J Surg Ultrasound.
2020 Nov;7(2):47-54. 10.46268/jsu.2020.7.2.47.
Targeted Axillary Biopsy with Preoperative Ultrasound-Guided Tattooing for Suspicious Axillary Lymph Nodes in Patients with Early Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 2Department of Pathology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 3Department of Nuclear Medicine, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- 4Department of Radiology, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Kyungpook National University Chilgok Hospital, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2511909
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.46268/jsu.2020.7.2.47
Abstract
- Purpose
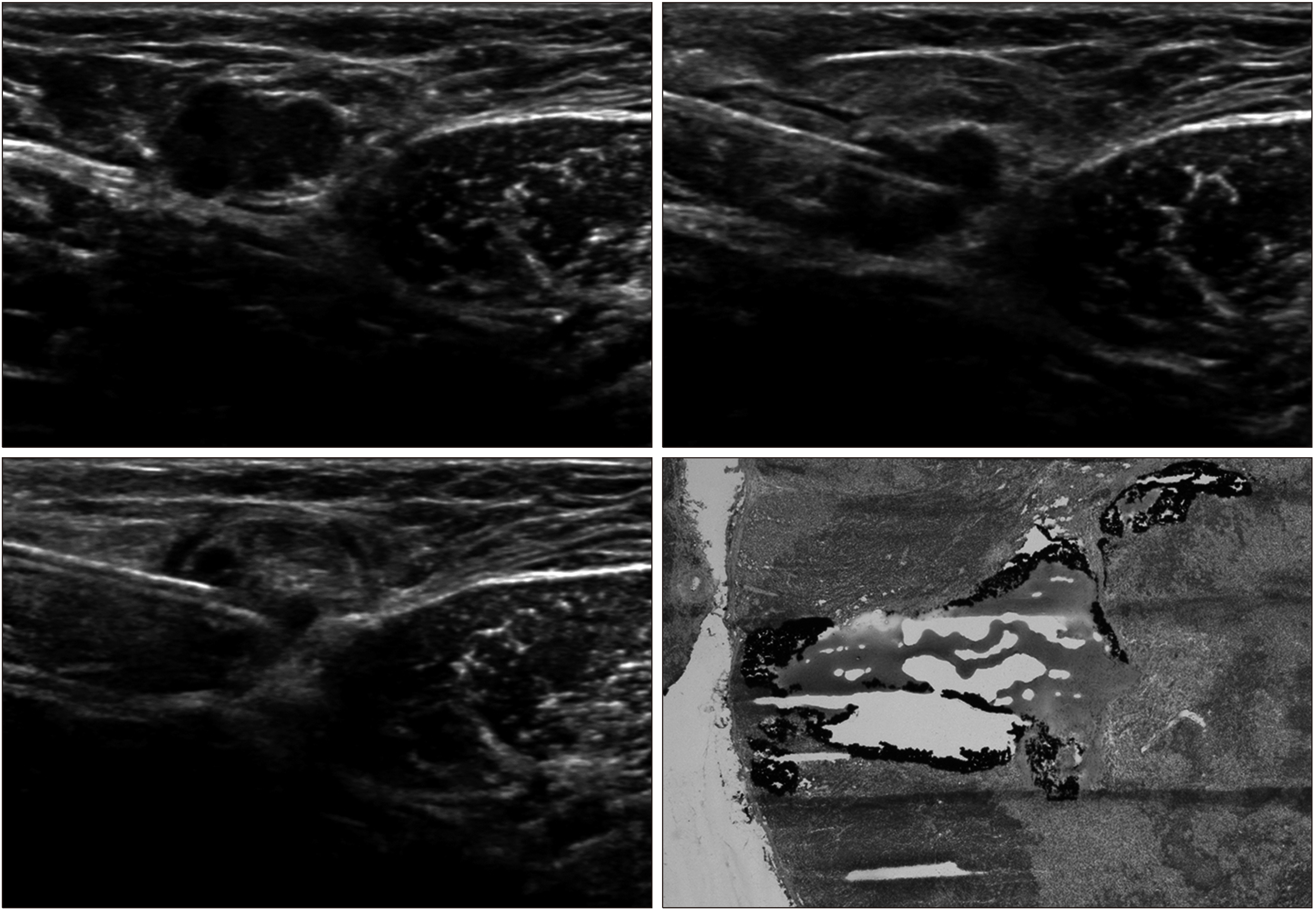
This study evaluated the efficiency of preoperative ultrasound (US)-guided tattooing of the axillary lymph nodes with activated charcoal and the correlation between sonographically suspicious nodes and final histologic results by node-to-node analysis. The concordance rate between the tattooed nodes and sentinel nodes was also determined.
