Ann Rehabil Med.
2020 Dec;44(6):468-480. 10.5535/arm.20100.
Exercise Program Improves Functional Capacity and Quality of Life in Uncorrected Atrial Septal Defect-Associated Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: A Randomized-Control Pilot Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Cardiology and Vascular Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Universitas Gadjah Mada/Dr. Sardjito Hospital, Jogjakarta, Indonesia
- 2Division of Cardiovascular Medicine, Department of Internal Medicine, Kobe University Graduate School of Medicine, Kobe, Japan
- 3Laboratory of Clinical Pharmaceutical Science, Kobe Pharmaceutical University, Kobe, Japan
- KMID: 2510814
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.20100
Abstract
Objective
To assess the effect of combined hospital and home-based exercise programs on functional capacity and quality of life (QoL) among uncorrected atrial septal defect-associated pulmonary arterial hypertension (ASD-PAH) patients.
Methods
This study was a randomized controlled trial with uncorrected ASD-PAH patients as the subjects. They were allocated randomly into control and exercise groups. Exercise group subjects performed hospital and home-based exercise programs, completing baseline 6-minute walking test (6MWT) and EQ-5D-3L QoL test (Utility Index and EQ-VAS scores), and were followed up for 12 weeks. The primary outcomes were 6MWT distance and EQ-5D-3L score at week 12. The N-terminal pro B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) level was also assessed. A repeated-measure ANOVA was performed to detect endpoint differences over time.
Results
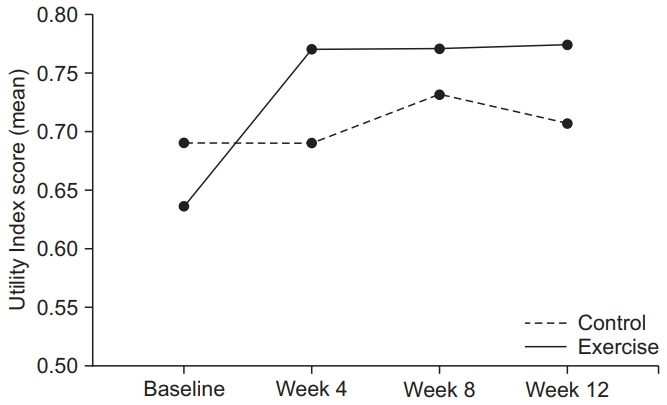
The exercise group contained 20 subjects and control group contained 19. In total, 19 exercise group subjects and 16 control group subjects completed the protocol. The 6MWT distance, Utility Index score, and EQ-VAS score incrementally improved significantly in the exercise group from baseline until week 12, with mean differences of 76.7 m (p<0.001), 0.137 (p<0.001) and 15.5 (p<0.001), respectively. Compared with the control group, the exercise group had significantly increased 6MWT distance and utility index score at week 12. The EQ-VAS score increased in the exercise group at week 12. The NT-proBNP level decreased at week 12 in the exercise group.
Conclusion
Combined hospital and home-based exercise program added to PAH-targeted therapy, improving functional capacity and QoL in uncorrected ASD-PAH patients.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lilly SL. Pathophysiology of heart disease: a collaborative project of medical students and faculty. 5th Ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2011.2. Galie N, Humbert M, Vachiery JL, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur Heart J. 2016; 37:67–119.3. D’Alto M, Merola A, Dimopoulos K. Pulmonary hypertension related to congenital heart disease: a comprehensive review. Glob Cardiol Sci Pract. 2015; 2015:42.4. Dinarti LK, Hartopo AB, Kusuma AD, Satwiko MG, Hadwiono MR, Pradana AD, et al. The COngenital HeARt Disease in adult and Pulmonary Hypertension (COHARD-PH) registry: a descriptive study from single-center hospital registry of adult congenital heart disease and pulmonary hypertension in Indonesia. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2020; 20:163.
Article5. Vijarnsorn C, Durongpisitkul K, Chungsomprasong P, Bositthipichet D, Ketsara S, Titaram Y, et al. Contemporary survival of patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension and congenital systemic to pulmonary shunts. PLoS One. 2018; 13:e0195092.
Article6. Sahni S, Capozzi B, Iftikhar A, Sgouras V, Ojrzanowski M, Talwar A. Pulmonary rehabilitation and exercise in pulmonary arterial hypertension: an underutilized intervention. J Exerc Rehabil. 2015; 11:74–9.
Article7. Lilyasari O, Subekti Y, Atika N, Dinarti LK, Putri S, Opitasari C, et al. Economic evaluation of sildenafil for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension in Indonesia. BMC Health Serv Res. 2019; 19:573.
Article8. Dalla Vecchia LAD, Bussotti M. Exercise training in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Thorac Dis. 2018; 10:508–21.
Article9. Gu S, Hu H, Dong H. Systematic review of health-related quality of life in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pharmacoeconomics. 2016; 34:751–70.
Article10. Ehlken N, Lichtblau M, Klose H, Weidenhammer J, Fischer C, Nechwatal R, et al. Exercise training improves peak oxygen consumption and haemodynamics in patients with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension and inoperable chronic thrombo-embolic pulmonary hypertension: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Eur Heart J. 2016; 37:35–44.
