Restor Dent Endod.
2020 Aug;45(3):e36. 10.5395/rde.2020.45.e36.
Bonding of a resin-modified glass ionomer cement to dentin using universal adhesives
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Restorative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Süleyman Demirel University, Isparta, Turkey
- KMID: 2512027
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/rde.2020.45.e36
Abstract
Objectives
This study aims to assess the effect of universal adhesives pretreatment on the bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement to dentin.
Materials and Methods
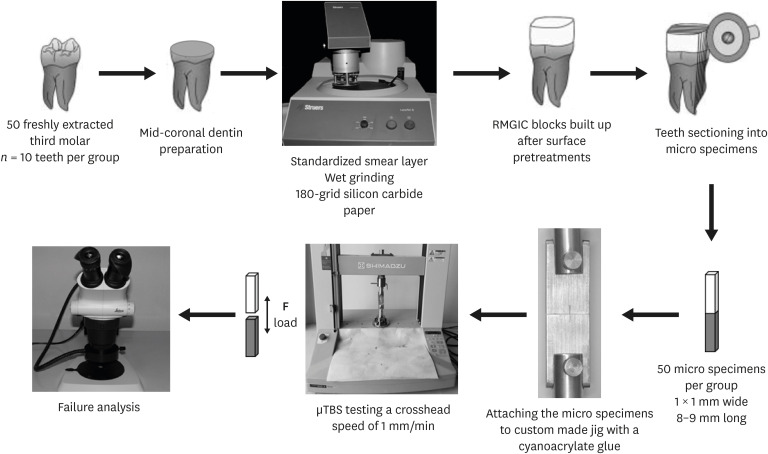
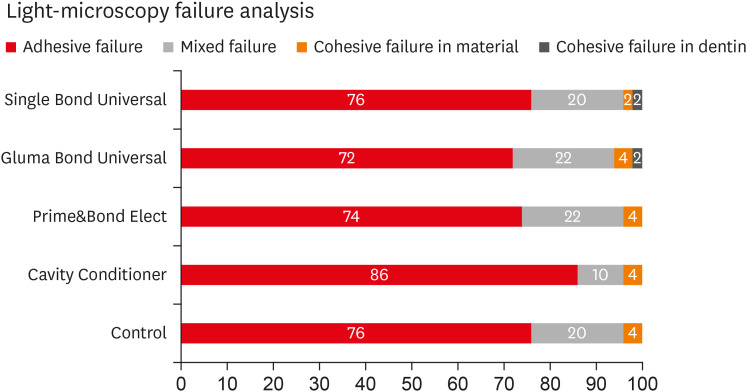
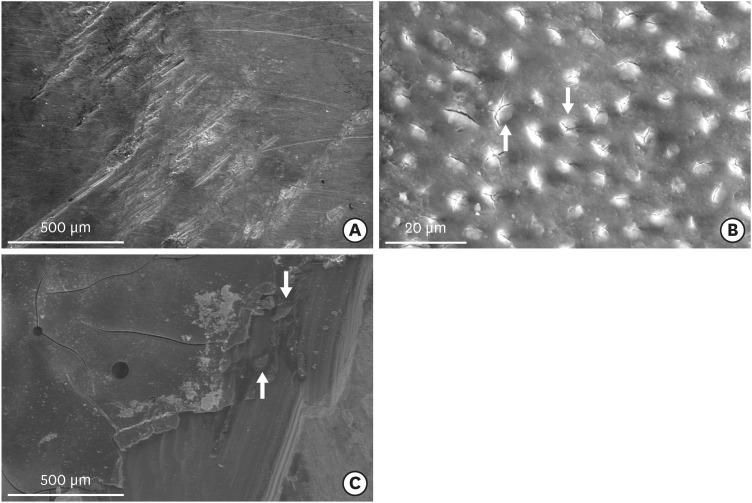
Fifty caries-free human third molars were employed. The teeth were randomly assigned into five groups (n = 10) based on dentin surface pretreatments: Single Bond Universal (3M Oral Care), Gluma Bond Universal (Heraeus Kulzer), Prime&Bond Elect (Dentsply), Cavity Conditioner (GC) and control (no surface treatment). After Fuji II LC (GC) was bonded to the dentin surfaces, the specimens were stored for 7 days at 37°C. The specimens were segmented into microspecimens, and the microspecimens were subjugated to microtensile bond strength testing (1.0 mm/min). The modes of failure analyzed using a stereomicroscope and scanning electron microscopy. Data were statistically analyzed with one-way analysis of variance and Duncan tests (p = 0.05).
