Neurointervention.
2016 Sep;11(2):92-98. 10.5469/neuroint.2016.11.2.92.
Anatomical Variations of Cerebral MR Venography: Is Gender Matter?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurology, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College & Hospital, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India. drgauravjaipur@yahoo.com
- 2MRI Centre, GBH American Hospital, Udaipur, Rajasthan, India.
- 3Department of Radiodiagnosis and Imaging, Mahatma Gandhi Medical College & Hospital, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India.
- 4Department of Neurology, SGPGIMS, Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh, India.
- KMID: 2350686
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2016.11.2.92
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Knowledge of variations in the cerebral dural venous sinus anatomy seen on magnetic resonance (MR) venography is essential to avoid over-diagnosis of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST). Very limited data is available on gender difference of the cerebral dural venous sinus anatomy variations.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective study was conducted to study the normal anatomy of the intracranial venous system and its normal variation, as depicted by 3D MR venography, in normal adults and any gender-related differences.
RESULTS
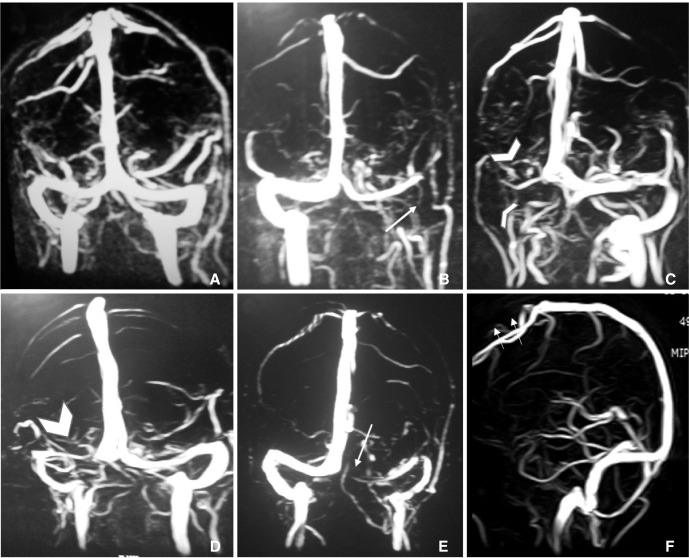
A total of 1654 patients (582 men, 1072 women, age range 19 to 86 years, mean age: 37.98±13.83 years) were included in the study. Most common indication for MR venography was headache (75.4%). Hypoplastic left transverse sinus was the most common anatomical variation in 352 (21.3%) patients. Left transverse sinus was hypoplastic in more commonly in male in comparison to female (24.9% versus 19.3%, p = 0.009). Most common variation of superior sagittal sinus (SSS) was atresia of anterior one third SSS (15, 0.9%). Except hypoplastic left transverse sinus, rest of anatomical variations of the transverse and other sinuses were not significantly differ among both genders.
CONCLUSION
Hypoplastic left transverse sinus is the most common anatomical variation and more common in male compared to female in the present study. Other anatomical variations of dural venous sinuses are not significantly differ among both genders.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Mattle HP, Wentz KU, Edelman RR, Wallner B, Finn JP, Barnes P, et al. Cerebral venography with MR. Radiology. 1991; 178:453–458. PMID: 1987608.
Article2. Ayanzen RH, Bird CR, Keller PJ, McCully FJ, Theobold MR, Heiserman JE. Cerebral MR venography: normal anatomy and potential diagnostic pitfalls. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 21:74–78. PMID: 10669228.3. Widjaja E, Griffiths PD. Intracranial MR venography in children: normal anatomy and variations. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004; 25:1557–1562. PMID: 15502138.4. Liauw L, van Buchem MA, Spilt A, de Bruine FT, van den Berg R, Hermans J, et al. MR angiography of the intracranial venous system. Radiology. 2000; 214:678–682. PMID: 10715029.
Article5. Wetzel SG, Kirsch E, Stock KW, Kolbe M, Kaim A, Radue EW. Cerebral veins: comparative study of CT venography with intraarterial digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:249–255. PMID: 10094346.6. Alper F, Kantarci M, Dane S, Gumustekin K, Onbas O, Durur I. Importance of anatomical asymmetries of transverse sinuses: an MR venographic study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004; 18:236–239. PMID: 15273441.
Article7. Curé JK, Van Tassel P, Smith MT. Normal and variant anatomy of the dural venous sinuses. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 1994; 15:499–519. PMID: 7880564.
Article8. Zouaoui A, Hidden G. Cerebral venous sinuses: anatomical variants or thrombosis? Acta Anat (Basel). 1988; 133:318–324. PMID: 3227793.
Article9. Rollins N, Ison C, Booth T, Chia J. MR venography in the pediatric patient. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 26:50–55. PMID: 15661699.10. Surendrababu NR, Subathira , Livingstone RS. Variations in the cerebral venous anatomy and pitfalls in the diagnosis of cerebral venous sinus thrombosis: low field MR experience. Indian J Med Sci. 2006; 60:135–142. PMID: 16679629.
Article11. Sharma UK, Sharma K. Intracranial MR venography using low-field magnet: normal anatomy and variations in Nepalese population. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2012; 52:61–65. PMID: 23478731.
Article12. Kaplan HA, Browder AA, Browder J. Atresia of the rostral superior sagittal sinus: associated cerebral venous patterns. Neuroradiology. 1972; 4:208–211. PMID: 4677615.
Article13. Hacker H. Superficial supratentorial veins and dural sinuses. In : Newton TH, Gordon Potts MDD, editors. Radiology of the Skull and Brain: Angiography. St. Louis: C.V. Mosby Company;1974. p. 1851–1902.14. Kaplan HA, Browder J. Atresia of the rostral superior sagittal sinus: substitute parasagittal venous channels. J Neurosurg. 1973; 38:602–607. PMID: 4711634.
Article15. San Millán Ruíz D, Fasel JH, Gailloud P. Unilateral hypoplasia of the rostral end of the superior sagittal sinus. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012; 33:286–291. PMID: 22051814.
Article16. San Millán Ruíz D, Gailloud P, Rufenacht DA, Delaville JH, Henry F, Fasel J. The craniocervical venous system in relation to cerebral venous drainage. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:1500–1508. PMID: 12372739.17. Lang J. The floor of the posterior cranial fossa. clinical Anatomy of the posterior cranial fossa and its foramina. New York: Thieme;1991. p. 6–9.18. Ruigrok AN, Salimi-Khorshidi G, Lai MC, Baron-Cohen S, Lombardo MV, Tait RJ, et al. A meta-analysis of sex differences in human brain structure. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2014; 39:34–50. PMID: 24374381.
Article19. Stefani MA, Schneider FL, Marrone ACH, Severino AG. Influence of the gender on cerebral vascular diameters observed during the magnetic resonance angiographic examination of willis circle. Braz Arch Biol Technol. 2013; 56:45–52.
Article20. Savelyeva L, Bogomyakova O, Prygova Y, Tulupov A. Anatomic variations of sigmoid sinuses on phase contrast MR-angiography. In : ECR 2012; 2012 March 1 - 5; Vienna, Austria. European Congress of Radiology;2012.