Anat Cell Biol.
2020 Dec;53(4):417-421. 10.5115/acb.20.159.
Anatomical variations of the stylopharyngeus and superior constrictors in relation to their function
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dental Hygiene, Catholic Kwandong University, Gangneung, Korea
- 2Department of Dental Hygiene, Division of Health Sciences, Namseoul University, Cheonan, Korea
- 3Division in Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Department of Oral Biology, Human Identification Research Center, BK21 PLUS Project, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2509687
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.20.159
Abstract
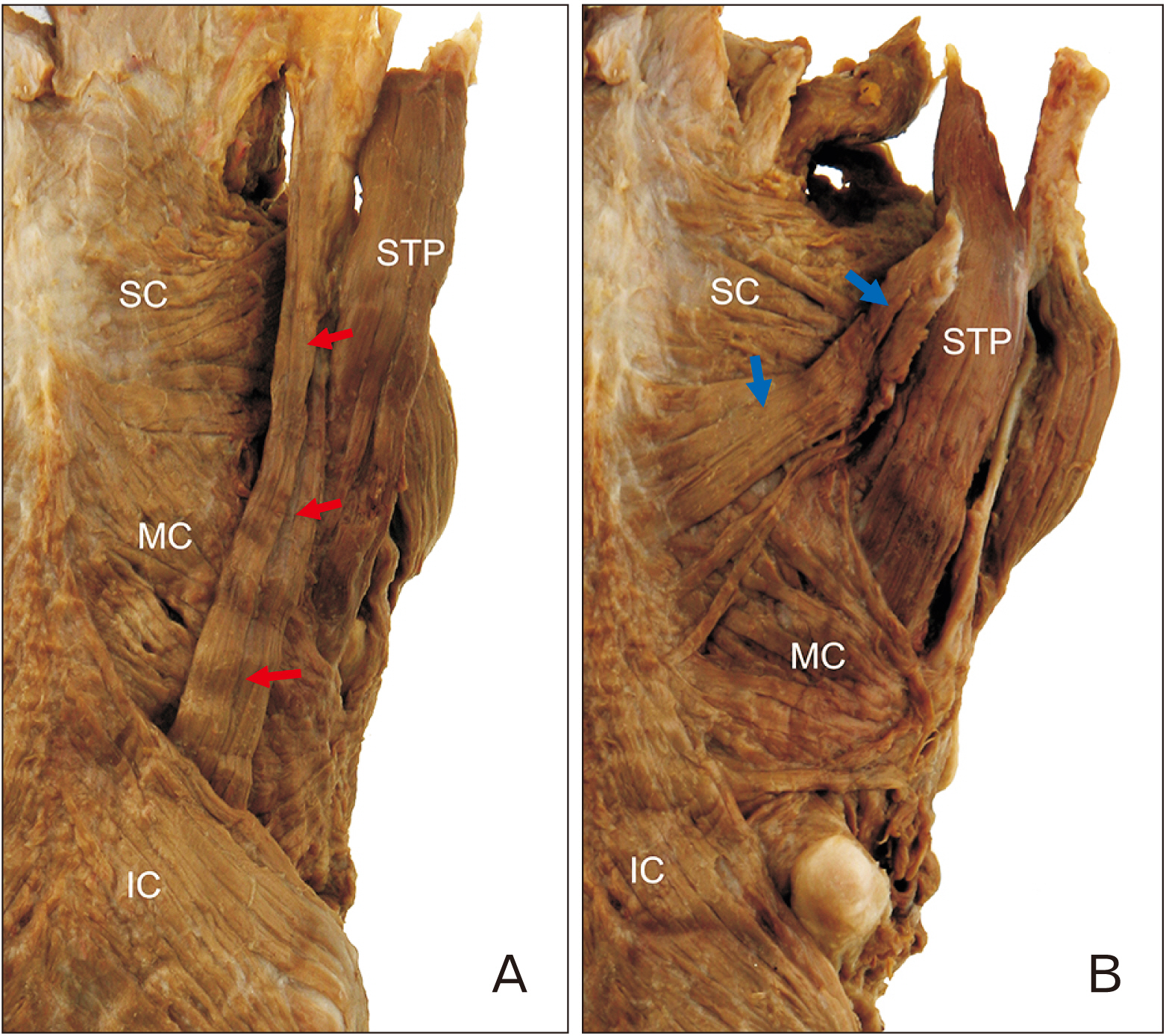
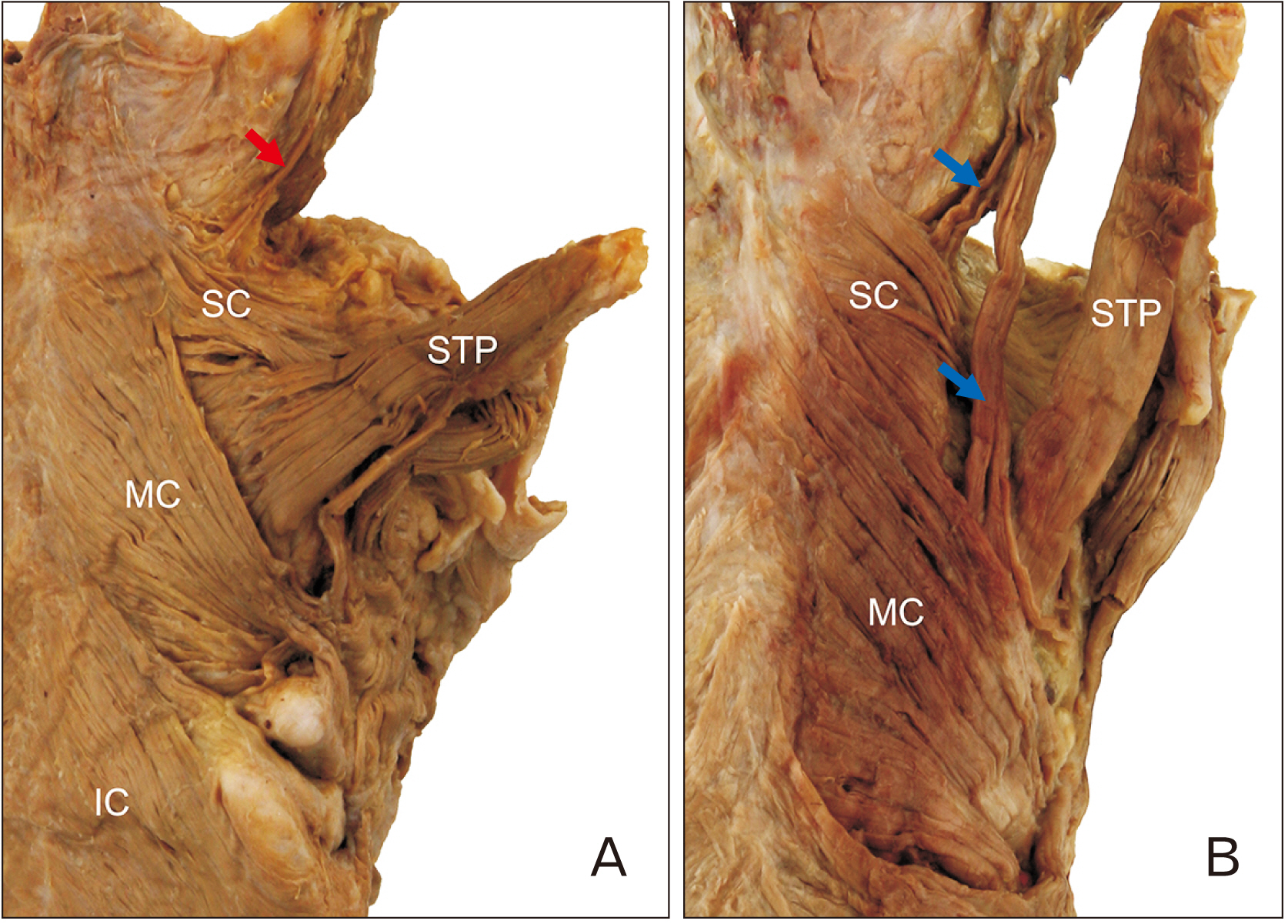
- The aims of this study were to clarify the topography and variations stylopharyngeus (STP) and superior constrictor (SC) muscles, and to examine what role they play in the pharyngeal movement. Forty-four specimens (22 right and 22 left sides) from embalmed Korean adult cadavers (13 males, 9 females; age range, 46–89 years; mean age, 69.2 years) were used in this study. The accessory bundle of STP and petropharyngeus was found in 18.2% (8/44) and 25.0% (11/44) of cases, respectively. A variation of the STP, in which it ran transversely and merged with the SC muscle, was found in 2.3% (1/44) of cases while a variation of the SC muscle, in which it ran