Methods
US-guided tattooing of sonographically suspicious axillary nodes was performed preoperatively by an injection of activated charcoal. The identification of black pigment and the concordance between the sentinel and tattooed nodes was evaluated.
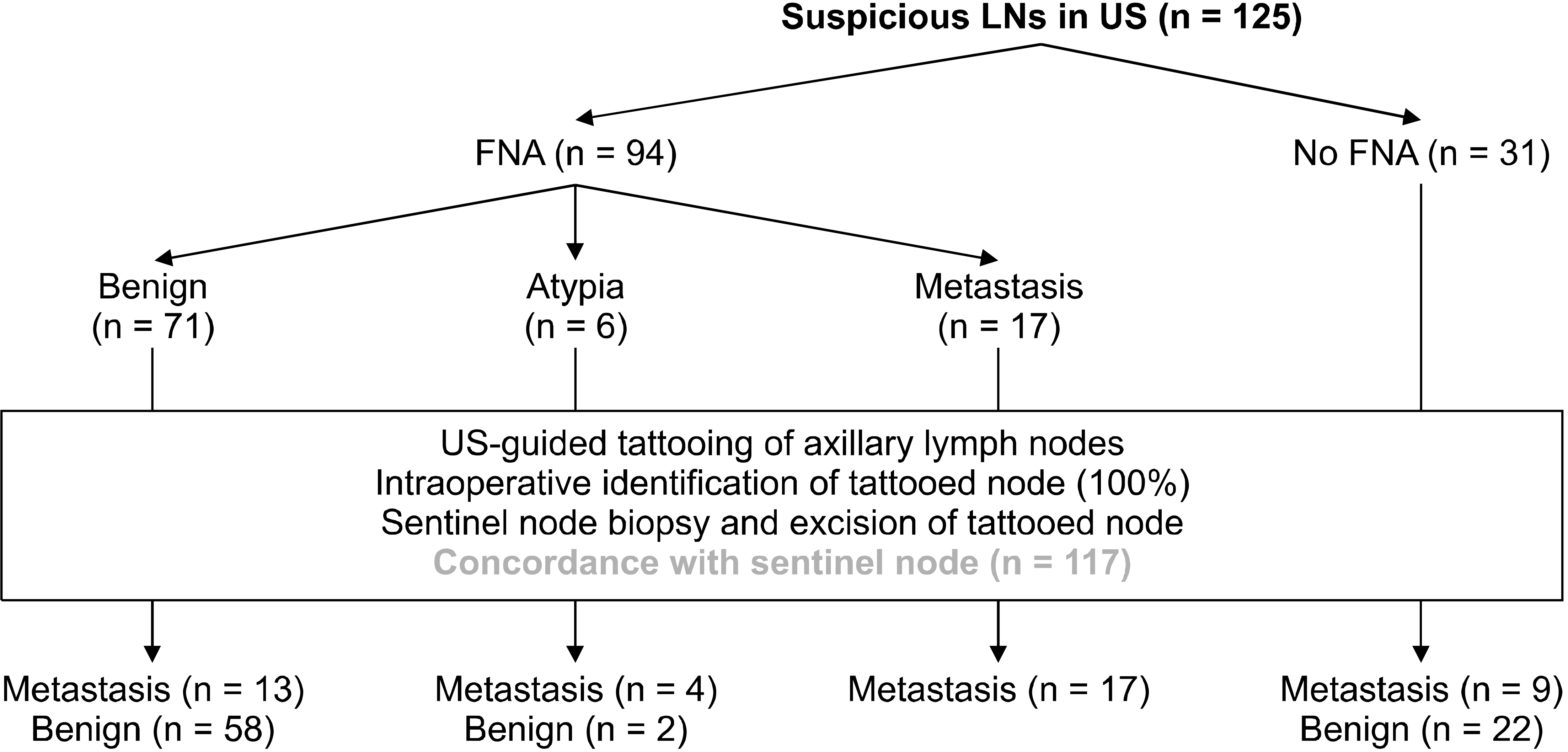
Results
Regarding node-to-node analysis, the false-negative rate of US-fine needle aspiration (FNA) was 43.3%. The sensitivity and negative predictive values were 56.7% and 81.7%, respectively. The specificity and positive predictive values were 100%. The accuracy of US-FNA was 85.2%. In the final pathology, 45/125 patients (36.0%) had positive nodes, including two micrometastases. The false-negative rate of sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) was 4.0%, but there were no skip metastases. The sensitivity and specificity of SLNB were 95.6% and 100%, respectively. The negative predictive value was 97.6%, and the positive predictive value was 100%. The accuracy of SLNB was 98.4%. In 117 of 125 patients (93.6%), there was concordance between the charcoal tattooed axillary lymph nodes and SLNs.
