Korean J Sports Med.
2020 Dec;38(4):208-216. 10.5763/kjsm.2020.38.4.208.
Efficacy of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Neck and Shoulder Pain Syndrome
- Affiliations
-
- 1210 Orthopedics, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chung-Ang University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, Kyungpook National University, Daegu, Korea
- 4Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Konkuk University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2509019
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2020.38.4.208
Abstract
- Purpose
The aim of current study is to verify the efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) in neck and shoulder pain syndrome.
Methods
We enrolled 23 patients with neck and shoulder pain syndrome (mean age, 55±16 years; onset, 12.65±8.90 months) who underwent ESWT from July to December 2019. ESWT (4 to 5 bar or 0.23–0.45 mJ/mm 2 , 1,500 to 2,000 times/region, 7 Hz) was performed at least 4 consecutive times per week. Evaluated outcomes were visual analogue scale (VAS) of pain and tenderness, neck disability index (NDI), and shoulder passive range of motion (ROM; forward flexion [FF], external rotation at neutral [ER], internal rotation at back [IR]). Pain and tenderness VAS scores were assessed at every follow-up, while NDI and shoulder ROM were evaluated two times before treatment and at the final follw-up (at 4.52±0.73 weeks).
Results
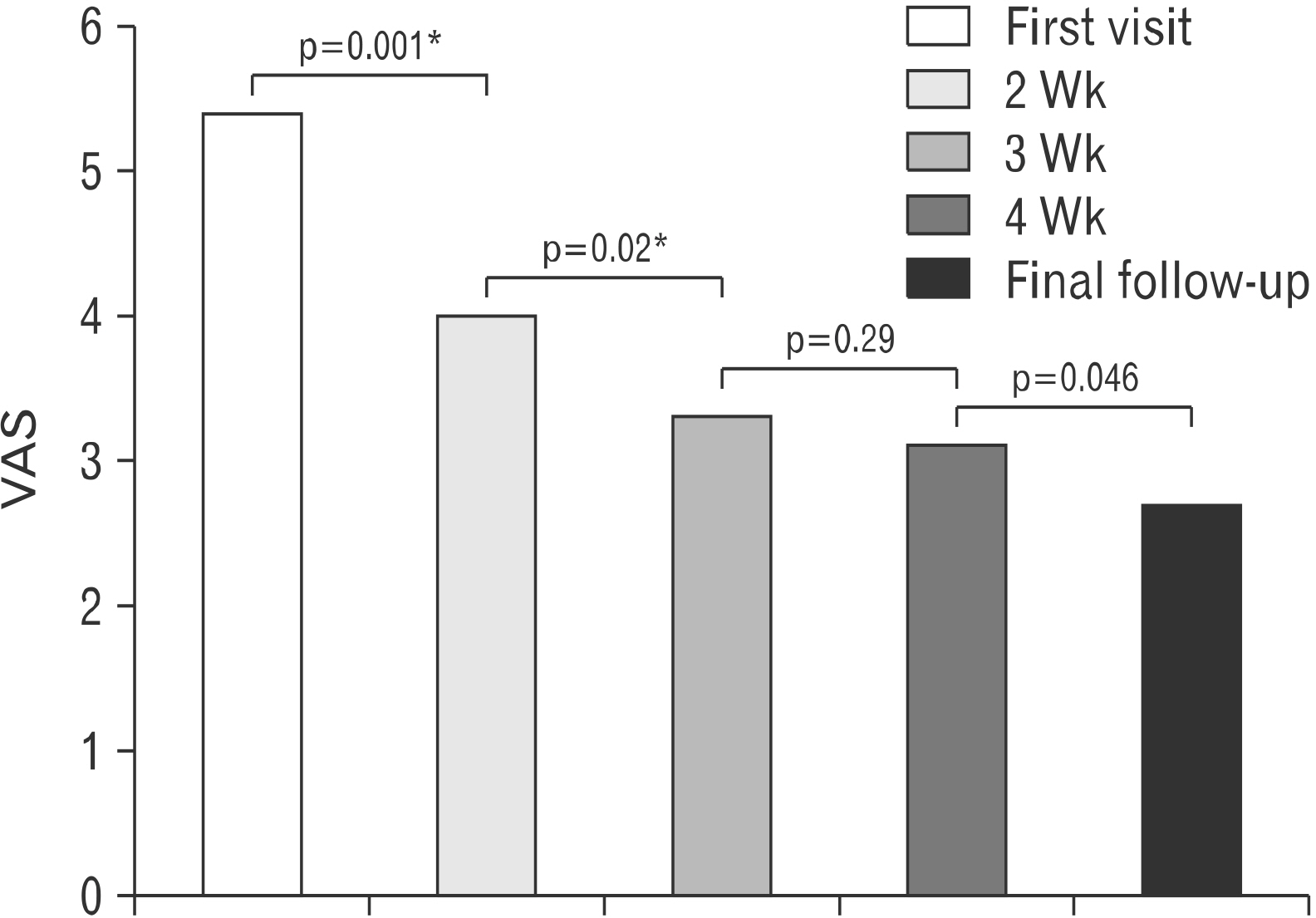
The pain VAS score decreased from 5.5±2.4 at first visit to 4.0±1.8 (p=0.001), 3.3±2.1 (p=0.02), and 3.1±2.2 (p=0.29) at the first, second, and third follow-up visits. The tenderness VAS at first visit was 5.98±1.89, which decreased to 5.17±1.83 (p=0.005), 4.61±1.67 (p=0.05), and 4.09±1.92 (p=0.06) at the first, second, and third follow-up visits. NDI was significantly reduced from 18.04±8.86 to 10.04±6.94 at last follow-up (p=0.001) and shoulder ROM was significantly improved after treatment (FF: 159.6°±28.0° to 177.8°±8.5°, p=0.001; ER: 72.2±15.7° to 79.6±2.1°, p=0.02; IR: 10.2±3.49 [T 10] to 6.9±1.7 [T 7], p=0.001).