longitudinally and merged with the contralateral constrictors, was found in 11.4% (5/44). The variant muscle bundles play their own role in pharyngeal movement according to their morphology. These results provide information that will help a comprehensive understanding of the effects of pharyngeal muscles on movement.
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Standring S, Borley NR, Gray H. 2008. Gray's anatomy: the anatomical basis of clinical practice. 40th ed. Churchill Livingstone;Edinburgh:2. Choi DY, Bae JH, Youn KH, Kim HJ, Hu KS. 2014; Anatomical considerations of the longitudinal pharyngeal muscles in relation to their function on the internal surface of pharynx. Dysphagia. 29:722–30. DOI: 10.1007/s00455-014-9568-z. PMID: 25142243.
Article3. Meng H, Murakami G, Suzuki D, Miyamoto S. 2008; Anatomical variations in stylopharyngeus muscle insertions suggest interindividual and left/right differences in pharyngeal clearance function of elderly patients: a cadaveric study. Dysphagia. 23:251–7. DOI: 10.1007/s00455-007-9131-2. PMID: 18427898.
Article4. Tsumori N, Abe S, Agematsu H, Hashimoto M, Ide Y. 2007; Morphologic characteristics of the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle in relation to the function during swallowing. Dysphagia. 22:122–9. DOI: 10.1007/s00455-006-9063-2. PMID: 17318687.
