Cancer Res Treat.
2021 Jan;53(1):93-103. 10.4143/crt.2020.459.
A Phase II Trial of Osimertinib as the First-Line Treatment of Non–Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring Activating EGFR Mutations in Circulating Tumor DNA: LiquidLung-O-Cohort 1
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital, Hwasun, Korea
- 2Department of Pathology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea
- KMID: 2510651
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2020.459
Abstract
- Purpose
Osimertinib is a potent, irreversible third-generation epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) tyrosine kinase inhibitor for both EGFR-activating and T790M resistant mutation. The treatment efficacy of osimertinib was assessed in previously untreated patients with metastatic non–small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) harboring activating EGFR mutations in circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) as well as tumor DNA.
Materials and Methods
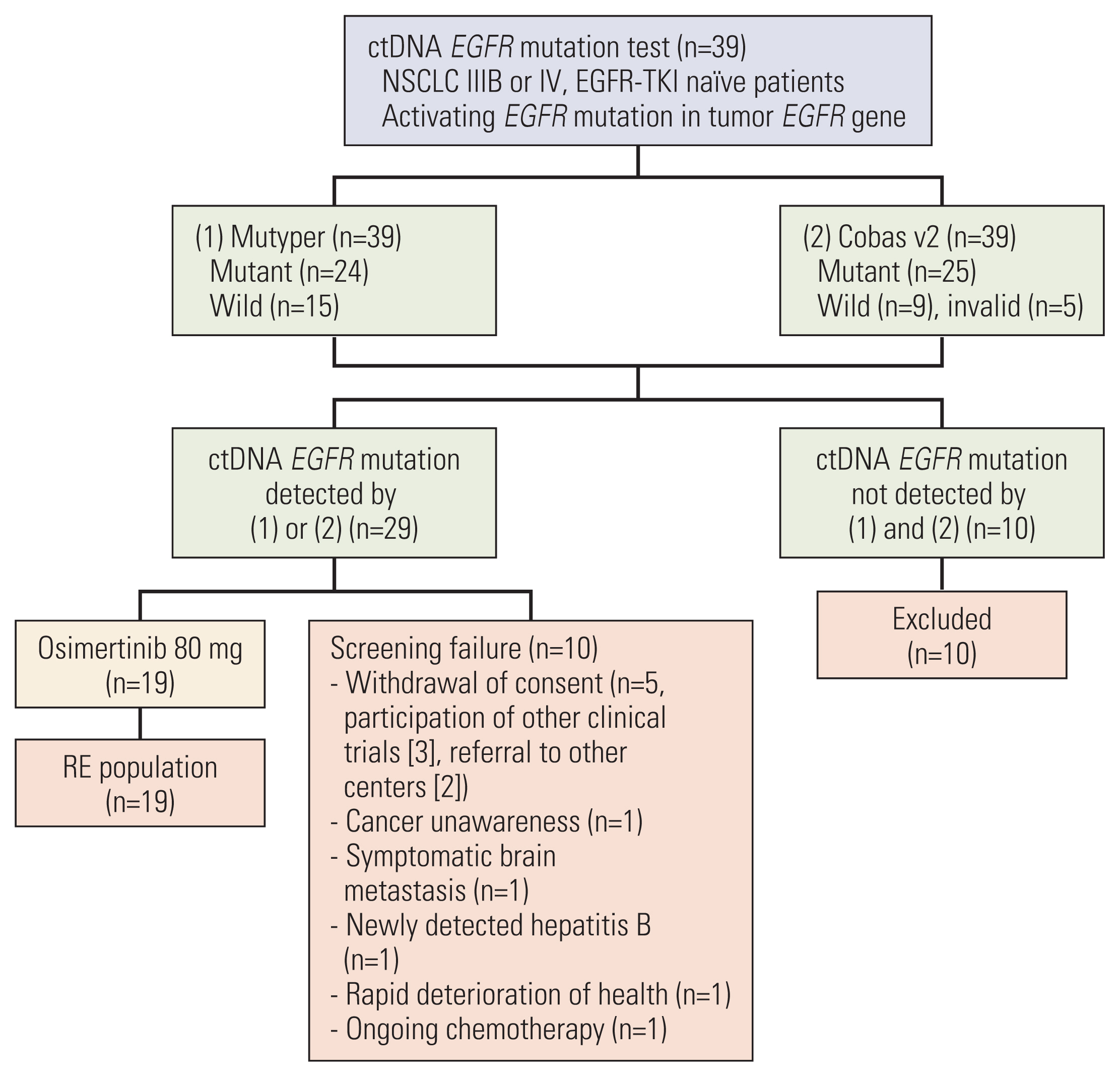
Patients with activating EGFR mutations in their tumor DNA underwent screening with ctDNA analysis using Mutyper and Cobas v2 assays. Enrolled subjects received osimertinib 80 mg, once daily. Primary endpoint was objective response rate (ORR) and secondary endpoints were ctDNA test sensitivity, progression-free survival (PFS), duration of response (DoR), and safety.
