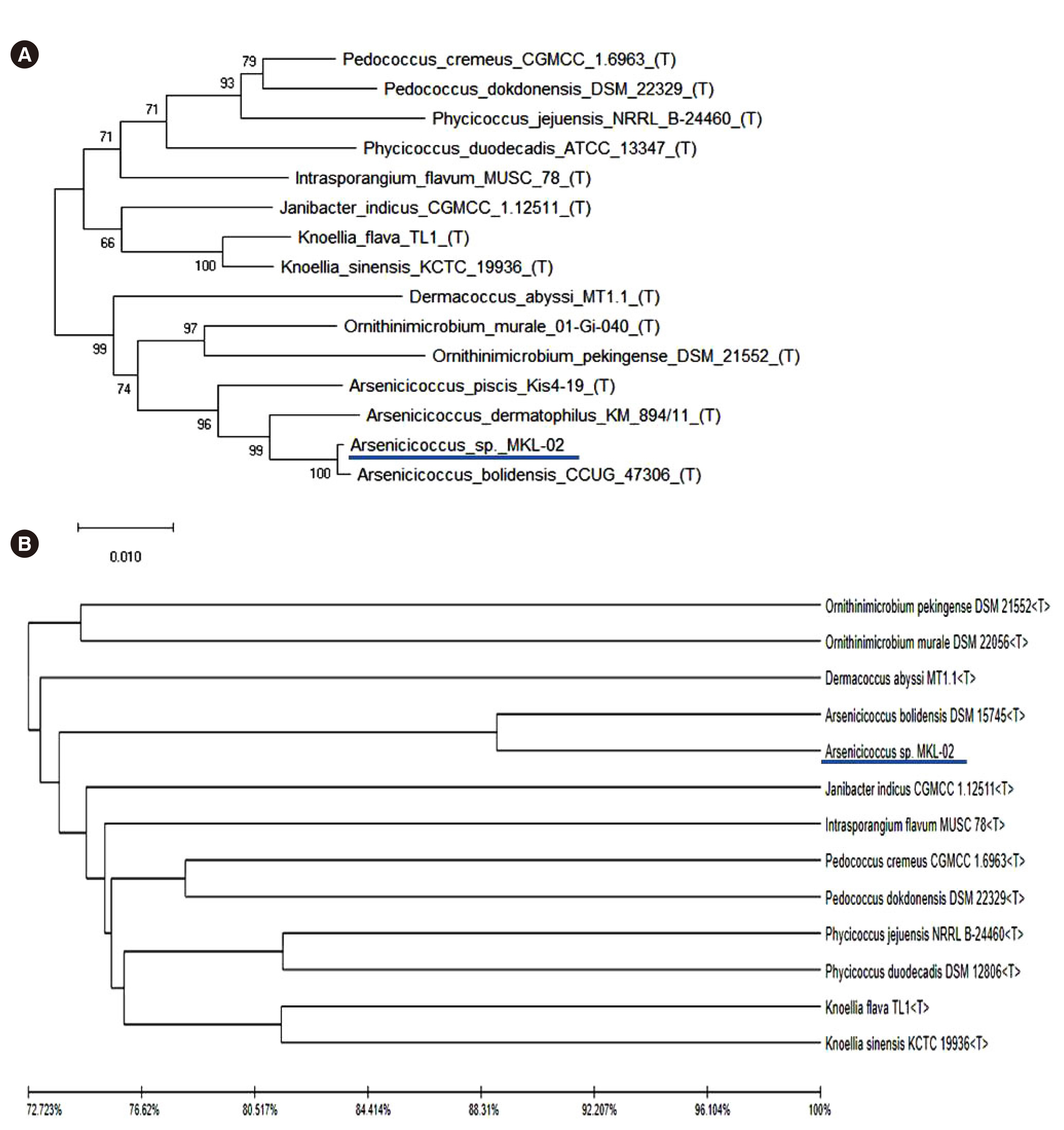
- Whole-genome sequencing (WGS) is an easily accessible and valuable tool in clinical microbiology, which can be used for identifying novel and rare species. We isolated grampositive cocci from the blood of a pediatric patient, which could not be phenotypically identified using matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) (BioMérieux, Marcy-l’Étoile, France). We could not identify the isolate to the species level using 16S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) sequencing. WGS was performed using the Illumina MiSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA); however, the subsequent genomic sequence database search using the TrueBac ID-Genome system (ChunLab, Inc., Seoul, Korea) did not yield any hits with an average nucleotide identity value > 95.0%, which is the cut-off for species-level identification. Phylogenetic analysis suggested that the isolate belonged to a new Arsenicicoccus species, forming a subcluster with Arsenicicoccus bolidensis. Our data demonstrate that WGS allows a more accurate annotation of microbial genomes than other clinical microbiology tools, such as MALDITOF MS and 16S rRNA sequencing. This is the first report of the isolation of a novelArsenicicoccus species from a clinical sample.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Collins MD, Routh J, Saraswathy A, Lawson PA, Schumann P, Welinder-Olsson C, et al. 2004; Arsenicicoccus bolidensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel actinomycete isolated from contaminated lake sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 54:605–8. DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.02918-0. PMID: 15023982.2. Hamada M, Iino T, Iwami T, Tamura T, Harayama S, Suzuki KI. 2009; Arsenicicoccus piscis sp. nov., a mesophilic actinobacterium isolated from the intestinal tract of a fish. Actinomycetologica. 23:40–5. DOI: 10.3209/saj.SAJ230206.3. Gobeli S, Thomann A, Wyss F, Kuehni-Boghenbor K, Brodard I, Perreten V. 2013; Arsenicicoccus dermatophilus sp. nov., a hypha-forming bacterium isolated from the skin of greater flamingos (Phoenicopterus roseus) with pododermatitis. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 63:4046–51. DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.048546-0. PMID: 23728373.4. Routh J, Saraswathy A, Collins MD. 2007; Arsenicicoccus bolidensis a novel arsenic reducing actinomycete in contaminated sediments near the Adak mine (northern Sweden): impact on water chemistry. Sci Total Environ. 