Article5. Perry JL. 2011; Anatomy and physiology of the velopharyngeal mechanism. Semin Speech Lang. 32:83–92. DOI: 10.1055/s-0031-1277712. PMID: 21948636.
Article6. Schünke M, Ross LM, Lamperti ED, Schulte E, Schumacher U, Rude J, Voll M, Wesker K. 2006. Thieme atlas of anatomy. Thieme;New York:7. Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. 2010. Clinically oriented anatomy. 6th ed. Wolters Kluwer/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;Philadelphia:8. Tank PW, Gest TR, Burkel WE. 2008. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins atlas of anatomy. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;Philadelphia:9. Shimada K, Yokoi A, Ozawa H, Kitagawa T, Tezuka M. 1991; Observation of the petropharyngeal muscle in Japanese. Anat Anz. 173:193–8. PMID: 1803943.10. Kahrilas PJ. 1993; Pharyngeal structure and function. Dysphagia. 8:303–7. DOI: 10.1007/BF01321767. PMID: 8269719.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Morphological classification, anatomical variations, innervation patterns, musculocutaneous nerve relation of the coracobrachialis muscle: anatomical study and clinical significance
- An Anatomical Study on the Variations of the Venous Sinuses at the Torcular Herophili
- Prevalence and clinical relevance of the anatomical variations of suprarenal arteries: a review
- A rare variation of the glossopharyngeal nerve
- Anatomical Variations of Cerebral MR Venography: Is Gender Matter?