Article11. American College of Sports Medicine. ACSM’s resource manual for guideline for exercise testing and prescription. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;2013.12. Mereles D, Ehlken N, Kreuscher S, Ghofrani S, Hoeper MM, Halank M, et al. Exercise and respiratory training improve exercise capacity and quality of life in patients with severe chronic pulmonary hypertension. Circulation. 2006; 114:1482–9.
Article13. ATS Committee on Proficiency Standards for Clinical Pulmonary Function Laboratories. ATS statement: guidelines for the six-minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002; 166:111–7.14. Brooks R. EuroQol: the current state of play. Health Policy. 1996; 37:53–72.
Article15. Tongsiri S, Cairns J. Estimating population-based values for EQ-5D health states in Thailand. Value Health. 2011; 14:1142–5.
Article16. Endarti D, Riewpaiboon A, Thavorncharoensap M, Praditsitthikorn N, Hutubessy R, Kristina SA. A comparison of EQ-5D-3L index scores using Malaysian, Singaporean, Thai, and UK value sets in Indonesian cervical cancer patients. Value Health Reg Issues. 2018; 15:50–5.
Article17. Ehlken N, Verduyn C, Tiede H, Staehler G, Karger G, Nechwatal R, Opitz CF, et al. Economic evaluation of exercise training in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Lung. 2014; 192:359–66.
Article18. Fox BD, Kassirer M, Weiss I, Raviv Y, Peled N, Shitrit D, et al. Ambulatory rehabilitation improves exercise capacity in patients with pulmonary hypertension. J Card Fail. 2011; 17:196–200.
Article19. Richter MJ, Grimminger J, Kruger B, Ghofrani HA, Mooren FC, Gall H, et al. Effects of exercise training on pulmonary hemodynamics, functional capacity and inflammation in pulmonary hypertension. Pulm Circ. 2017; 7:20–37.
Article20. Amedro P, Guillaumont S, Bredy C, Matecki S, Gavotto A. Atrial septal defect and exercise capacity: value of cardio-pulmonary exercise test in assessment and follow-up. J Thorac Dis. 2018; 10(Suppl 24):S2864–73.
Article21. Nashat H, Montanaro C, Li W, Kempny A, Wort SJ, Dimopoulos K, et al. Atrial septal defects and pulmonary arterial hypertension. J Thorac Dis. 2018; 10(Suppl 24):S2953–65.
Article22. Marra AM, Arcopinto M, Bossone E, Ehlken N, Cittadini A, Grunig E. Pulmonary arterial hypertension-related myopathy: an overview of current data and future perspectives. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2015; 25:131–9.
Article23. Tran DL, Lau EMT, Celermajer DS, Davis GM, Cordina R. Pathophysiology of exercise intolerance in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respirology. 2018; 23:148–59.
Article24. Dyer MT, Goldsmith KA, Sharples LS, Buxton MJ. A review of health utilities using the EQ-5D in studies of cardiovascular disease. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2010; 8:13.
Article25. Pepke-Zaba J, Gilbert C, Collings L, Brown MC. Sildenafil improves health-related quality of life in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Chest. 2008; 133:183–9.
Article26. Chan L, Chin LMK, Kennedy M, Woolstenhulme JG, Nathan SD, Weinstein AA, et al. Benefits of intensive treadmill exercise training on cardiorespiratory function and quality of life in patients with pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 2013; 143:333–43.
Article27. Kukkonen M, Puhakka A, Halme M. Quality of life among pulmonary hypertension patients in Finland. Eur Clin Respir J. 2016; 3:26405.
Article28. Grunig E, Lichtblau M, Ehlken N, Ghofrani HA, Reichenberger F, Staehler G, et al. Safety and efficacy of exercise training in various forms of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Respir J. 2012; 40:84–92.
Article29. Eshtehardi P, Mojadidi MK, Khosraviani K, Pamerla M, Zolty R. Effect of digoxin on mortality in patients with isolated right ventricular dysfunction secondary to severe pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014; 63(12_Suppl):A750.
Article30. So PP, Davies RA, Chandy G, Stewart D, Beanlands RS, Haddad H, et al. Usefulness of beta-blocker therapy and outcomes in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Am J Cardiol. 2012; 109:1504–9.
Article31. van Campen JS, de Boer K, van de Veerdonk MC, van der Bruggen CE, Allaart CP, Raijmakers PG, et al. Bisoprolol in idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension: an explorative study. Eur Respir J. 2016; 48:787–96.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Pulmonary arterial hypertension in congenital heart disease: correlation of radiologic index with hemodynamicdata
- The effect of perioperative inhaled iloprost on congenital heart disease with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension
- Transient Use of Oral Bosentan Can Be an Additional Option to Reduce Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in a Patient with Severe Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Associated with Atrial Septal Defect
- Large Atrial Septal Defect Closure in a Patient with Severe Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
- Device Closure of a Large Atrial Septal Defect in a Patient with Severe Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension after 1 Year Use of an Oral Endothelin Receptor Antagonist