Results
The surface pretreatments with the universal adhesives and conditioner increased the bond strength of Fuji II LC to dentin (p < 0.05). Single Bond Universal and Gluma Bond Universal provided higher bond strength to Fuji II LC than Cavity Conditioner (p < 0.05). The bond strengths obtained from Prime&Bond Elect and Cavity Conditioner were not statistically different (p> 0.05).
Conclusions
The universal adhesives and polyacrylic acid conditioner could increase the bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement (RMGIC) to dentin. The use of universal adhesives before the application of RMGIC may be more beneficial in improving bond strength.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wilson AD, Kent BE. A new translucent cement for dentistry. The glass ionomer cement. Br Dent J. 1972; 132:133–135. PMID: 4501690.
Article2. Garoushi S, Vallittu PK, Lassila L. Characterization of fluoride releasing restorative dental materials. Dent Mater J. 2018; 37:293–300. PMID: 29279547.
Article3. Burgess J, Norling B, Summitt J. Resin ionomer restorative materials: the new generation. J Esthet Dent. 1994; 6:207–215. PMID: 8593217.
Article4. Saad A, Inoue G, Nikaido T, Ikeda M, Burrow MF, Tagami J. Microtensile bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement to sound and artificial caries-affected root dentin with different conditioning. Oper Dent. 2017; 42:626–635. PMID: 28857710.
Article5. Imbery TA, Namboodiri A, Duncan A, Amos R, Best AM, Moon PC. Evaluating dentin surface treatments for resin-modified glass ionomer restorative materials. Oper Dent. 2013; 38:429–438. PMID: 23088188.
Article6. Hoshika S, De Munck J, Sano H, Sidhu SK, Van Meerbeek B. Effect of conditioning and aging on the bond strength and interfacial morphology of glass-ionomer cement bonded to dentin. J Adhes Dent. 2015; 17:141–146. PMID: 25859569.7. Cardoso MV, Delmé KI, Mine A, Neves Ade A, Coutinho E, De Moor RJ, Van Meerbeek B. Towards a better understanding of the adhesion mechanism of resin-modified glass-ionomers by bonding to differently prepared dentin. J Dent. 2010; 38:921–929. PMID: 20728505.
Article8. Coutinho E, Van Landuyt K, De Munck J, Poitevin A, Yoshida Y, Inoue S, Peumans M, Suzuki K, Lambrechts P, Van Meerbeek B. Development of a self-etch adhesive for resin-modified glass ionomers. J Dent Res. 2006; 85:349–353. PMID: 16567557.
Article9. Vargas MA, Fortin D, Swift EJ Jr. Bond strengths of glass ionomers using a dentin adhesive. Am J Dent. 1995; 8:197–200. PMID: 7576387.10. El-Askary F, Nassif M. Bonding nano-filled resin-modified glass ionomer to dentin using different self-etch adhesives. Oper Dent. 2011; 36:413–421. PMID: 21819202.
Article11. Poggio C, Beltrami R, Scribante A, Colombo M, Lombardini M. Effects of dentin surface treatments on shear bond strength of glass-ionomer cements. Ann Stomatol (Roma). 2014; 5:15–22.
Article12. Saad A, Inoue G, Nikaido T, Abdou AMA, Sayed M, Burrow MF, Tagami J. Effect of dentin contamination with two hemostatic agents on bond strength of resin-modified glass ionomer cement with different conditioning. Dent Mater J. 2019; 38:257–263. PMID: 30504695.
