J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2020 Dec;22(4):237-244. 10.7461/jcen.2020.E2020.08.002.
Endovascular coil embolization for unruptured intracranial aneurysms in patients over 80 years of age
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Chungnam National University Hospital, Daejeon, Korea
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Chungnam National University, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2511037
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2020.E2020.08.002
Abstract
Objective
As the average life span in modern society continues to increase, much interest is focused on high-risk procedures in elderly patients, including major surgical operations. We investigated the results of endovascular coiling of unruptured intracranial aneurysms (UIA) in patients over 80 years of age.
Methods
We retrospectively analyzed 39 patients aged over 80 years who underwent coil embolization for UIA between April 2007 and April 2019 at our hospital.
Results
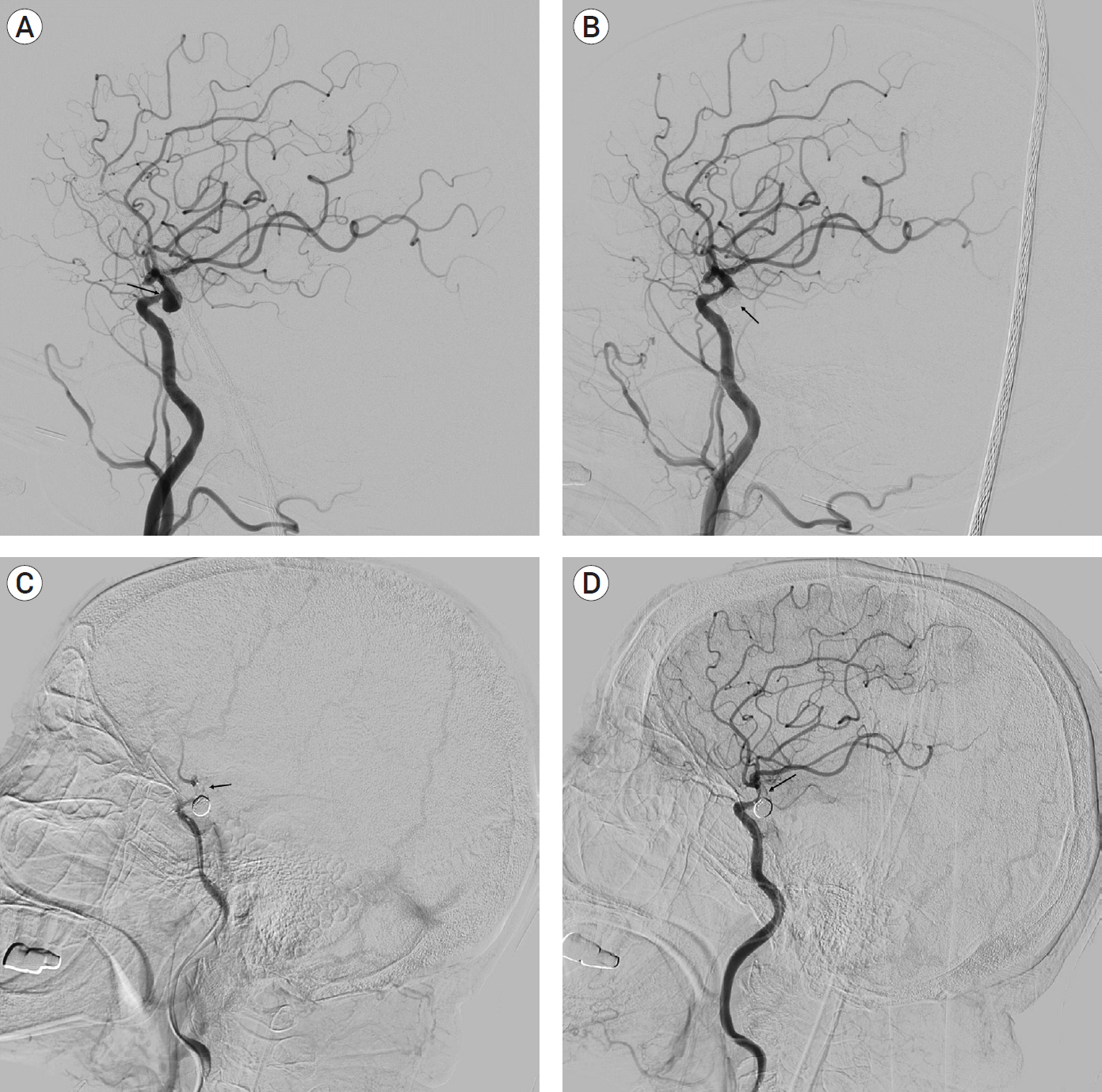
Complete occlusion on digital subtraction angiography (DSA) immediately after surgery was performed in 44 (84.6%) of 52 cases of cerebral aneurysms. Four patients (7.7%) had residual aneurysmal necks, and four (7.7%) had contrast flow in the aneurysmal sac. Follow-up magnetic resonance angiography (mean: 8.2 months) was performed in 37 aneurysms in 24 patients. There was evidence of blood flow in the neck in seven cases (18.9%) and aneurysm in two cases (5.4%). Follow-up DSA (mean: 20.5 months) was performed in 14 aneurysms in 11 patients, and 11 aneurysms (78.6%) had complete occlusion, 1 aneurysm (7.1%) had an aneurysmal neck, and 2 aneurysms (14.3%) had contrast filling into the aneurysmal sac. Coil embolization procedure-related complications occurred in 3 patients (7.7%). Cerebral infarction occurred in 1 (2.6%), arterial dissection in 1 (2.6%), and hypoesthesia in 1 (2.6%).