Results
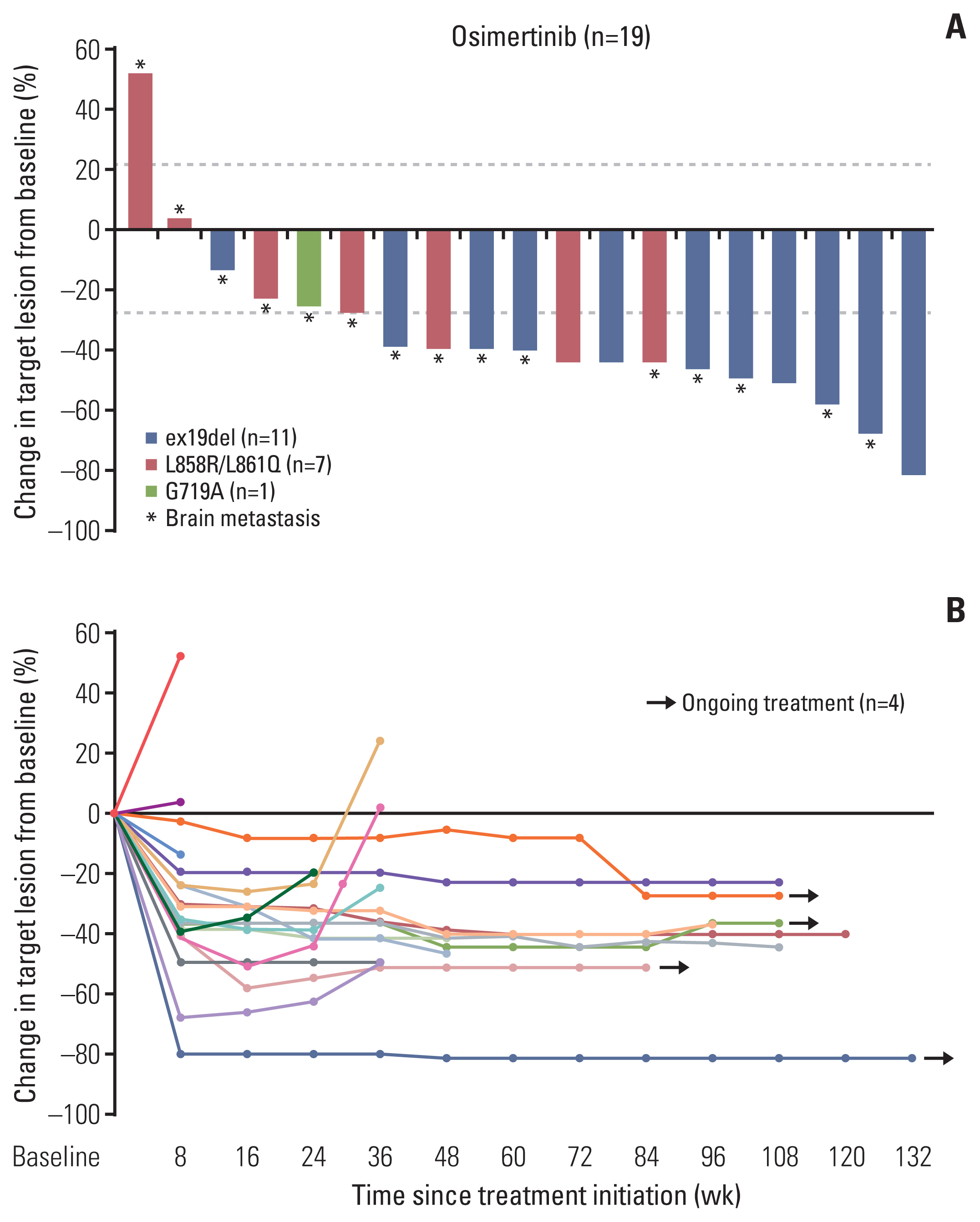
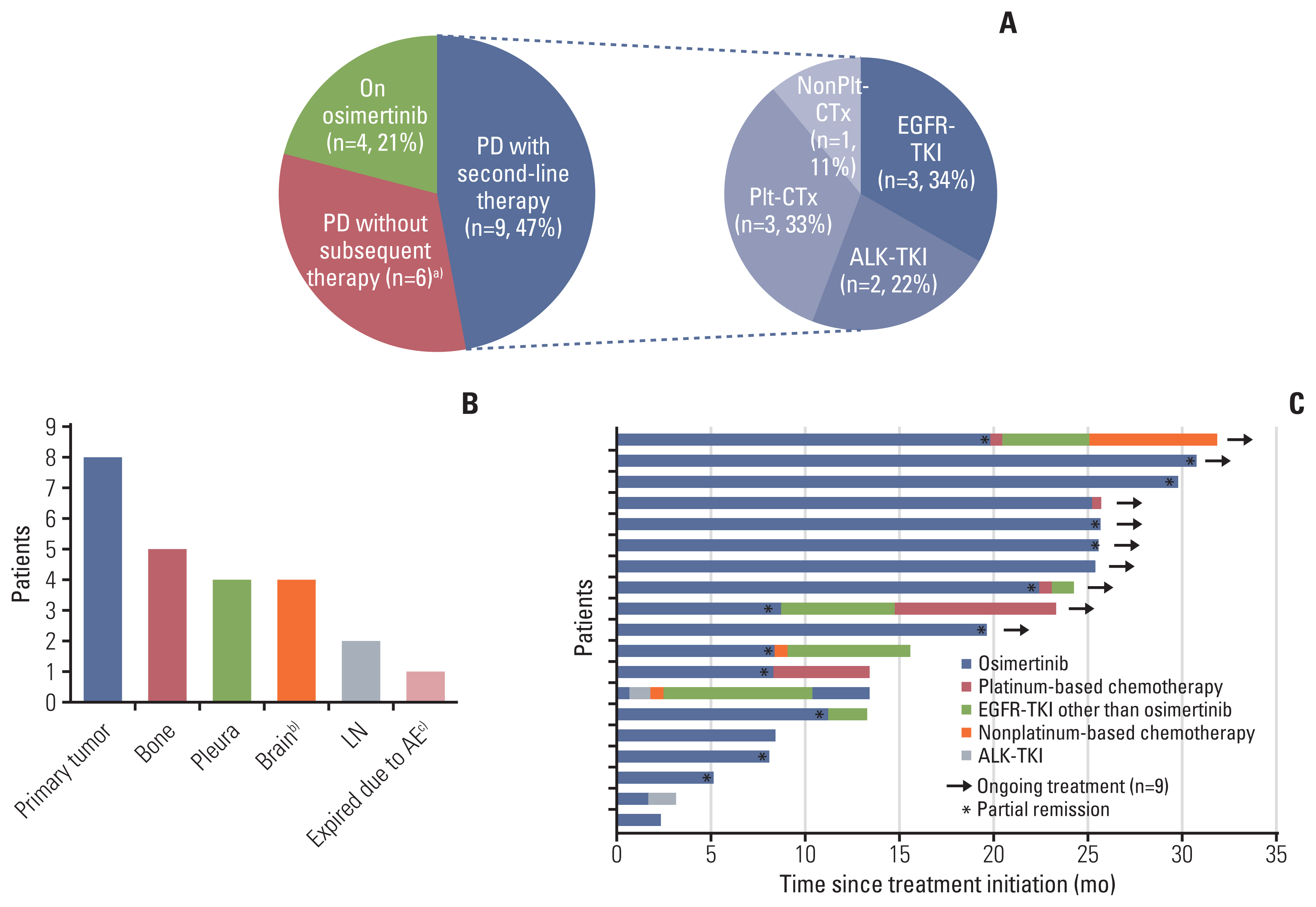
Among 39 screened patients, 29 were ctDNA positive for activating EGFR mutations and 19 were enrolled (ex19del, n=11; L858R/L861Q, n=7; G719A, n=1). Median age was 70 and most patients had brain metastases (15/19, 79%). ctDNA test sensitivity for activating EGFR mutations was 74% using both methods and 62% (Mutyper) or 64% (Cobas v2) for individual methods. ORR was 68% (13/19), median PFS was 11.1 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.0 to 26.7), and median DoR was 17.6 months (95% CI, 3.5 to 31.7). ORR and median PFS were significantly superior with ex19del (91%; 21.9 months; 95% CI, 5.5 to 38.3) than with L858R/L861Q (43%; 5.1 months; 95% CI, 2.3 to 7.9). One patient discontinued the drug because of drug-related interstitial pneumonitis.
Conclusion
Osimertinib had favorable efficacy in the first-line treatment of metastatic NSCLC harboring activating EGFR mutations in ctDNA as well as tumor DNA.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Cross DA, Ashton SE, Ghiorghiu S, Eberlein C, Nebhan CA, Spitzler PJ, et al. AZD9291, an irreversible EGFR TKI, overcomes T790M-mediated resistance to EGFR inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 2014; 4:1046–61.