379:216–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2006.06.027. PMID: 17064754.5. CLSI. 2008. Interpretive criteria for identification of bacteria and fungi by DNA target sequencing; approved guideline. CLSI MM18-AE. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:6. Chun J, Oren A, Ventosa A, Christensen H, Arahal DR, da Costa MS, et al. 2018; Proposed minimal standards for the use of genome data for the taxonomy of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 68:461–6. DOI: 10.1099/ijsem.0.002516. PMID: 29292687.
Article7. CLSI. 2019. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing. CLSI supplement M100-S29. 29th ed. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute;Wayne, PA:8. Doern GV, Brecher SM. 2011; The clinical predictive value (or lack thereof) of the results of in vitro antimicrobial susceptibility tests. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 49:S11–S4. DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00580-11. PMCID: PMC3185848.
Article9. Yoon SH, Ha SM, Lim J, Kwon S, Chun J. 2017; A large-scale evaluation of algorithms to calculate average nucleotide identity. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 110:1281–6. DOI: 10.1007/s10482-017-0844-4. PMID: 28204908.
Article10. Ha SM, Kim CK, Roh J, Byun JH, Yang SJ, Choi SB, et al. 2019; Application of the whole genome-based bacterial identification system, TrueBac ID, using clinical isolates that were not identified with three matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) systems. Ann Lab Med. 39:530–6. DOI: 10.3343/alm.2019.39.6.530. PMID: 31240880. PMCID: PMC6660342.
Article11. Kim M, Oh HS, Park SC, Chun J. 2014; Towards a taxonomic coherence between average nucleotide identity and 16S rRNA gene sequence similarity for species demarcation of prokaryotes. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 64:346–51. DOI: 10.1099/ijs.0.059774-0. PMID: 24505072.
Article12. Richter M, Rosselló-Móra R. 2009; Shifting the genomic gold standard for the prokaryotic species definition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 106:19126–31. DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0906412106. PMID: 19855009. PMCID: PMC2776425.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Distribution of Malassezia Species on the Normal Human Skin According to Body Region
- Exome Sequencing in Mendelian Disorders
- National human genome projects: an update and an agenda
- A New Marine Species of Miracula (Oomycota) Parasitic to Minidiscus sp. in Iceland
- Next Generation DNA Sequencing and Its Application in Clinical Medicine