Conclusions
Active treatment of UIA in elderly patients over 80 years of age through endovascular coil embolization can be considered.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Barker FG 2nd, Amin-Hanjani S, Butler WE, Hoh BL, Rabinov JD, Pryor JC, et al. Age-dependent differences in short-term outcome after surgical or endovascular treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in the United States, 1996-2000. Neurosurgery. 2004; Jan. 54(1):18–28. discussion 28-30.
Article2. Bracard S, Lebedinsky A, Anxionnat R, Neto JM, Audibert G, Long Y, et al. Endovascular treatment of Hunt and Hess grade IV and V aneuryms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; Jun-Jul. 23(6):953–7.3. Brilstra EH, Rinkel GJ, van der Graaf Y, van Rooij WJJ, Algra A. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms by embolization with coils: a systematic review. Stroke. 1999; Feb. 30(2):470–6.4. Cai Y, Spelle L, Wang H, Piotin M, Mounayer C, Vanzin JR, et al. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms in the elderly: single-center experience in 63 consecutive patients. Neurosurgery. 2005; Dec. 57(6):1096–102.
Article5. Chung RY, Carter BS, Norbash A, Budzik R, Putnam C, Ogilvy CS. Management outcomes for ruptured and unruptured aneurysms in the elderly. Neurosurgery. 2000; Oct. 47(4):827–32. discussion 832-3.
Article6. Fridriksson SM, Hillman J, Säveland H, Brandt L. Intracranial aneurysm surgery in the 8th and 9th decades of life: impact on population-based management outcome. Neurosurgery. 1995; Oct. 37(4):627–31. discussion 631-2.7. Gonzalez NR, Dusick JR, Duckwiler G, Tateshima S, Jahan R, Martin NA, et al. Endovascular coiling of intracranial aneurysms in elderly patients: report of 205 treated aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2010; Apr. 66(4):714–20. discussion 720-1.8. Guglielmi G, Vinuela F, Dion J, Duckwiler G. Electrothrombosis of saccular aneurysms via endovascular approach: part 2: preliminary clinical experience. J Neurosurg. 1991; Jul. 75(1):8–14.9. Hamada J, Hasegawa S, Kai Y, Morioka M, Fujioka S, Ushio Y. Surgery and long-term outcome for ruptured anterior circulation aneurysms in patients in their ninth decade of life. Surg Neurol. 1999; Aug. 52(2):123–6. discussion 126-7.
Article10. Hwang G, Jung C, Park SQ, Kang HS, Lee SH, Oh CW, et al. Thromboembolic complications of elective coil embolization of unruptured aneurysms: the effect of oral antiplatelet preparation on periprocedural thromboembolic complication. Neurosurgery. 2010; Sep. 67(3):743–8. discussion 748.11. Hwang SK, Hwang G, Oh CW, Jin SC, Park H, Bang JS, et al. Endovascular treatment for unruptured intracranial aneurysms in elderly patients: single-center report. American journal of neuroradiology. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. Jun-Jul. 2011; 32(6):1087–90.12. Inagawa T, Yamamoto M, Kamiya K, Ogasawara H. Management of elderly patients with aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg. 1988; Sep. 69(3):332–9.
Article13. Iwamoto H, Kiyohara Y, Fujishima M, Kato I, Nakayama K, Sueishi K, et al. Prevalence of intracranial saccular aneurysms in a Japanese community based on a consecutive autopsy series during a 30-year observation period: the Hisayama study. Stroke. 1999; Jul. 30(7):1390–5.14. Johansson M, Cesarini KG, Contant CF, Persson L, Enblad P. Changes in intervention and outcome in elderly patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stroke. 2001; Dec. 32(12):2845–949.
Article15. Johansson M, Norbäck O, Gál G, Cesarini KG, Tovi M, Solander S, et al. Clinical outcome after endovascular coil embolization in elderly patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neuroradiology. 2004; May. 46(5):385–91.
