Kosin Med J.
2020 Dec;35(2):101-113. 10.7180/kmj.2020.35.2.101.
Therapeutic Effects of Prolonged Release Melatonin (Circadin® ) in Patients with Overactive Bladder and Chronic Insomnia in More Than 55 Years Old
- Affiliations
-
- 1The Korea Institute for Public Sperm Bank, Busan, Korea
- 2Department of Urology, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2510271
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7180/kmj.2020.35.2.101
Abstract
Objectives
Bladder storage symptoms including nocturia is the most common cause of sleep disturbance in all age groups. Sleep disturbance is also a main cause of nocturia so that sleep recovery can clinically improve nocturia. Melatonin has main action to induce sleep and additional effects of smooth muscle relaxation, free radical scavenging, anti-inflammation, et cetera. This study was evaluated the improvement of sleep quality after administrating prolonged-release melatonin in elderly patients with overactive bladder and chronic insomnia.
Methods
This clinical trial was performed with a randomized single open study. Thirty-seven patients with overactive bladder and chronic insomnia were initially enrolled in this study. After 4 or 12 weeks treating with 2 mg of prolongedrelease melatonin, clinical outcomes were evaluated with OABSS, IPSS, PSQI and WHO 5 well-being index.
Results
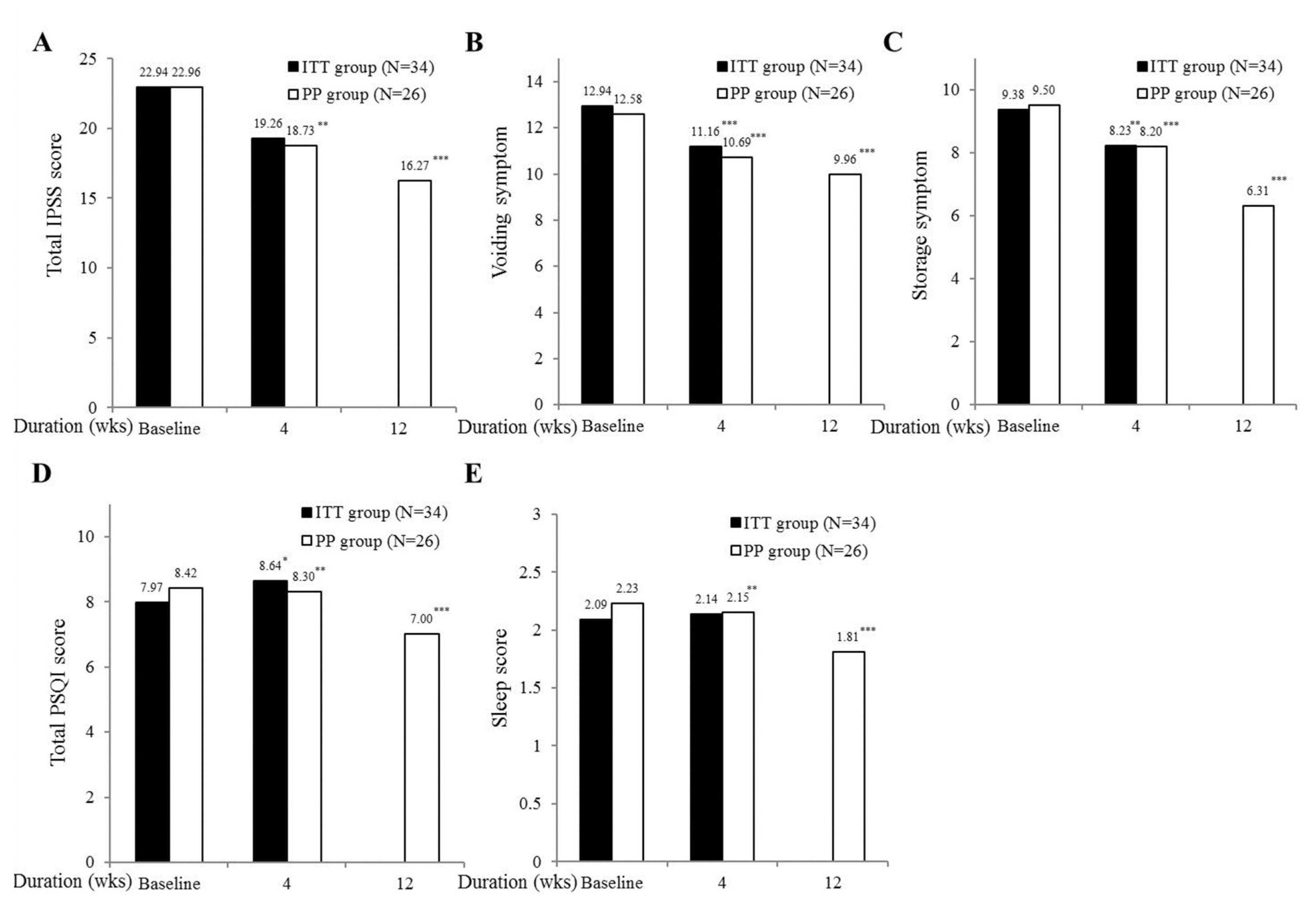
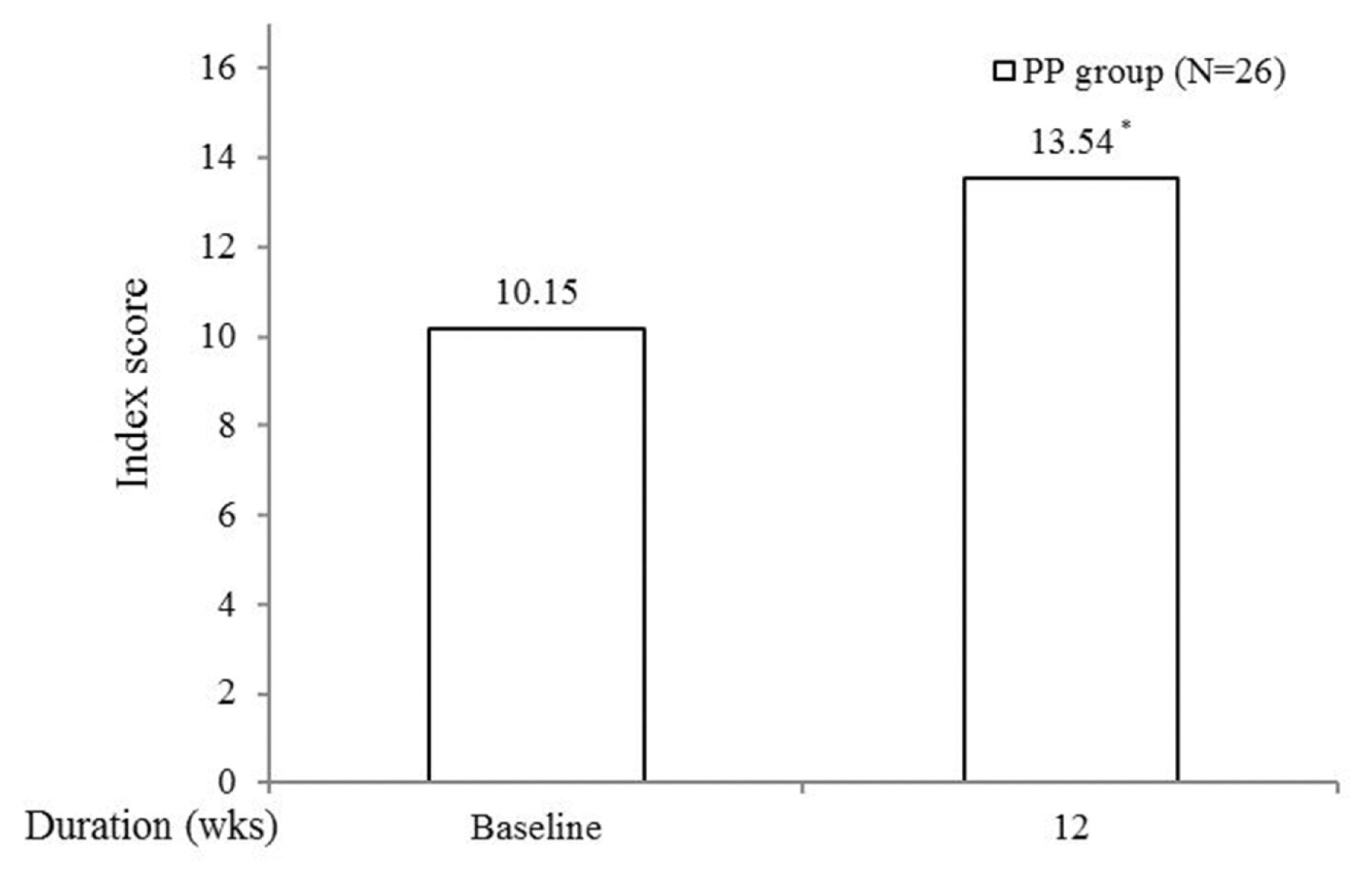
Of the 37 patients, 34 (91.9%) were included in the ITT group and 26 (76.5%) in the PP group. In the primary outcome of PP group, significant improvements were observed in total OABSS and nocturia frequencies at 12 weeks, respectively. Secondary outcome measurement including in voiding, storage symptoms, and total IPSS scores showed the improvement at 4 and 12 weeks and in total and sleep quality PSQI scores at 12 weeks, and in quality of life scores of the WHO 5 well-being index at 12 weeks. Only one (3.8%) adverse event was observed.
Conclusions
These results suggest clearly that prolonged-release melatonin in elderly patients with overactive bladder and chronic insomnia has the potential to control concomitant voiding and sleep difficulty.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kryger MH, Roth T, Dement WC. Principles and practice of sleep medicine. 5th ed. Philadelphia (PA): Elsevier Saunders;2010. p. p489–90.2. Chartier-Kastler E, Leger D, Comet D, Haab F, Ohayon MM. Prostatic hyperplasia is highly associated with nocturia and excessive sleepiness: a cross-sectional study. BMJ Open. 2012; 30:e000505.
Article3. Kim SC, Kim SW, Chung YJ. Men’s health in South Korea. Asian J Androl. 2011; 13:519–25.
Article4. Cho JW, Duffy JF. Sleep, Sleep Disorders, and Sexual Dysfunction. World J Mens Health. 2019; 37:261–75.
Article5. Ohayon MM. Nocturnal awakenings and comorbid disorders in the American general population. J Psychiatr Res. 2008; 43:48–54.