Conclusion
SLNB, in conjunction with US-guided tattooing of sonographically suspicious axillary lymph nodes, is a useful procedure to reduce the false-negative rate of SLNB and improve the accuracy of an intraoperative evaluation of axillary nodes in breast cancer patients. This paper proposes the concept of targeted axillary node biopsy with preoperative US-guided tattooing for the most accurate axillary staging in patients with breast cancer.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Naik AM, Fey J, Gemignani M, Heerdt A, Montgomery L, Petrek J, et al. 2004; The risk of axillary relapse after sentinel lymph node biopsy for breast cancer is comparable with that of axillary lymph node dissection: a follow-up study of 4008 procedures. Ann Surg. 240:462–8. discussion 468–71. DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000137130.23530.19. PMID: 15319717. PMCID: PMC1356436.2. Caudle AS, Cupp JA, Kuerer HM. 2014; Management of axillary disease. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 473–86. DOI: 10.1016/j.soc.2014.03.007. PMID: 24882346.
Article3. Lyman GH, Temin S, Edge SB, Newman LA, Turner RR, Weaver DL, et al. 2014; Sentinel lymph node biopsy for patients with early-stage breast cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J Clin Oncol. 32:1365–83. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2013.54.1177. PMID: 24663048.
Article4. Krag DN, Anderson SJ, Julian TB, Brown AM, Harlow SP, Ashikaga T, et al. 2007; Technical outcomes of sentinel-lymph-node resection and conventional axillary-lymph-node dissection in patients with clinically node-negative breast cancer: results from the NSABP B-32 randomised phase III trial. Lancet Oncol. 8:881–8. DOI: 10.1016/S1470-2045(07)70278-4. PMID: 17851130.
Article5. White RL Jr, Wilke LG. 2004; Update on the NSABP and ACOSOG breast cancer sentinel nodetrials. Am Surg. 70:420–4. PMID: 15156950.6. Goyal A, Newcombe RG, Chhabra A, Mansel RE. ALMANAC Trialists Group. 2006; Factors affecting failed localisation and false-negative rates of sentinel node biopsy in breast cancer--results of the ALMANAC validation phase. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 99:203–8. DOI: 10.1007/s10549-006-9192-1. PMID: 16541308.
Article7. Wang H, Mao XY, Zhao TT, Zheng XY, Jin F, Li JG. 2012; Study on the skip metastasis of axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer and their relation with Gli1 expression. Tumour Biol. 33:1943–50. DOI: 10.1007/s13277-012-0455-7. PMID: 22797820.
Article8. Sun J, Yin J, Ning L, Liu J, Liu H, Gu L, et al. 2012; Clinico-pathological characteristics of breast cancers with axillary skip metastases. J Invest Surg. 25:33–6. DOI: 10.3109/08941939.2011.598605. PMID: 22272635.
Article9. van Rijk MC, Teertstra HJ, Peterse JL, Nieweg OE, Olmos RA, Hoefnagel CA, et al. 2006; Ultrasonography and fine-needle aspiration cytology in the preoperative evaluation of melanoma patients eligible for sentinel node biopsy. Ann Surg Oncol. 13:1511–6. DOI: 10.1245/s10434-006-9106-9. PMID: 17009151.
Article10. Krishnamurthy S, Sneige N, Bedi DG, Edieken BS, Fornage BD, Kuerer HM, et al. 2002; Role of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration of indeterminate and suspicious axillary lymph nodes in the initial staging of breast carcinoma. Cancer. 95:982–8. DOI: 10.1002/cncr.10786. PMID: 12209680.
