J Pathol Transl Med.
2020 Nov;54(6):462-470. 10.4132/jptm.2020.07.11.
A machine-learning expert-supporting system for diagnosis prediction of lymphoid neoplasms using a probabilistic decision-tree algorithm and immunohistochemistry profile database
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Hospital Pathology, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 2Postech-Catholic Biomedical Engineering Institute, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Creative Information Technology, POSTECH, Pohang, Korea
- 4University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston, TX, USA
- 5Computer Science and Engineering, POSTECH, Pohang, Korea
- 6Department of Pathology, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
- KMID: 2509499
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4132/jptm.2020.07.11
Abstract
- Background
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) has played an essential role in the diagnosis of hematolymphoid neoplasms. However, IHC interpretations can be challenging in daily practice, and exponentially expanding volumes of IHC data are making the task increasingly difficult. We therefore developed a machine-learning expert-supporting system for diagnosing lymphoid neoplasms.
Methods
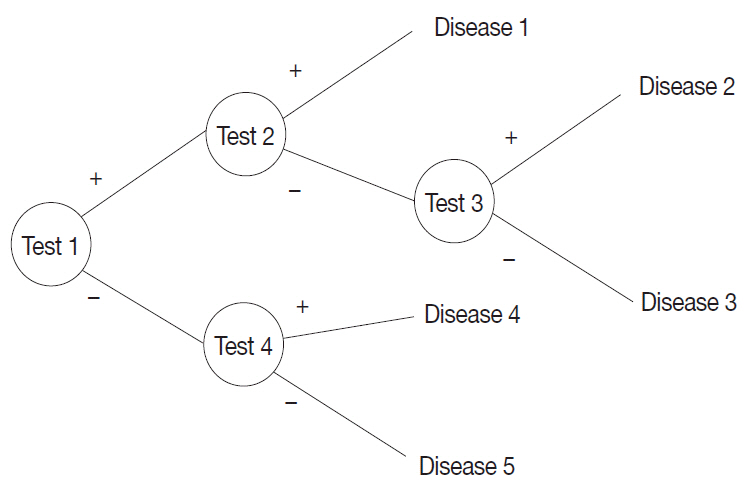
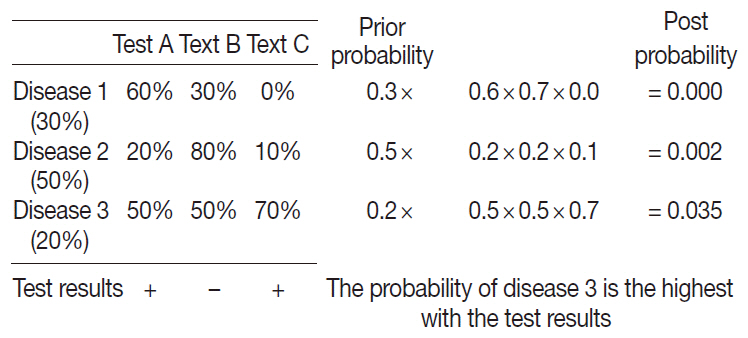
A probabilistic decision-tree algorithm based on the Bayesian theorem was used to develop mobile application software for iOS and Android platforms. We tested the software with real data from 602 training and 392 validation cases of lymphoid neoplasms and compared the precision hit rates between the training and validation datasets.
Results
IHC expression data for 150 lymphoid neoplasms and 584 antibodies was gathered. The precision hit rates of 94.7% in the training data and 95.7% in the validation data for lymphomas were not statistically significant. Results in most B-cell lymphomas were excellent, and generally equivalent performance was seen in T-cell lymphomas. The primary reasons for lack of precision were atypical IHC profiles for certain cases (e.g., CD15-negative Hodgkin lymphoma), a lack of disease-specific markers, and overlapping IHC profiles of similar diseases.