Article16. Kazumata K, Kamiyama H, Ishikawa T. Reference table predicting the outcome of subarachnoid hemorrhage in the elderly, stratified by age. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2006; Jan-Feb. 15(1):14–7.
Article17. Kim JE, Lim DJ, Hong CK, Joo SP, Yoon SM, Kim BT. Treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in South Korea in 2006: a nationwide multicenter survey from the korean society of cerebrovascular surgery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; Feb. 47(2):112–8.18. Lanzino G, Kassell NF, Germanson TP, Kongable GL, Truskowski LL, Torner JC, et al. Treatment of unruptured intracranial aneurysms in South Korea in 2006: a nationwide multicenter survey from the korean society of cerebrovascular surgery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010; Feb. 47(2):112–8.19. Lubicz B, Leclerc X, Gauvrit JY, Lejeune JP, Pruvo JP. Endovascular treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms in elderly people. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; Apr. 25(4):592–5.20. Mont’alverne F, Musacchio M, Tolentino V, Riquelme C, Tournade A. Endovascular management for intracranial ruptured aneurysms in elderly patients: outcome and technical aspects. Neuroradiology. 2005; Jun. 47(6):446–57.
Article21. Nelson PK, Levy DI. Balloon-assisted coil embolization of wide-necked aneurysms of the internal carotid artery: medium-term angiographic and clinical follow-up in 22 patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001; Jan. 22(1):19–26.22. O'sullivan MG, Dorward N, Whittle IR, James A, Steers W, Miller JD. Management and long-term outcome following subarachnoid haemorrhage and intracranial aneurysm surgery in elderly patients: an audit of 199 consecutive cases. Br J Neurosurg. 1994; 8(1):23–30.23. Pelz DM, Lownie SP, Fox AJ. Thromboembolic events associated with the treatment of cerebral aneurysms with Guglielmi detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; Sep. 19(8):1541–7.24. Piotin M, Spelle L, Mounayer C, Salles-Rezende MT, Giansante-Abud D, Vanzin-Santos R, et al. Intracranial aneurysms: treatment with bare platinum coils—aneurysm packing, complex coils, and angiographic recurrence. Radiology. 2007; May. 243(2):500–8.
Article25. Raftopoulos C, Mathurin P, Boscherini D, Billa RF, Van Boven M, Hantson P. Prospective analysis of aneurysm treatment in a series of 103 consecutive patients when endovascular embolization is considered the first option. J Neurosurg. 2000; Aug. 93(2):175–82.
Article26. Rosenørn J, Eskesen V, Schmidt K. Age as a prognostic factor after intracranial aneurysm rupture. Br J Neurosurg. 1987; 1(3):335–41.27. Ryttlefors M, Enblad P, Kerr RS, Molyneux AJ. International subarachnoid aneurysm trial of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling: subgroup analysis of 278 elderly patients. Stroke. 2008; Oct. 39(10):2720–6.28. Sarti C, Tuomilehto J, Salomaa V, Sivenius J, Kaarsalo E, Narva EV, et al. Epidemiology of subarachnoid hemorrhage in Finland from 1983 to 1985. Stroke. 1991; Jul. 22(7):848–53.
Article29. Sawada M, Kaku Y, Hayashi K, Ueda T, Yoshimura S, Sakai N. Endovascular treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms using platinum coils in patients over 70 years of age. Interv Neuroradiol. 2000; Nov. 6(Suppl 1):85–7.
Article30. Sedat J, Dib M, Lonjon M, Litrico S, Von Langsdorf D, Fontaine D, et al. Endovascular treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms in patients aged 65 years and older: follow-up of 52 patients after 1 year. Stroke. 2002; Nov. 33(11):2620–5.31. Soeda A, Sakai N, Sakai H, Iihara K, Yamada N, Imakita S, et al. Thromboembolic events associated with Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of asymptomatic cerebral aneurysms: evaluation of 66 consecutive cases with use of diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; Jan. 24(1):127–32.32. Weir RU, Marcellus ML, Do HM, Steinberg GK, Marks MP. Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage in patients with Hunt and Hess grade 4 or 5: treatment using the Guglielmi detachable coil system. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2003; Apr. 24(4):585–90.33. Yamashita K, Kashiwagi S, Kato S, Takasago T, Ito H. Cerebral aneurysms in the elderly in Yamaguchi, Japan: analysis of the Yamaguchi Data Bank of cerebral aneurysm from 1985 to 1995. Stroke. 1997; Oct. 28(10):1926–31.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Delayed Complications after Uneventful Coil Embolization of Unruptured Aneurysms : Case Report
- Unruptured Aneurysms-Endovascular Treatment
- Recent Trends in the Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms: Comparison between Endovascular Coil Embolization and Surgical Clipping
- Clinical Analysis of Surgical and Endovascular Treatment of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm
- Ruptured Very Small Cerebral Aneurysms and the Usefulness of Coil Embolization