Acute Crit Care.
2020 Nov;35(4):249-254. 10.4266/acc.2020.00381.
Risk factors for intensive care unit admission and mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Medical College, Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan
- 3Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care, Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan
- 4Department of Infectious Diseases, Aga Khan University, Karachi, Pakistan
- KMID: 2510543
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4266/acc.2020.00381
Abstract
- Background
This study investigated the clinical features and outcome of hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients admitted to our quaternary care hospital.
Methods
In this retrospective cohort study, we included all adult patients with COVID-19 infection admitted to a quaternary care hospital in Pakistan from March 1 to April 15, 2020. The extracted variables included demographics, comorbidities, presenting symptoms, laboratory tests and radiological findings during admission. Outcome measures included in-hospital mortality and length of stay.
Results
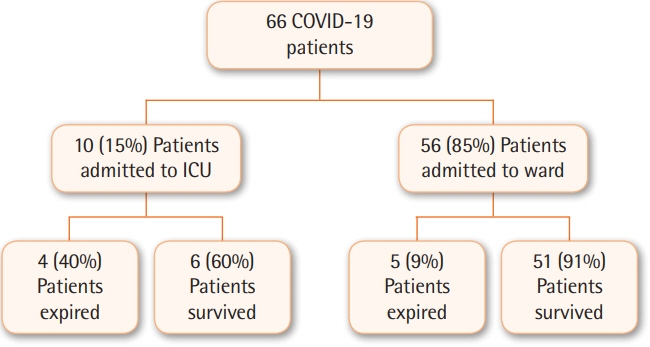
Sixty-six COVID-19 patients were hospitalized during the study period. Sixty-one percent were male and 39% female; mean age was 50.6±19.1 years. Fever and cough were the most common presenting symptoms. Serial chest X-rays showed bilateral pulmonary opacities in 33 (50%) patients. The overall mortality was 14% and mean length of stay was 8.4±8.9 days. Ten patients (15%) required intensive care unit (ICU) care during admission, of which six (9%) were intubated. Age ≥60 years, diabetes, ischemic heart disease, ICU admission, neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio ≥3.3, and international normalized ratio ≥1.2 were associated with increased risk of mortality.
Conclusions
We found a mortality rate of 14% in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. COVID-19 cases are still increasing exponentially around the world and may overwhelm healthcare systems in many countries soon. Our findings can be used for early identification of patients who may require intensive care and aggressive management in order to improve outcomes.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Comparison of characteristics and ventilatory course between coronavirus disease 2019 and Middle East respiratory syndrome patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome
Imran Khalid, Romaysaa M Yamani, Maryam Imran, Muhammad Ali Akhtar, Manahil Imran, Rumaan Gul, Tabindeh Jabeen Khalid, Ghassan Y Wali
Acute Crit Care. 2021;36(3):223-231. doi: 10.4266/acc.2021.00388.
Reference
-
1. Fauci AS, Lane HC, Redfield RR. Covid-19: navigating the uncharted. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:1268–9.2. Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, et al. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:1199–207.
Article3. Open COVID-19 Data Curation Group. Novel corona virus (COVID-19)-healthMap [Internet]. Open COVID-19 Data Curation Group;2020. [cited 2020 Nov 12]. Available from: https://www.healthmap.org/covid-19/.4. Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet. 2020; 395:507–13.
Article5. Mehta P, McAuley DF, Brown M, Sanchez E, Tattersall RS, Manson JJ, et al. COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression. Lancet. 2020; 395:1033–4.
Article6. Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:1708–20.
Article7. Goyal P, Choi JJ, Pinheiro LC, Schenck EJ, Chen R, Jabri A, et al. Clinical characteristics of Covid-19 in New York City. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:2372–4.
Article8. Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S. Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA. 2020; 323:1775–6.
Article9. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020; 395:497–506.
Article10. Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA. 2020; 323:1061–9.
Article11. Mao B, Liu Y, Chai YH, Jin XY, Lu HW, Yang JW, et al. Assessing risk factors for SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients presenting with symptoms in Shanghai, China: a multicentre, observational cohort study. Lancet Digit Health. 2020; 2:e323–30.
Article12. Ai T, Yang Z, Hou H, Zhan C, Chen C, Lv W, et al. Correlation of chest CT and RT-PCR testing for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China: a report of 1014 cases. Radiology. 2020; 296:E32–40.13. Huang P, Liu T, Huang L, Liu H, Lei M, Xu W, et al. Use of chest CT in combination with negative RT-PCR assay for the 2019 novel coronavirus but high clinical suspicion. Radiology. 2020; 295:22–3.14. Chung M, Bernheim A, Mei X, Zhang N, Huang M, Zeng X, et al. CT imaging features of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Radiology. 2020; 295:202–7.15. Volpicelli G, Lamorte A, Villén T. What’s new in lung ultrasound during the COVID-19 pandemic. Intensive Care Med. 2020; 46:1445–8.
Article16. Tang W, Cao Z, Han M, Wang Z, Chen J, Sun W, et al. Hydroxychloroquine in patients with mainly mild to moderate coronavirus disease 2019: open label, randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2020; 369:m1849.
Article17. Beigel JH, Tomashek KM, Dodd LE, Mehta AK, Zingman BS, Kalil AC, et al. Remdesivir for the treatment of Covid-19: final report. N Engl J Med. 2020; 383:1813–26.18. Mahase E. Coronavirus covid-19 has killed more people than SARS and MERS combined, despite lower case fatality rate. BMJ. 2020; 368:m641.
Article19. Gudbjartsson DF, Helgason A, Jonsson H, Magnusson OT, Melsted P, Norddahl GL, et al. Spread of SARS-CoV-2 in the Icelandic population. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:2302–15.
Article20. Arentz M, Yim E, Klaff L, Lokhandwala S, Riedo FX, Chong M, et al. Characteristics and outcomes of 21 critically ill patients with COVID-19 in Washington State. JAMA. 2020; 323:1612–4.
Article21. Bhatraju PK, Ghassemieh BJ, Nichols M, Kim R, Jerome KR, Nalla AK, et al. Covid-19 in critically ill patients in the Seattle region: case series. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382:2012–22.22. Yang J, Zheng Y, Gou X, Pu K, Chen Z, Guo Q, et al. Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Infect Dis. 2020; 94:91–5.
Article23. Rodriguez-Morales AJ, Cardona-Ospina JA, Gutiérrez-Ocampo E, Villamizar-Peña R, Holguin-Rivera Y, Escalera-Antezana JP, et al. Clinical, laboratory and imaging features of COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Travel Med Infect Dis. 2020; 34:101623.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of critically ill COVID-19 and influenza patients with acute respiratory failure
- Evaluation of Patients Treated in Intensıve Care Due to COVID-19: A Retrospective Study
- New-Onset Seizures in Patients With COVID-19: A Case Series From a Single Public Hospital in Korea
- Diabesity Associates with Poor COVID-19 Outcomes among Hospitalized Patients
- COVID-19 infection in lung transplantation patients: single center analysis