J Neurocrit Care.
2020 Dec;13(2):105-108. 10.18700/jnc.200013.
Anti-Yo-associated autoimmune encephalitis after colon cancer treatment
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Yangsan, Republic of Korea
- 2Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Republic of Korea
- KMID: 2509940
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.200013
Abstract
- Background
Anti-Yo antibodies are classically associated with paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration in ovarian and breast cancers and are rarely seen in colon cancer. Anti-Yo-associated paraneoplastic autoimmune encephalitis in colon cancer is rare.
Case Report
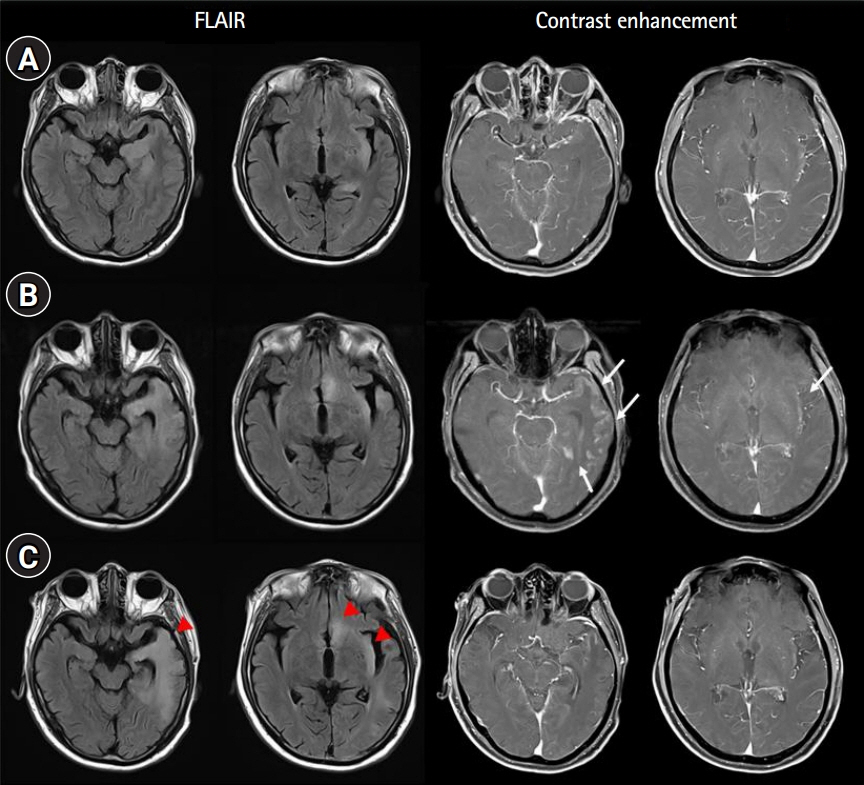
A 66-year-old man presented with new-onset seizures after completion of a scheduled treatment for colon cancer. Magnetic resonance imaging showed hyperintense signals with enhancement in the left temporal lobe and insular cortex. Cerebrospinal fluid findings included pleocytosis and elevated protein levels, while Yo antibodies were detected in the serum. There was no relapse of colon cancer, nor were any new cancers found. The patient’s symptoms and laboratory test results improved after the administration of high-dose steroids, intravenous immunoglobulin, and plasmapheresis with antiepileptic drugs.
Conclusion
This is a rare case of autoimmune encephalitis with anti-Yo antibodies. The appearance of new-onset seizures during the treatment of malignancy should raise suspicions for paraneoplastic autoimmune encephalitis, even after surgery and chemotherapy are completed.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Darnell RB, Posner JB. Paraneoplastic syndromes involving the nervous system. N Engl J Med. 2003; 349:1543–54.
Article2. Graus F, Titulaer MJ, Balu R, Benseler S, Bien CG, Cellucci T, et al. A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol. 2016; 15:391–404.
Article3. Pelosof LC, Gerber DE. Paraneoplastic syndromes: an approach to diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clin Proc. 2010; 85:838–54.
Article4. Martel S, De Angelis F, Lapointe E, Larue S, Speranza G. Paraneoplastic neurologic syndromes: clinical presentation and management. Curr Probl Cancer. 2014; 38:115–34.
Article5. Gultekin SH, Rosenfeld MR, Voltz R, Eichen J, Posner JB, Dalmau J. Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis: neurological symptoms, immunological findings and tumour association in 50 patients. Brain. 2000; 123(Pt 7):1481–94.
Article6. Leypoldt F, Wandinger KP. Paraneoplastic neurological syndromes. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014; 175:336–48.
Article7. Ebright MJ, Li SH, Reynolds E, Burke JF, Claytor BR, Grisold A, et al. Unintended consequences of Mayo paraneoplastic evaluations. Neurology. 2018; 91:e2057–66.
Article8. Seluk L, Taliansky A, Yonath H, Gilburd B, Amital H, Shoenfeld Y, et al. A large screen for paraneoplastic neurological autoantibodies; diagnosis and predictive values. Clin Immunol. 2019; 199:29–36.
Article9. Adam VN, Budinčević H, Mršić V, Stojčić EG, Matolić M, Markić A. Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis in a patient with adenocarcinoma of the colon: a case report. J Clin Anesth. 2013; 25:491–5.
Article10. Berger B, Bischler P, Dersch R, Hottenrott T, Rauer S, Stich O. "Non-classical" paraneoplastic neurological syndromes associated with well-characterized antineuronal antibodies as compared to "classical" syndromes: more frequent than expected. J Neurol Sci. 2015; 352:58–61.11. Said S, Cooper CJ, Reyna E, Alkhateeb H, Diaz J, Nahleh Z. Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis, an uncommon presentation of a common cancer: case report and discussion. Am J Case Rep. 2013; 14:391–4.
Article12. Attademo L, De Falco S, Rosanova M, Esposito M, Mazio F, Foschini F, et al. A case report of limbic encephalitis in a metastatic colon cancer patient during first-line bevacizumab-combined chemotherapy. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97:e0011.
Article13. Silsby M, Clarke CJ, Lee K, Sharpe D. Anti-Hu limbic encephalitis preceding the appearance of mediastinal germinoma by 9 years. Neurol Neuroimmunol Neuroinflamm. 2020; 7:e685.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Corticosteroid Treatment in Autoimmune Encephalitis
- The Diagnosis and Treatment of Autoimmune Encephalitis
- Anti-GABA-B Receptor Autoimmune Encephalitis
- Coexistence of Anti-Hu and Anti-SOX1 Autoantibodies in Atezolizumab-related Encephalitis
- Case of anti-N-methyl D-aspartate receptor encephalitis associated with ovarian teratoma presenting as suicidal ideation