Arch Hand Microsurg.
2020 Dec;25(4):326-330. 10.12790/ahm.20.0074.
The Retrograde Limb of the Internal Mammary Artery: An Alternative Inflow Option for Free Flap Breast Reconstruction
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
- KMID: 2508949
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.20.0074
Abstract
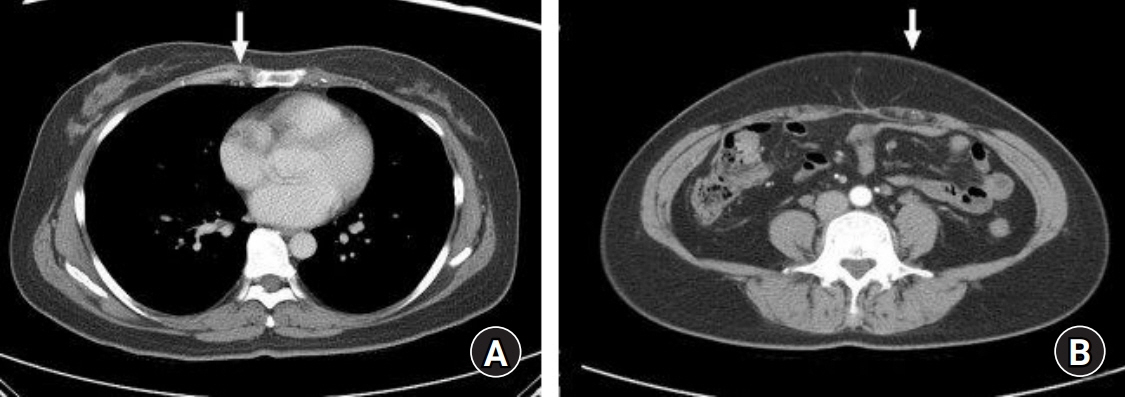
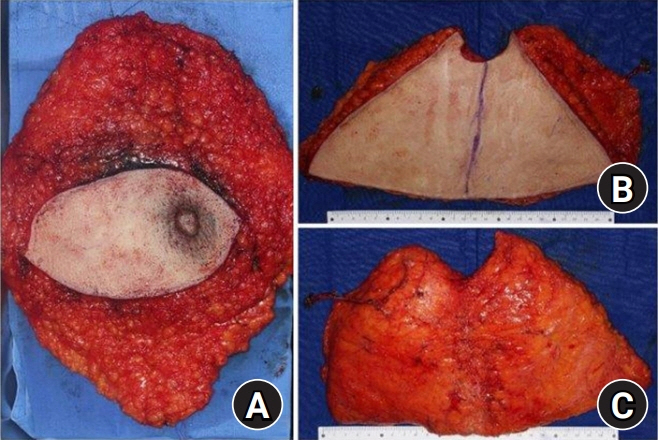
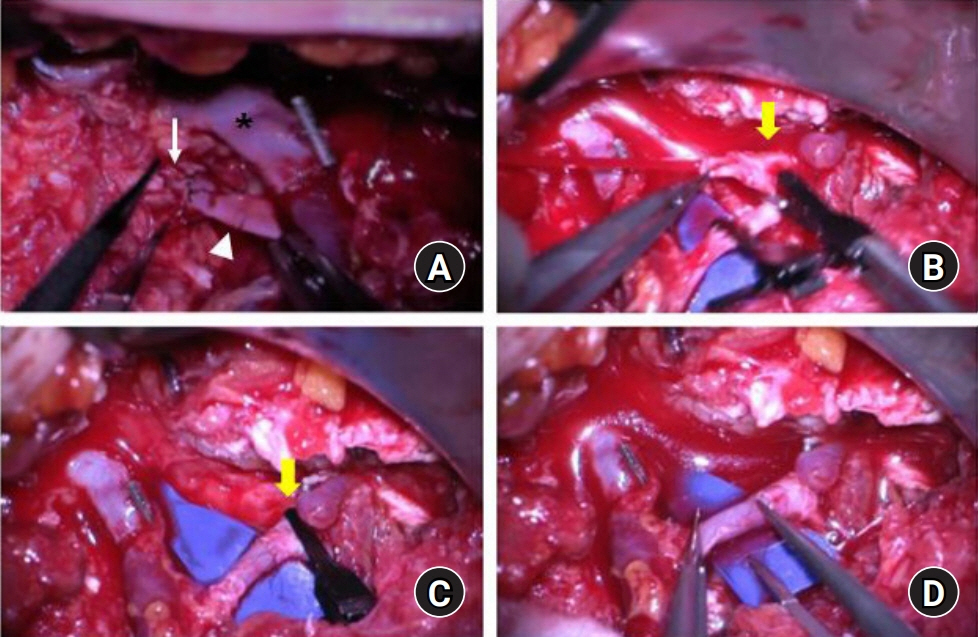
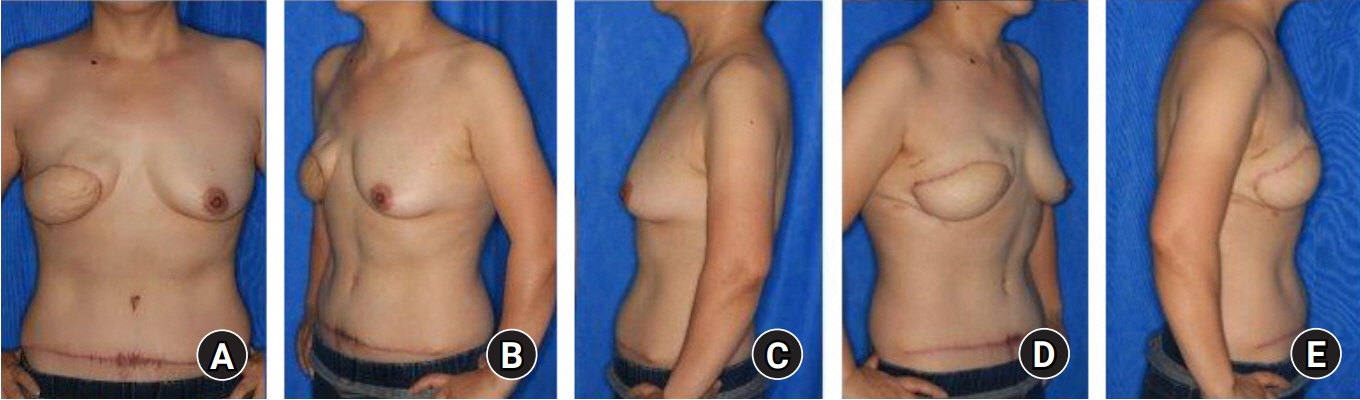
- Autologous breast reconstruction using a free flap is a popular option for breast reconstruction after mastectomy. The internal mammary system is the recipient of choice in autologous breast reconstruction. We present our experience utilizing the caudal limb of the internal mammary artery as the recipient artery. A 44-year-old female patient with invasive ductal carcinoma in her right breast received total mastectomy and reconstruction with the deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap was planned. During the operation, arterial insufficiency occurred three times; therefore, we decided to change the plan and to perform anastomosis to the caudal limb of the internal mammary artery. Retrograde blood flow of the internal mammary artery was successfully achieved. Immediate postoperative and long-term outcomes of the flap were satisfactory. This inflow option may be useful in cases with arterial insufficiency on conventional anastomosis or in cases with bipedicled or stacked flaps for unilateral breast reconstruction.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Cordeiro PG. Breast reconstruction after surgery for breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1590–601.
Article2. Saint-Cyr M, Youssef A, Bae HW, Robb GL, Chang DW. Changing trends in recipient vessel selection for microvascular autologous breast reconstruction: an analysis of 1483 consecutive cases. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2007; 119:1993–2000.
Article3. Li S, Mu L, Li Y, et al. Breast reconstruction with the free bipedicled inferior TRAM flap by anastomosis to the proximal and distal ends of the internal mammary vessels. J Reconstr Microsurg. 2002; 18:161–8.