Conclusion
Consecutive ESWT was effective in treating neck and shoulder pain syndrome with functional improvement and pain reductio
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kiraly M, Bender T, Hodosi K. 2018; Comparative study of shockwave therapy and low-level laser therapy effects in patients with myofascial pain syndrome of the trapezius. Rheumatol Int. 38:2045–52. DOI: 10.1007/s00296-018-4134-x. PMID: 30171341.
Article2. Badley EM, Tennant A. 1992; Changing profile of joint disorders with age: findings from a postal survey of the population of Calderdale, West Yorkshire, United Kingdom. Ann Rheum Dis. 51:366–71. DOI: 10.1136/ard.51.3.366. PMID: 1533506. PMCID: PMC1004663.
Article3. March LM, Brnabic AJ, Skinner JC, et al. 1998; Musculoskeletal disability among elderly people in the community. Med J Aust. 168:439–42. DOI: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1998.tb139023.x. PMID: 9612455.
Article4. Okuno H, Takeda T, Sasaoka T, et al. 2008; Relationship between katakori (shoulder stiffness) and shoulder hardness. J Japan Soc Acupunct Moxibustion. 59:30–7. DOI: 10.3777/jjsam.59.30.
Article5. Brandt M, Sundstrup E, Jakobsen MD, et al. 2014; Association between neck/shoulder pain and trapezius muscle tenderness in office workers. Pain Res Treat. 2014:352735. DOI: 10.1155/2014/352735. PMID: 24800070. PMCID: PMC3985383.
Article6. van der Windt DA, Thomas E, Pope DP, et al. 2000; Occupational risk factors for shoulder pain: a systematic review. Occup Environ Med. 57:433–42. DOI: 10.1136/oem.57.7.433. PMID: 10854494. PMCID: PMC1739981.
Article7. Gerwin RD. 2005; A review of myofascial pain and fibromyalgia: factors that promote their persistence. Acupunct Med. 23:121–34. DOI: 10.1136/aim.23.3.121. PMID: 16259310.8. Cho YS, Park SJ, Jang SH, Choi YC, Lee JH, Kim JS. 2012; Effects of the combined treatment of extracorporeal shock wave therapy (ESWT) and stabilization exercises on pain and functions of patients with myofascial pain syndrome. J Phys Ther Sci. 24:1319–23. DOI: 10.1589/jpts.24.1319.
Article9. Fisher AA, Chang CH. 1986; Temperature and pressure threshold measurement in trigger points. Thermology. 1:212–5.10. Travell JG, Simons DG. 1983. Myofascial pain and dysfunction. the trigger point manual. Volume 1:Williams &Wilkins;Baltimore, MD: p. 37–40.11. Ramon S, Gleitz M, Hernandez L, Romero LD. 2015; Update on the efficacy of extracorporeal shockwave treatment for myofascial pain syndrome and fibromyalgia. Int J Surg. 24(Pt B):201–6. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2015.08.083. PMID: 26363497.
Article12. Yap EC. 2007; Myofascial pain: an overview. Ann Acad Med Singap. 36:43–8. PMID: 17285185.13. Ji HM, Kim HJ, Han SJ. 2012; Extracorporeal shock wave therapy in myofascial pain syndrome of upper trapezius. Ann Rehabil Med. 36:675–80. DOI: 10.5535/arm.2012.36.5.675. PMID: 23185732. PMCID: PMC3503943.
