Prog Med Phys.
2020 Dec;31(4):189-193. 10.14316/pmp.2020.31.4.189.
Characteristics of Magnetic Resonance-Based Attenuation Correction Map on Phantom Study in Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Imaging System
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiological Science, Daegu Catholic University, Daegu, Korea
- KMID: 2510480
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2020.31.4.189
Abstract
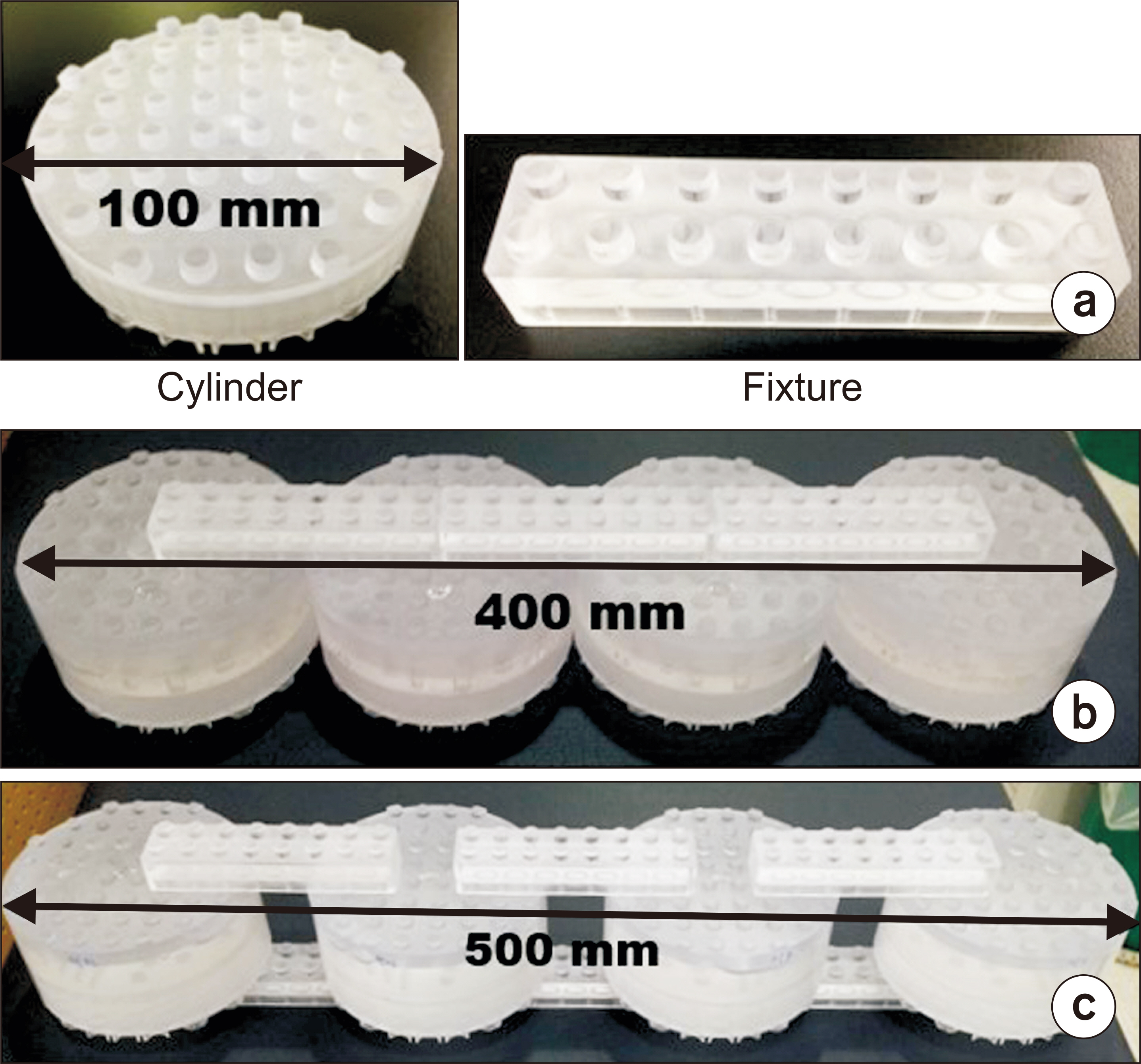
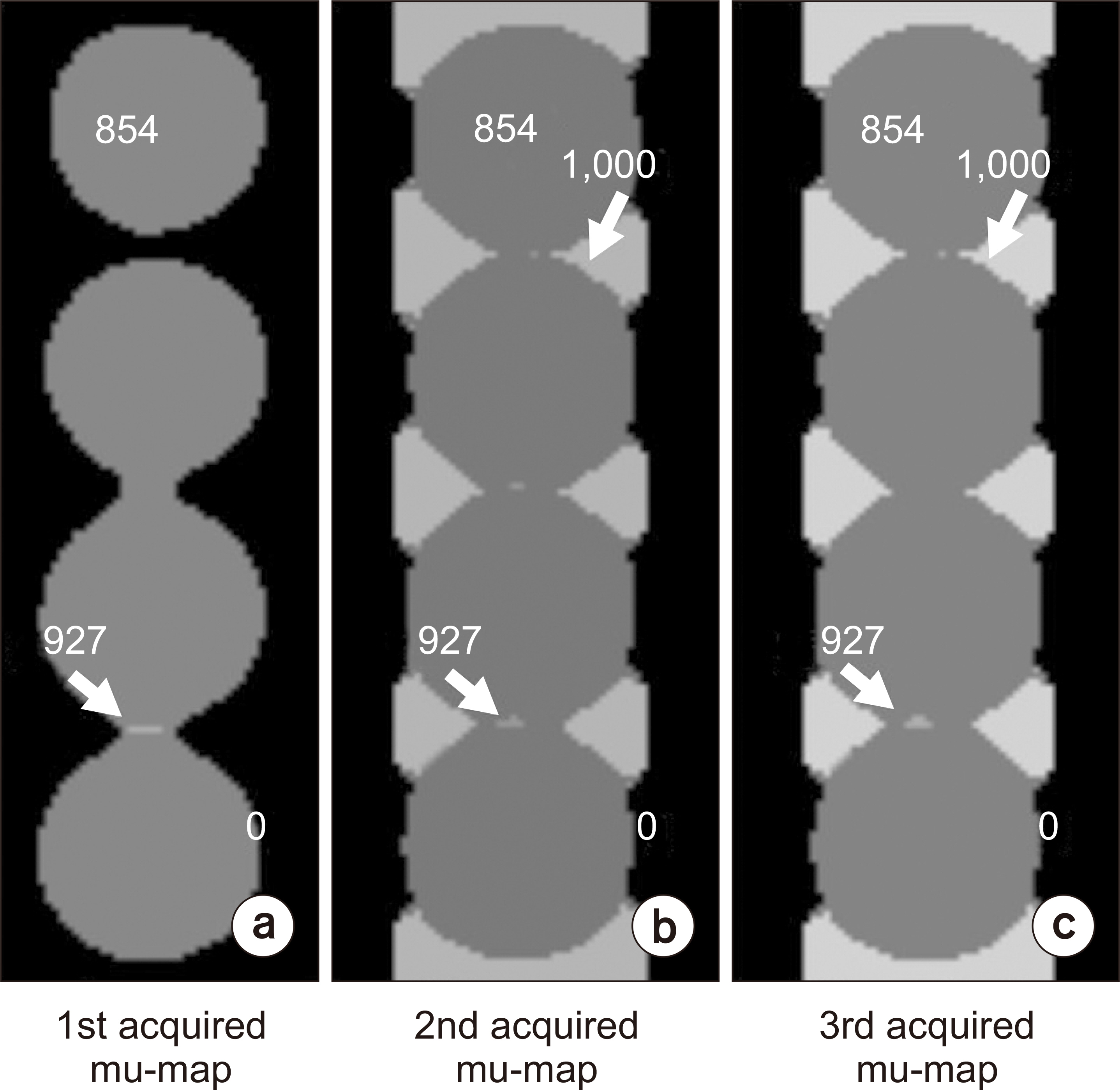
- An MR-based attenuation correction (MRAC) map plays an important role in quantitative positron emission tomography (PET) image evaluation in PET/magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems.However, the MRAC map is affected by the magnetic field inhomogeneity of MRIs. This study aims to evaluate the characteristics of MRAC maps of physical phantoms on PET/MRI images. Phantom measurements were performed using the Siemens Biograph mMR. The modular type physical phantoms that provide assembly versatility for phantom construction were scanned in a fourchannel Body Matrix coil. The MRAC map was generated using the two-point Dixon-based segmentation method for whole-body imaging. The modular phantoms were scanned in compact and non-compact assembly configurations. In addition, the phantoms were scanned repeatedly to generate MRAC maps. The acquired MRAC maps show differently assigned values for void areas.An incorrect assignment of a void area was shown on a locally compact space between phantoms. The assigned MRAC values were distorted using a wide field-of-view (FOV). The MRAC values also differed after repeated scans. However, the erroneous MRAC values appeared outside of phantom, except for a large FOV. The MRAC map of the phantom was affected by phantom configuration and the number of scans. A quantitative study using a phantom in a PET/MRI system should be performed after evaluation of the MRAC map characteristics.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bushberg JT, Boone JM. 2011. The essential physics of medical imaging. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;Philadelphia:2. Kinahan PE, Townsend DW, Beyer T, Sashin D. 1998; Attenuation correction for a combined 3D PET/CT scanner. Med Phys. 25:2046–2053. DOI: 10.1118/1.598392. PMID: 9800714.