Article2. Janne PA, Yang JC, Kim DW, Planchard D, Ohe Y, Ramalingam SS, et al. AZD9291 in EGFR inhibitor-resistant non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372:1689–99.
Article3. Yang JC, Ahn MJ, Kim DW, Ramalingam SS, Sequist LV, Su WC, et al. Osimertinib in pretreated T790M-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: AURA study phase II extension component. J Clin Oncol. 2017; 35:1288–96.
Article4. Mok TS, Wu YL, Ahn MJ, Garassino MC, Kim HR, Ramalingam SS, et al. Osimertinib or platinum-pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2017; 376:629–40.
Article5. Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2018; 378:113–25.6. Ramalingam SS, Yang JC, Lee CK, Kurata T, Kim DW, John T, et al. Osimertinib as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018; 36:841–9.
Article7. Ramalingam SS, Vansteenkiste J, Planchard D, Cho BC, Gray JE, Ohe Y, et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:41–50.
Article8. Cho BC, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, Dechaphunkul A, Sriuranpong V, Imamura F, et al. Osimertinib versus standard of care EGFR TKI as first-line treatment in patients with EGFRm advanced NSCLC: FLAURA Asian Subset. J Thorac Oncol. 2019; 14:99–106.
Article9. Ballard P, Yates JW, Yang Z, Kim DW, Yang JC, Cantarini M, et al. Preclinical comparison of osimertinib with other EGFR-TKIs in EGFR-mutant NSCLC brain metastases models, and early evidence of clinical brain metastases activity. Clin Cancer Res. 2016; 22:5130–40.
Article10. Reungwetwattana T, Nakagawa K, Cho BC, Cobo M, Cho EK, Bertolini A, et al. CNS response to osimertinib versus standard epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in patients with untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2018; 36:3290–7.
Article11. Douillard JY, Ostoros G, Cobo M, Ciuleanu T, Cole R, McWalter G, et al. Gefitinib treatment in EGFR mutated caucasian NSCLC: circulating-free tumor DNA as a surrogate for determination of EGFR status. J Thorac Oncol. 2014; 9:1345–53.
Article12. Qiu M, Wang J, Xu Y, Ding X, Li M, Jiang F, et al. Circulating tumor DNA is effective for the detection of EGFR mutation in non-small cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2015; 24:206–12.
Article13. Thress KS, Brant R, Carr TH, Dearden S, Jenkins S, Brown H, et al. EGFR mutation detection in ctDNA from NSCLC patient plasma: a cross-platform comparison of leading technologies to support the clinical development of AZD9291. Lung Cancer. 2015; 90:509–15.