Article14. Ramon S, Hernandez-Sierra L, Gomez-Centeno A, Ares O, Garcia-Manrique de Lara M, Vidiella F, Cugat R. 2014. Radial extracorporeal shockwave therapy in fibromyalgia. In : Proceedings of the 17th International Congress of the International Society for Medical Shockwave Treatment; 2014 Jun 26-28; Milan, Italy. ISMST.15. Heller KD, Niethard FU. 1998; Using extracorporeal shockwave therapy in orthopedics: a meta-analysis. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 136:390–401. DOI: 10.1055/s-2008-1053674. PMID: 9823633.16. Muller-Ehrenberg H, Licht G. 2005; Diagnosis and therapy of myofascial pain syndrome with focused shock waves (ESWT). Med Orthop Tech. 5:1–6.17. Gur A, Koca I, Karagullu H, Altindag O, Madenci E. 2013; Comparison of the efficacy of ultrasound and extracorporeal shock wave therapies in patients with myofascial pain syndrome: a randomized controlled study. J Musculoskelet Pain. 21:210–6. DOI: 10.3109/10582452.2013.828824.
Article18. Hong JO, Park JS, Jeon DG, Yoon WH, Park JH. 2017; Extracorporeal shock wave therapy versus trigger point injection in the treatment of myofascial pain syndrome in the quadratus lumborum. Ann Rehabil Med. 41:582–8. DOI: 10.5535/arm.2017.41.4.582. PMID: 28971042. PMCID: PMC5608665.
Article19. Jeon JH, Jung YJ, Lee JY, et al. 2012; The effect of extracorporeal shock wave therapy on myofascial pain syndrome. Ann Rehabil Med. 36:665–74. DOI: 10.5535/arm.2012.36.5.665. PMID: 23185731. PMCID: PMC3503942.
Article20. Zimmermann R, Cumpanas A, Miclea F, Janetschek G. 2009; Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain syndrome in males: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur Urol. 56:418–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2009.03.043. PMID: 19372000.21. Hausdorf J, Lemmens MA, Heck KD, et al. 2008; Selective loss of unmyelinated nerve fibers after extracorporeal shockwave application to the musculoskeletal system. Neuroscience. 155:138–44. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.062. PMID: 18579315.
Article22. Hausdorf J, Lemmens MA, Kaplan S, et al. 2008; Extracorporeal shockwave application to the distal femur of rabbits diminishes the number of neurons immunoreactive for substance P in dorsal root ganglia L5. Brain Res. 1207:96–101. DOI: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.013. PMID: 18371941.
Article23. Wang CJ, Wang FS, Yang KD, et al. 2003; Shock wave therapy induces neovascularization at the tendon-bone junction: a study in rabbits. J Orthop Res. 21:984–9. DOI: 10.1016/S0736-0266(03)00104-9. PMID: 14554209.
Article24. Davis TA, Stojadinovic A, Anam K, et al. 2009; Extracorporeal shock wave therapy suppresses the early proinflammatory immune response to a severe cutaneous burn injury. Int Wound J. 6:11–21. DOI: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2008.00540.x. PMID: 19291111.
Article25. Kvalvaag E, Brox JI, Engebretsen KB, et al. 2017; Effectiveness of radial extracorporeal shock wave therapy (rESWT) when combined with supervised exercises in patients with subacromial shoulder pain: a double-masked, randomized, sham- controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 45:2547–54. DOI: 10.1177/0363546517707505. PMID: 28586628.26. Chuckpaiwong B, Berkson EM, Theodore GH. 2009; Extracorporeal shock wave for chronic proximal plantar fasciitis: 225 patients with results and outcome predictors. J Foot Ankle Surg. 48:148–55. DOI: 10.1053/j.jfas.2008.11.001. PMID: 19232966.
Article27. Kudo P, Dainty K, Clarfield M, Coughlin L, Lavoie P, Lebrun C. 2006; Randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trial evaluating the treatment of plantar fasciitis with an extracoporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) device: a North American confirmatory study. J Orthop Res. 24:115–23. DOI: 10.1002/jor.20008. PMID: 16435344.
Article28. Liao CD, Tsauo JY, Chen HC, Liou TH. 2018; Efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for lower-limb tendinopathy: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 97:605–19. DOI: 10.1097/PHM.0000000000000925. PMID: 29557811.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Clinical Results of Radial and Focused Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy on Periscapular Myofascial Pain Syndrome
- How Can We Treat Calcific Tendinitis of the Shoulder?
- Current Concepts in Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy
- Effect of Radial Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy in Patients With Fabella Syndrome
- Suggestions for Effective Extracorporeal Shock Wave Treatment Methods for Lateral Epicondylitis