Conclusions
Application of the machine-learning algorithm to diagnosis precision produced acceptable hit rates in training and validation datasets. Because of the lack of origin- or disease- specific markers in differential diagnosis, contextual information such as clinical and histological features should be taken into account to make proper use of this system in the pathologic decision-making process.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Elias JM. Immunohistochemistry: a brief historical perspective: commentary. In : Shi SR, Gu J, Taylor CR, editors. Antigen retrieval techniques: immunohistochemistry and molecular morphology. Natick: Eaton Pub;2000. p. 7–13.2. Buchwalow IB, Bocker W. Immunohistochemistry: basics and methods. Heidelberg: Springer;2010.3. Matos LL, Trufelli DC, de Matos MG, da Silva Pinhal MA. Immunohistochemistry as an important tool in biomarkers detection and clinical practice. Biomark Insights. 2010; 5:9–20.4. Chu P, Weiss L. Modern immunohistochemistry. 2nd ed. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press;2014.5. Dabbs DJ. Diagnostic immunohistochemistry: theranostic and genomic applications. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier/Saunders;2014.6. Kalyuzhny AE. Immunohistochemistry: essential elements and beyond. Cham: Springer;2016.7. Coons AH. Labeling Techniques in the diagnosis of viral diseases. Bacteriol Rev. 1964; 28:397–9.
Article8. Werner B, Campos AC, Nadji M, Torres LF. Practical use of immunohistochemistry in surgical pathology. J Bras Patol Med Lab. 2005; 41:353–64.9. DeYoung BR, Wick MR. Immunohistologic evaluation of metastatic carcinomas of unknown origin: an algorithmic approach. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2000; 17:184–93.10. Bishop JA, Sharma R, Illei PB. Napsin A and thyroid transcription factor-1 expression in carcinomas of the lung, breast, pancreas, colon, kidney, thyroid, and malignant mesothelioma. Hum Pathol. 2010; 41:20–5.
Article11. Yu H, Li L, Liu D, Li WM. Expression of TTF-1, napsinA, P63, CK5/6 in lung cancer and its diagnostic values for histological classification. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2017; 48:336–41.12. El-Maqsoud NM, Tawfiek ER, Abdelmeged A, Rahman MF, Moustafa AA. The diagnostic utility of the triple markers Napsin A, TTF-1, and PAX8 in differentiating between primary and metastatic lung carcinomas. Tumour Biol. 2016; 37:3123–34.
Article13. Gweon HM, Kim JA, Youk JH, et al. Can galectin-3 be a useful marker for conventional papillary thyroid microcarcinoma? Diagn Cytopathol. 2016; 44:103–7.
Article14. Kandalaft PL, Gown AM. Practical applications in immunohistochemistry: carcinomas of unknown primary site. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016; 140:508–23.
Article15. Nam S, Chong Y, Jung CK, et al. Introduction to digital pathology and computer-aided pathology. J Pathol Transl Med. 2020; 54:125–34.
Article16. Lin F, Prichard J. Handbook of practical immunohistochemistry: frequently asked questions. 2nd ed. New York: Springer;2015.17. Lesaffre E, Lawson AB. Bayesian biostatistics. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons;2012.18. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2008.19. Swerdlow SH, Campo E, Harris NL, et al. WHO classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues. Revised 4th ed. Lyon: International Agency for Research on Cancer;2017.20. Rekhtman N, Bishop JA. Quick reference handbook for surgical pathologists. Heidelberg: Springer;2011.21. ImmunoQuery [Internet]. Philadelphia: Elsevier;2020. [cited 2020 Mar 1]. Available from: http://www.immunoquery.com.22. Dorfman DM, Brown JA, Shahsafaei A, Freeman GJ. Programmed death-1 (PD-1) is a marker of germinal center-associated T cells and angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006; 30:802–10.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Prediction of dental caries in 12-year-old children using machine-learning algorithms
- Machine Learning vs. Statistical Model for Prediction Modelling: Application in Medical Imaging Research
- Machine Learning on Early Diagnosis of Depression
- Determination of the stage and grade of periodontitis according to the current classification of periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions (2018) using machine learning algorithms
- Development of a Pressure Injury Machine Learning Prediction Model and Integration into Clinical Practice: A Prediction Model Development and Validation Study