Article3. Hofmann M, Steinke F, Scheel V, Charpiat G, Farquhar J, Aschoff P, et al. 2008; MRI-based attenuation correction for PET/MRI: a novel approach combining pattern recognition and atlas registration. J Nucl Med. 49:1875–1883. DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.107.049353. PMID: 18927326.
Article4. Judenhofer MS, Wehrl HF, Newport DF, Catana C, Siegel SB, Becker M, et al. 2008; Simultaneous PET-MRI: a new approach for functional and morphological imaging. Nat Med. 14:459–465. DOI: 10.1038/nm1700. PMID: 18376410.
Article5. Hofmann M, Pichler B, Schölkopf B, Beyer T. 2009; Towards quantitative PET/MRI: a review of MR-based attenuation correction techniques. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 36 Suppl 1:S93–S104. DOI: 10.1007/s00259-008-1007-7. PMID: 19104810.
Article6. Berker Y, Franke J, Salomon A, Palmowski M, Donker HC, Temur Y, et al. 2012; MRI-based attenuation correction for hybrid PET/MRI systems: a 4-class tissue segmentation technique using a combined ultrashort-echo-time/Dixon MRI sequence. J Nucl Med. 53:796–804. DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.111.092577. PMID: 22505568.
Article7. Wagenknecht G, Kaiser HJ, Mottaghy FM, Herzog H. 2013; MRI for attenuation correction in PET: methods and challenges. MAGMA. 26:99–113. DOI: 10.1007/s10334-012-0353-4. PMID: 23179594. PMCID: PMC3572388.
Article8. Eiber M, Martinez-Möller A, Souvatzoglou M, Holzapfel K, Pickhard A, Löffelbein D, et al. 2011; Value of a Dixon-based MR/PET attenuation correction sequence for the localization and evaluation of PET-positive lesions. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 38:1691–1701. DOI: 10.1007/s00259-011-1842-9. PMID: 21688050.
Article9. Samarin A, Burger C, Wollenweber SD, Crook DW, Burger IA, Schmid DT, et al. 2012; PET/MR imaging of bone lesions--implications for PET quantification from imperfect attenuation correction. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 39:1154–1160. DOI: 10.1007/s00259-012-2113-0. PMID: 22526955.10. Coombs BD, Szumowski J, Coshow W. 1997; Two-point Dixon technique for water-fat signal decomposition with B0 inhomogeneity correction. Magn Reson Med. 38:884–889. DOI: 10.1002/mrm.1910380606. PMID: 9402188.11. Keller SH, Holm S, Hansen AE, Sattler B, Andersen F, Klausen TL, et al. 2013; Image artifacts from MR-based attenuation correction in clinical, whole-body PET/MRI. MAGMA. 26:173–181. DOI: 10.1007/s10334-012-0345-4. PMID: 22996323.
Article12. Hofmann M, Bezrukov I, Mantlik F, Aschoff P, Steinke F, Beyer T, et al. 2011; MRI-based attenuation correction for whole-body PET/MRI: quantitative evaluation of segmentation- and atlas-based methods. J Nucl Med. 52:1392–1399. DOI: 10.2967/jnumed.110.078949. PMID: 21828115.
Article13. Keller SH, Jakoby B, Svalling S, Kjaer A, Højgaard L, Klausen TL. 2016; Cross-calibration of the Siemens mMR: easily acquired accurate PET phantom measurements, long-term stability and reproducibility. EJNMMI Phys. 3:11. DOI: 10.1186/s40658-016-0146-3. PMID: 27387738. PMCID: PMC4936986.
Article14. Bezrukov I, Mantlik F, Schmidt H, Schölkopf B, Pichler BJ. 2013; MR-Based PET attenuation correction for PET/MR imaging. Semin Nucl Med. 43:45–59. DOI: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2012.08.002. PMID: 23178088.
Article15. Mehranian A, Arabi H, Zaidi H. 2016; Vision 20/20: magnetic resonance imaging-guided attenuation correction in PET/MRI: challenges, solutions, and opportunities. Med Phys. 43:1130–1155. DOI: 10.1118/1.4941014. PMID: 26936700.
Article16. Delso G, ter Voert E, de Galiza Barbosa F, Veit-Haibach P. 2015; Pitfalls and limitations in simultaneous PET/MRI. Semin Nucl Med. 45:552–559. DOI: 10.1053/j.semnuclmed.2015.04.002. PMID: 26522396.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Sacroiliitis Diagnosed with Positron-Emission Tomography with Normal Magnetic Resonance Imaging Finding
- Potential Clinical Applications of ¹â¸F-Fluorodeoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Magnetic Resonance Mammography in Breast Cancer
- Radiologic Evaluation and Differential Diagnosis of Gallbladder Cancer
- Positron Emission Tomography-CT, CT, and MR Imaging Findings of Tumor-Mimicking Organized Hematoma in the Maxillary Sinus: Two Case Reports
- Molecular Imaging of Atherosclerosis