Article4. Salgarello M, Visconti G, Barone-Adesi L, Cina A. The retrograde limb of internal mammary vessels as reliable recipient vessels in DIEP flap breast reconstruction: a clinical and radiological study. Ann Plast Surg. 2015; 74:447–53.5. Caulfield RH, Maleki-Tabrizi A, Mathur B, Ramakrishnan V. Salvage of a DIEP flap using a retrograde flow anastomosis. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008; 61:346–7.
Article6. Parker PA, Youssef A, Walker S, et al. Short-term and long-term psychosocial adjustment and quality of life in women undergoing different surgical procedures for breast cancer. Ann Surg Oncol. 2007; 14:3078–89.
Article7. Rubino C, Figus A, Lorettu L, Sechi G. Post-mastectomy reconstruction: a comparative analysis on psychosocial and psychopathological outcomes. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2007; 60:509–18.
Article8. Miller AM, Steiner CA, Barrett ML, Fingar KR, Elixhauser A. Breast reconstruction surgery for mastectomy in hospital inpatient and ambulatory settings, 2009–2014 [Internet]. Rockville, MD: Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality;c2017. [cited 2020 Nov 1]. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK481368/pdf/Bookshelf_NBK481368.pdf.9. Koshima I, Soeda S. Inferior epigastric artery skin flaps without rectus abdominis muscle. Br J Plast Surg. 1989; 42:645–8.
Article10. Salgarello M, Barone-Adesi L, Visconti G. Double-pedicle DIEP and SIEA flaps and their application in breast reconstruction. In : Salgarello M, editor. Breast reconstruction-current techniques. Rijeka, Croatia: InTek;p. 171–6.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Incidental finding of subclavian artery occlusion and subsequent hypoplastic internal mammary artery as a candidate recipient vessel in DIEP flap breast reconstruction
- Approach to Internal Mammary Vessel without Rib Cartilage Resection in Free Abdominal Flap Breast Reconstruction
- Breast Reconstruction with Superior Gluteal Artery Perforator Flap in Asian
- Selection of Recipient Vessels in Delayed Breast Reconstruction with Free TRAM Flap
- An Algorithmic Approach to Total Breast Reconstruction with Free Tissue Transfer