Article11. Swinson C, Ravichandran D, Nayagam M, Allen S. 2009; Ultrasound and fine needle aspiration cytology of the axilla in the pre-operative identification of axillary nodal involvement in breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol. 35:1152–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejso.2009.03.008. PMID: 19446994.
Article12. Boughey JC, Ballman KV, Hunt KK, McCall LM, Mittendorf EA, Ahrendt GM, et al. 2015; Axillary ultrasound after neoadjuvant chemotherapy and its impact on sentinel lymph node surgery: results from the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z1071 trial (Alliance). J Clin Oncol. 33:3386–93. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2014.57.8401. PMID: 25646192. PMCID: PMC4606058.
Article13. Hyun SJ, Kim EK, Moon HJ, Yoon JH, Kim MJ. 2016; Preoperative axillary lymph node evaluation in breast cancer patients by breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): can breast MRI exclude advanced nodal disease? Eur Radiol. 26:3865–73. DOI: 10.1007/s00330-016-4235-4. PMID: 26843011.
Article14. Park SH, Kim EK, Park BW, Kim SI, Moon HJ, Kim MJ. 2013; False negative results in axillary lymph nodes by ultrasonography and ultrasonography-guided fine-needle aspiration in patients with invasive ductal carcinoma. Ultraschall Med. 34:559–67. DOI: 10.1055/s-0032-1313113. PMID: 23258771.
Article15. Cho N, Moon WK, Han W, Park IA, Cho J, Noh DY. 2009; Preoperative sonographic classification of axillary lymph nodes in patients with breast cancer: node-to-node correlation with surgical histology and sentinel node biopsy results. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 193:1731–7. DOI: 10.2214/AJR.09.3122. PMID: 19933672.
Article16. Donker M, Straver ME, Wesseling J, Loo CE, Schot M, Drukker CA, et al. 2015; Marking axillary lymph nodes with radioactive iodine seeds for axillary staging after neoadjuvant systemic treatment in breast cancer patients: the MARI procedure. Ann Surg. 261:378–82. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000000558. PMID: 24743607.17. Caudle AS, Yang WT, Krishnamurthy S, Mittendorf EA, Black DM, Gilcrease MZ, et al. 2016; Improved axillary evaluation following neoadjuvant therapy for patients with node-positive breast cancer using selective evaluation of clipped nodes: implementation of targeted axillary dissection. J Clin Oncol. 34:1072–8. DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2015.64.0094. PMID: 26811528. PMCID: PMC4933133.
Article18. Yu YH, Mo QG, Zhu X, Gao LQ, Liang C, Huang Z, et al. 2016; Axillary fine needle aspiration cytology is a sensitive and highly specific technique for the detection of axillary lymph node metastasis: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Cytopathology. 27:59–69. DOI: 10.1111/cyt.12224. PMID: 25496004.
Article19. Cserni G. 1999; Estimating the overlap between sentinel lymph nodes and axillary node samples in breast cancer. Pathol Oncol Res. 5:129–33. DOI: 10.1053/paor.1999.0174. PMID: 10393365.
Article20. Macmillan RD, Barbera D, Hadjiminas DJ, Rampaul RS, Lee AH, Pinder SE, et al. 2001; Sentinel node biopsy for breast cancer may have little to offer four-node-samplers. results of a prospective comparison study. Eur J Cancer. 37:1076–80. DOI: 10.1016/S0959-8049(00)00367-1. PMID: 11378336.21. Nathanson SD. 2007; Preclinical models of regional lymph node tumor metastasis. Cancer Treat Res. 135:129–56. DOI: 10.1007/978-0-387-69219-7_10. PMID: 17953413.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Core Needle Biopsy in Detecting Metastatic Axillary Lymph Nodes in Breast Cancer
- Ultrasonography for Staging Axillary Lymph Node in Breast Cancer Patients
- Efficiency of Ultrasound and Ultrasound-Guided Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology in Preoperative Assessment of Axillary Lymph Node Metastases in Breast Cancer
- Surgical Treatment of Breast Cancer
- Evaluation of the Role of Axillary Lymph Node Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology in Early Breast Cancer With or Without Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy