J Korean Acad Oral Health.
2020 Dec;44(4):180-186. 10.11149/jkaoh.2020.44.4.180.
The effect of dentifrice including dental type silica, tocopherol acetate, sodium fluoride and sodium pyrophosphate on mineral density in enamel
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Preventive Dentistry, College of Dentistry, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea
- 2Aekyung Industrial Co., Ltd. R&D Division Dental Care Team, Daejeon, Korea
- KMID: 2510247
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.11149/jkaoh.2020.44.4.180
Abstract
Objectives
In this study, we aimed to investigate the preventive and protective effects of new dentifrice containing dental type silica, tocopheryl acetate, fluorides, and sodium pyrophosphate on the mineral density of teeth and demineralization of tooth surfaces.
Methods
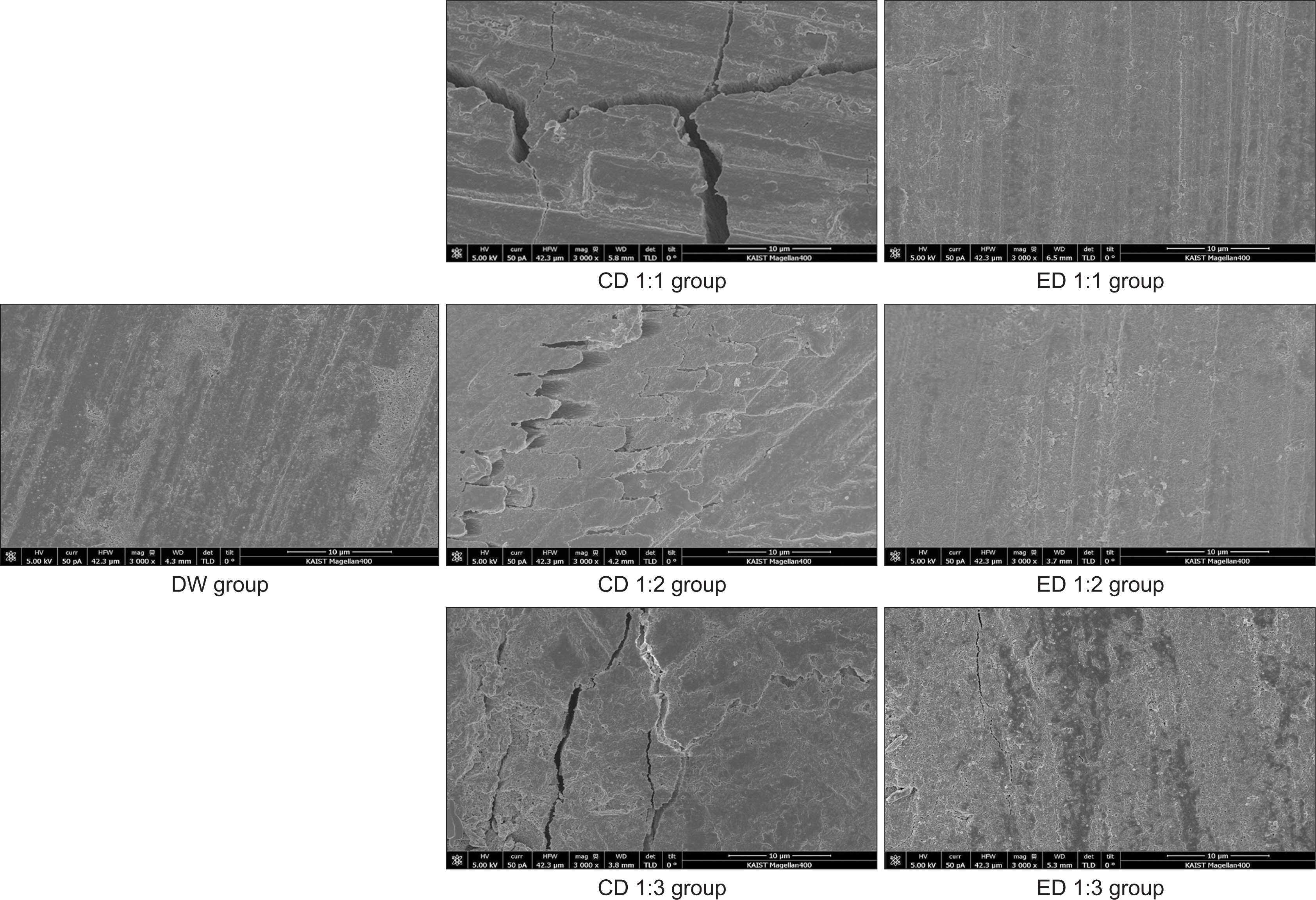
A total of 119 bovine teeth pre-treated with the new dentifrice at three different concentrations for the experiment were randomly allocated into two control (DW and PW) and one experimental (EC) groups. The enamel surface of all bovine teeth were demineralized using an artificial demineralization solution. The dentifrice was diluted with distilled water (DW) at 1:1, 1:2, and 1:3 ratios. The samples were treated with the demineralization solution for 4 h after treatment with the supernatants of each diluted dentifrice for 30 min, and this procedure was repeated 3 times over a period of 24 h. The samples were examined using micro-CT to determine the amount of reduced bone mineral density (BMD) comparing the control and experimental dentifrices. The surface changes of the samples were also examined using the scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Results
The average BMD of the bovine enamel surface between the treated and non-treated area with the dimineralization solution was significantly different in the control, DW, PW 1:1, PW 1:2, and PW 1:3 groups. However, there was no significant difference observed in the experimental groups, including EC 1:1, EC 1:2, and EC 1:3. The average BMD of the dimineralized surfaces based on the results of the 7 groups was significantly higher in every EC group when compared to the DW and three PW groups.
Conclusions
The new dentifrice containing dental type silica, tocopheryl acetate, fluorides, and sodium pyrophosphate is effective in inhibiting the decrease in BMD and demineralization of enamel surface, which was observed when the new dentifrice and demineralization solution was repeatedly applied to the samples for 24 h.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Preventive effect of dentifrice containing 1,450 ppm fluoride and sodium pyrophosphate
Min-Ji Park, Ja-Won Cho, Hyun-Jun Yoo, Mi-Hae Yun, Kyong-Hoon Shin, Young-Hoon Park
J Korean Acad Oral Health. 2022;46(2):63-69. doi: 10.11149/jkaoh.2022.46.2.63.
Reference
-
References
1. Huang TTY, Jones AS, He LH, Darendeliler MA, Swain MV. 2007; Characterisation of enamel white spot lesions using X-ray micro-tomography. J Dent. 35:737–743. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdent.2007.06.001. PMID: 17683844.
Article2. Songsiripradubboon S, Hamba H, Trairatvorakul C, Tagami J. 2014; Sodium fluoride mouthrinse used twice daily increased incipient caries lesion remineralization in an in situ model. J Dent. 42:271–278. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdent.2013.12.012. PMID: 24394584.
Article3. Tschoppe P, Zandim DL, Martus P, Kielbassa AM. 2011; Enamel and dentine remineralization by nano-hydroxyapatite toothpastes. J Dent. 39:430–437. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdent.2011.03.008. PMID: 21504777.
Article4. Cho EJ, Lee HW, Park SM, Koo HS, Cho IS, Cho JW. 2016; The Effect of Zinc-Citrate-Containing Dentifrice for Oral Malodor Control: A Clinical Study. Int J Clin Prev Dent. 12:57–64. DOI: 10.15236/ijcpd.2016.12.2.57.5. Lee HW, Cho EJ, Shin KH, Koo HS, Cho IS, Cho JW. 2016; A Clinical Study on the Desensitization Effect by Use of Calcium-Glycerophosphate-Containing Dentifrice. Int J Clin Prev Dent. 12:103–109. DOI: 10.15236/ijcpd.2016.12.2.103.6. Kim SS, Cho JW, Lee CH. 2017; Gingivitis reducing effect of calcium glycerophosphate, cetylpyridinium chloride and dipotassium glycyrrhizate containing dentifrice. J Korean Soc Dent Hyg. 17:983–992. DOI: 10.13065/jksdh.2017.17.06.983.
Article7. Song HN, Park JH, Cho JW. 2017; Desensitization Effects by Night Time Using of a Dentifrice Containing Calcium Glycerophosphate before Bedtime. Int J Clin Prev Dent. 13:165–169. DOI: 10.15236/ijcpd.2017.13.4.165.
Article8. Kim SA, Cho JW. 2017; Gingivitis Reducing Effect of Dentifrices Containing Zinc Citrate. Int J Clin Prev Dent. 13:217–222. DOI: 10.15236/ijcpd.2017.13.4.217.
Article9. Na EJ, Yun MH, Cho JW. 2018; A Study on the Evaluation of Oral Malodor Reduction Effect of Zinc Citrate-Containing Dentifrice on Night Use. Int J Clin Prev Dent. 14:23–27. DOI: 10.15236/ijcpd.2018.14.1.23.
Article10. Nakata K, Nikaido T, Nakashima S, Nango N, Tagami J. 2012; An approach to normalizing micro-CT depth profiles of mineral density for monitoring enamel remineralization progress. Dent Mater J. 31:533–540. DOI: 10.4012/dmj.2011-228. PMID: 22864205.
Article11. ten Cate JM, Duijsters PP. 1982; Alternating demineralization and remineralization of artificial enamel lesions. Caries Res. 16:201–210. DOI: 10.1159/000260599. PMID: 6953998.
Article12. Mohanty P, Padmanabhan S, Chitharanjan AB. 2014; An in Vitro Evaluation of Remineralization Potential of Novamin® on Artificial Enamel Sub-Surface Lesions Around Orthodontic Brackets Using Energy Dispersive X-Ray Analysis (EDX). J Clin Diagn Res. 8:ZC88–91. DOI: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/9340.5177. PMID: 25584326. PMCID: PMC4290336.13. Barbour ME, Shellis RP, Parker DM, Allen GC, Addy M. 2005; An investigation of some food-approved polymers as agents to inhibit hydroxyapatite dissolution. Eur J Oral Sci. 113:457–461. DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.2005.00248.x. PMID: 16324134.
Article14. Teruel Jde D, Alcolea A, Hernandez A, Ruiz AJ. 2015; Comparison of chemical composition of enamel and dentine in human, bovine, porcine and ovine teeth. Arch Oral Biol. 60:768–775. DOI: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2015.01.014. PMID: 25766469.15. Hamba H, Nikaido T, Inoue G, Sadr A, Tagami J. 2011; Effects of CPP-ACP with sodium fluoride on inhibition of bovine enamel demineralization: a quantitative assessment using micro-computed tomography. J Dent. 39:405–413. DOI: 10.1016/j.jdent.2011.03.005. PMID: 21453746.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Preventive effect of dentifrice containing 1,450 ppm fluoride and sodium pyrophosphate
- Evaluation of In-Vitro Efficacy of Active Ingredients in Dentifrice Used for Different Treatment Times
- Evaluation of the remineralization effect of bamboo salt and sodium fluoride solutions
- Effect of Silver Diamine Fluoride and Sodium Fluoride Varnish on Remineralization in Artificially Induced Enamel Caries: An in vitro Study
- An experimental study on the effect of topical application of stannous fluoride to the stripped enamel surface