Article14. Park CK, Cho HJ, Choi YD, Oh IJ, Kim YC. A phase II trial of osimertinib in the second-line treatment of non-small cell lung cancer with the EGFR T790M mutation, detected from circulating tumor DNA: LiquidLung-O-Cohort 2. Cancer Res Treat. 2019; 51:777–87.
Article15. Oxnard GR, Thress KS, Alden RS, Lawrance R, Paweletz CP, Cantarini M, et al. Association between plasma genotyping and outcomes of treatment with osimertinib (AZD9291) in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2016; 34:3375–82.
Article16. Gray JE, Okamoto I, Sriuranpong V, Vansteenkiste J, Imamura F, Lee JS, et al. Tissue and plasma EGFR mutation analysis in the FLAURA trial: osimertinib versus comparator EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor as first-line treatment in patients with EGFR-mutated advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2019; 25:6644–52.
Article17. Molina-Vila MA, Stahel RA, Dafni U, Jordana-Ariza N, Balada-Bel A, Garzon-Ibanez M, et al. Evolution and clinical impact of EGFR mutations in circulating free DNA in the BELIEF trial. J Thorac Oncol. 2020; 15:416–25.
Article18. Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, et al. New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer. 2009; 45:228–47.
Article19. Weber B, Meldgaard P, Hager H, Wu L, Wei W, Tsai J, et al. Detection of EGFR mutations in plasma and biopsies from non-small cell lung cancer patients by allele-specific PCR assays. BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:294.
Article20. Jenkins S, Yang JC, Ramalingam SS, Yu K, Patel S, Weston S, et al. Plasma ctDNA analysis for detection of the EGFR T790M mutation in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2017; 12:1061–70.21. Choi CM, Kim HC, Jung CY, Cho DG, Jeon JH, Lee JE, et al. Report of the Korean Association of Lung Cancer Registry (KALC-R), 2014. Cancer Res Treat. 2019; 51:1400–10.
Article22. Sacher AG, Komatsubara KM, Oxnard GR. Application of plasma genotyping technologies in non-small cell lung cancer: a practical review. J Thorac Oncol. 2017; 12:1344–56.
Article23. Bhatt VR, D’Souza SP, Smith LM, Cushman-Vokoun AM, Noronha V, Verma V, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutational status and brain metastases in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Glob Oncol. 2017; 3:208–17.
Article24. Sheng M, Wang F, Zhao Y, Li S, Wang X, Shou T, et al. Comparison of clinical outcomes of patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring epidermal growth factor receptor exon 19 or exon 21 mutations after tyrosine kinase inhibitors treatment: a meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2016; 72:1–11.
Article25. Yang JC, Wu YL, Schuler M, Sebastian M, Popat S, Yamamoto N, et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015; 16:141–51.
Article26. Hong MH, Kim HR, Ahn BC, Heo SJ, Kim JH, Cho BC. Real-world analysis of the efficacy of rebiopsy and EGFR mutation test of tissue and plasma samples in drug-resistant non-small cell lung cancer. Yonsei Med J. 2019; 60:525–34.27. Zhou C, Imamura F, Cheng Y, Okamoto I, Cho BC, Lin MC, et al. Early clearance of plasma EGFR mutations as a predictor of response to osimertinib and comparator EGFR-TKIs in the FLAURA trial. J Clin Oncol. 2019; 37(15 Suppl):9020.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Phase II Trial of Osimertinib in the Second-Line Treatment of Non-small Cell Lung Cancer with the EGFR T790M Mutation, Detected from Circulating Tumor DNA: LiquidLung-O-Cohort 2
- Lazertinib: on the Way to Its Throne
- Assessment of Anti-tumor Efficacy of Osimertinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients by Liquid Biopsy Using Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid, Plasma, or Pleural Effusion
- Real-World Analysis of the Efficacy of Rebiopsy and EGFR Mutation Test of Tissue and Plasma Samples in Drug-Resistant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Long Term Therapeutic Plan for Patients with Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Harboring EGFR Mutation