Article6. Aldhous M, Franey C, Wright J, Arendt J. Plasma concentrations of melatonin in man following oral absorption of different preparations. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985; 19:517–21.
Article7. Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989; 28:193–213.
Article8. Jeong SJ, Homma Y, Oh SJ, Jeong SJ. Korean version of the overactive bladder symptom score questionnaire: translation and linguistic validation. Int Neurourol J. 2011; 15:135–42.
Article9. Kim JH, Doo SW, Yang WJ, Song YS. Homogeneity among the korean international prostate symptom score questionnaires used in real practice. Korean J Urol. 2013; 54:249–51.
Article10. Mollayeva T, Thurairajah P, Burton K, Mollayeva S, Shapiro CM, Colantonio A. The Pittsburgh sleep quality index as a screening tool for sleep dysfunction in clinical and non-clinical samples: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev. 2016; 25:52–73.
Article11. Moon YS, Kim HJ, Kim DH. The relationship of the Korean version of the WHO Five Well-Being Index with depressive symptoms and quality of life in the community-dwelling elderly. Asian J Psychiatr. 2014; 9:26–30.
Article12. Griebling TL. Incidence and Remission of Nocturia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Urol. 2016; 196:1710–1.13. Irwin DE, Milsom I, Kopp Z, Abrams P, Artibani W, Herschorn S. Prevalence, severity, and symptom bother of lower urinary tract symptoms among men in the EPIC study: impact of overactive bladder. Eur Urol. 2009; 56:14–20.