Article13. Dursun E, Attal JP. Combination of a self-etching adhesive and a resin-modified glass ionomer: effect of water and saliva contamination on bond strength to dentin. J Adhes Dent. 2011; 13:439–443. PMID: 20978640.14. Besnault C, Attal JP, Ruse D, Degrange M. Self-etching adhesives improve the shear bond strength of a resin-modified glass-ionomer cement to dentin. J Adhes Dent. 2004; 6:55–59. PMID: 15119588.15. Pereira PN, Yamada T, Inokoshi S, Burrow MF, Sano H, Tagami J. Adhesion of resin-modified glass ionomer cements using resin bonding systems. J Dent. 1998; 26:479–485. PMID: 9699441.
Article16. Van Meerbeek B, Yoshihara K, Yoshida Y, Mine A, De Munck J, Van Landuyt KL. State of the art of self-etch adhesives. Dent Mater. 2011; 27:17–28. PMID: 21109301.
Article17. Wagner A, Wendler M, Petschelt A, Belli R, Lohbauer U. Bonding performance of universal adhesives in different etching modes. J Dent. 2014; 42:800–807. PMID: 24814138.
Article18. Cuevas-Suárez CE, da Rosa WLO, Lund RG, da Silva AF, Piva E. Bonding performance of universal adhesives: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. J Adhes Dent. 2019; 21:7–26. PMID: 30799468.19. Rosa WL, Piva E, Silva AF. Bond strength of universal adhesives: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Dent. 2015; 43:765–776. PMID: 25882585.
Article20. Sofan E, Sofan A, Palaia G, Tenore G, Romeo U, Migliau G. Classification review of dental adhesive systems: from the IV generation to the universal type. Ann Stomatol (Roma). 2017; 8:1–17. PMID: 28736601.21. Hanabusa M, Mine A, Kuboki T, Momoi Y, Van Ende A, Van Meerbeek B, De Munck J. Bonding effectiveness of a new ‘multi-mode’ adhesive to enamel and dentine. J Dent. 2012; 40:475–484. PMID: 22381614.
Article22. Takamizawa T, Imai A, Hirokane E, Tsujimoto A, Barkmeier WW, Erickson RL, Latta MA, Miyazaki M. SEM observation of novel characteristic of the dentin bond interfaces of universal adhesives. Dent Mater. 2019; 35:1791–1804. PMID: 31727447.
Article23. Cook NB, Feitosa SA, Patel A, Alfawaz Y, Eckert GJ, Bottino MC. Bonding ability of paste-paste glass ionomer systems to tooth structure: in vitro studies. Oper Dent. 2015; 40:304–312. PMID: 25535780.24. Nakanuma K, Hayakawa T, Tomita T, Yamazaki M. Effect of the application of dentin primers and a dentin bonding agent on the adhesion between the resin-modified glass-ionomer cement and dentin. Dent Mater. 1998; 14:281–286. PMID: 10379257.
Article25. Pashley DH. Smear layer: overview of structure and function. Proc Finn Dent Soc. 1992; 88(Supplement 1):215–224. PMID: 1508877.26. Abdalla AI. Morphological interface between hybrid ionomers and dentin with and without smear-layer removal. J Oral Rehabil. 2000; 27:808–814. PMID: 11012857.
Article27. Coutinho E, Yoshida Y, Inoue S, Fukuda R, Snauwaert J, Nakayama Y, De Munck J, Lambrechts P, Suzuki K, Van Meerbeek B. Gel phase formation at resin-modified glass-ionomer/tooth interfaces. J Dent Res. 2007; 86:656–661. PMID: 17586714.
Article28. Yiu CK, Tay FR, King NM, Pashley DH, Carvalho RM, Carrilho MR. Interaction of resin-modified glass-ionomer cements with moist dentine. J Dent. 2004; 32:521–530. PMID: 15304297.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The shear bond strength of two adhesives bonded to composite resin and glass ionomer cement restorations
- COMPARISON OF SHEAR BOND STRENGTH AND MARGINAL LEAKAGE OF RESIN MODIFIED GLASS IONOMER CEMENTS
- The effects of crystal growth on shear bond strength of orthodontic bracket adhesives to enamel surface
- SHEAR BOND STRENGTH OF LUTING CEMENTS TO DENTIN TREATED WITH RESIN BONDING AGENTS
- THE EFFECT OF SURFACE TREATMENT ON FRACTURE STRENGTH OF DENTAL CERAMICS