Article14. Thomas S. Some effects of changes of posture on water and electrolyte excretion by the human kidney. J Physiol. 1957; 139:337–52.15. George CP, Messerli FH, Genest J, Nowaczynski W, Boucher R, Kuchel Orofo-Oftega M. Diurnal variation of plasma vasopressin in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1975; 41:332–8.
Article16. Ohashi M, Fujio N, Nawata H, Kato K, Ibayashi H, Kangawa K, et al. High plasma concentrations of human atrial natriuretic polypeptide in aged men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987; 64:81–5.
Article17. Roehrborn CG, Van Kerrebroeck P, Nordling J. Safety and efficacy of alfuzosin 10 mg once-daily in the treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms and clinical benign prostatic hyperplasia: a pooled analysis of three double-blind, placebo-controlled studies. BJU Int. 2003; 92:257–61.
Article18. Choi S, Cho WY, Min K, Lee JZ, Moon KH, Kwon T, et al. Influence of daytime or nighttime dosing with solifenacin for overactive bladder with nocturia: impact on nocturia and sleep quality. J Korean Med Sci. 2017; 32:1491–5.
Article19. Weiss JP, Wein AJ, van Kerrebroeck P, Dmochowski R, Fitzgerald M, Tikkinen KA, et al. Nocturia: new directions. Neurourol Urodyn. 2011; 30:700–3.
Article20. Claustrat B, Brun J, Chazot G. The basic physiology and pathophysiology of melatonin. Sleep Med Rev. 2005; 9:11–24.
Article21. Zisapel N. New perspectives on the role of melatonin in human sleep, circadian rhythms and their regulation. Br J Pharmacol. 2018; 175:3190–9.
Article22. Fathollahi A, Daneshgari F, Hanna-Mitchell AT. Melatonin and its role in lower urinary tract function: An article review. Curr Urol. 2015; 8:113–8.
Article23. Gomez-Pinilla PJ, Gomez MF, Swärd K, Hedlund P, Hellstrand P, Camello PJ, et al. Melatonin restores impaired contractility in aged guinea pig urinary bladder. J Pineal Res. 2008; 44:416–25.
Article24. Han JH, Chang IH, Myung SC, Lee MY, Kim WY, Lee SY, et al. A novel pathway underlying the inhibitory effects of melatonin on isolated rat urinary bladder contraction. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012; 16:37–42.
Article25. Dobrek Ł, Thor PJ. The influence of melatonin and agomelatine on urodynamic parameters in experimental overactive bladder model-preliminary results. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online). 2011; 65:725–33.26. Semerciöz A, Onur R, Ayar A, Orhan I. The inhibitory role of melatonin on isolated guinea-pig urinary bladder: an endogenous hormone effect. BJU Int. 2004; 94:1373–6.
Article27. Juszczak K, Ziomber A, Machowska A, Furgała A, Dobrek Ł, Wyczółkowski M, et al. The ameliorating effect of exogenous melatonin on urinary bladder function in hyperosmolar bladder overactivity and its influence on the autonomic nervous system activity. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove). 2011; 54:63–8.
Article28. Sener G, Sehirli AO, Paskaloğlu K, Dülger GA, Alican I. Melatonin treatment protects against ischemia/reperfusion-induced functional and biochemical changes in rat urinary bladder. J Pineal Res. 2003; 34:226–30.29. Sener G, Atasoy BM, Ersoy Y, Arbak S, Sengöz M, Yeğen BC. Melatonin protects against ionizing radiation-induced oxidative damage in corpus cavernosum and urinary bladder in rats. J Pineal Res. 2004; 37:241–6.30. Matsuta Y, Yusup A, Tanase K, Ishida H, Akino H, Yokoyama O. Melatonin increases bladder capacity via GABAergic system and decreases urine volume in rats. J Urol. 2010; 184:386–91.
Article