Nutr Res Pract.
2020 Dec;14(6):637-653. 10.4162/nrp.2020.14.6.637.
Food consumption frequency of Korean adults based on whether or not having chewing difficulty using 2013–2016 KNHANES by sex-stratified comparative analysis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Food and Nutrition, Prevention and Rehabilitation Center for Aging and Dementia, Silla University, Busan 46958, Korea
- KMID: 2508796
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4162/nrp.2020.14.6.637
Abstract
- BACKGROUND/OBJECTIVES
This study examined the associations between food consumption frequency of Korean adults and self-perceived chewing difficulty, using the food frequency questionnaire (FFQ, 112 items) from 2013–2016 of the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
SUBJECTS/METHODS
Subjects were divided into not difficult in chewing (NDC) and difficult in chewing (DC) groups, with 24.17% being classified into DC. Males and females consumed 35 and 37 items less frequently than the other sex, respectively. Due to the remarkable gender difference in food consumption, gender-stratified one-sided survey regression analysis was performed after adjusted for the effect of age, household income, and self-rated health status.
RESULTS
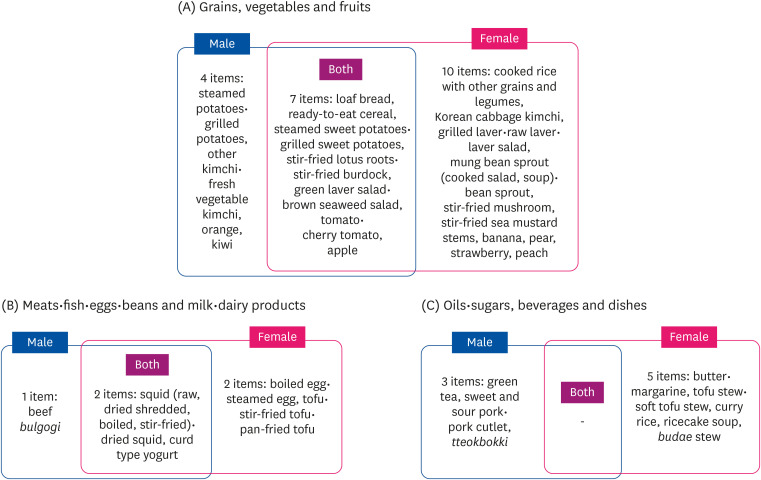
Thirty-four items of FFQ were significantly less consumed by the DC group. Females exclusively consumed less beverages and alcohol while males showed the same for fruits and milk·dairy products. Consumption frequency of 8 items such as steamed potatoes·grilled potatoes, stir fried beef, other kimchi·fresh vegetable kimchi, orange, sour pork·pork cutlet, tteokbokki and green tea were significant only in males. In contrast, 17 items including cooked rice with other grains and legumes, boiled egg·steamed egg, Korean cabbage kimchi, banana, and tofu stew·soft tofu stew were significant only for females. Finally, items that showed significance for both were 9 items including loaf bread, readyto-eat cereal, steamed sweet potatoes·grilled sweet potatoes, stir-fried lotus roots·stir-fried burdock, green laver salad·brown seaweed salads, apples, tomato·cherry tomatoes, squid (raw, dried shredded, boiled, stir-fried), and curd type yogurt.
CONCLUSIONS
Findings in this study suggest chewing difficulty may be an important nutritional issue that has to be dealt with for healthful food consumption, with distinct interest of gender.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. KOrean Statistical Information Service (KOSIS). Estimate of future population [Internet]. Daejeon: Statistics Korea;c2020. cited 2020 February 20. Available from: http://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1BPA002&vw_cd=&list_id=&scrId=&seqNo=&lang_mode=ko&obj_var_id=&itm_id=&conn_path=E1.2. United Nations. World population aging 2017 highlights [Internet]. New York (NY): 2017. cited 2019 August 10. Available from: https://www.un.org/en/development/desa/population/theme/ageing/WPA2017.asp.3. Kim SH. Effects of nutrient intake on oral health and chewing difficulty by age group. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2018; 19:202–209.4. Bortoluzzi MC, Traebert J, Lasta R, Da Rosa TN, Capella DL, Presta AA. Tooth loss, chewing ability and quality of life. Contemp Clin Dent. 2012; 3:393–397. PMID: 23633796.
Article5. Jang HH, Lee SJ. Preferences of commercial elderly-friendly foods among elderly people at senior welfare centers in Seoul. J East Asian Soc Diet Life. 2017; 27:124–136.
Article6. Kwon SH, Park HR, Lee YM, Kwon SY, Kim OS, Kim HY, Lim YS. Difference in food and nutrient intakes in Korean elderly people according to chewing difficulty: using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 (6th). Nutr Res Pract. 2017; 11:139–146. PMID: 28386387.
Article7. Park JE, An HJ, Jung SU, Lee YN, Kim C, Jang YA. Characteristics of the dietary intake of Korean elderly by chewing ability using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007–2010. J Nutr Health. 2013; 46:285–295.
Article8. Lexomboon D, Trulsson M, Wårdh I, Parker MG. Chewing ability and tooth loss: association with cognitive impairment in an elderly population study. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2012; 60:1951–1956. PMID: 23035667.
Article9. Kim EK, Lee SK, Choi YH, Tanaka M, Hirotsu K, Kim HC, Lee HK, Jung YS, Amano A. Relationship between chewing ability and cognitive impairment in the rural elderly. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2017; 70:209–213. PMID: 28214402.
Article10. Grath CM, Bedi R, Gilthorpe MS. Oral health related quality of life--views of the public in the United Kingdom. Community Dent Health. 2000; 17:3–7. PMID: 11039623.11. Naska A, Lagiou A, Lagiou P. Dietary assessment methods in epidemiological research: current state of the art and future prospects. F1000Res. 2017; 6:926. PMID: 28690835.
Article12. Pisani P, Faggiano F, Krogh V, Palli D, Vineis P, Berrino F. Relative validity and reproducibility of a food frequency dietary questionnaire for use in the Italian EPIC centres. Int J Epidemiol. 1997; 26 Suppl 1:S152–60. PMID: 9126543.
Article13. Sharma S, Cao X, Gittelsohn J, Anliker J, Ethelbah B, Caballero B. Dietary intake and a food-frequency instrument to evaluate a nutrition intervention for the Apache in Arizona. Public Health Nutr. 2007; 10:948–956. PMID: 17408518.
Article14. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The Guidelines for Use of Raw Data of Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013–2015, 2016–2017) [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2019. cited 2019 August 10. Available from: https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/sub03/sub03_06_02.do.15. Cupisti A, Kovesdy CP, D'Alessandro C, Kalantar-Zadeh K. Dietary approach to recurrent or chronic hyperkalaemia in patients with decreased kidney function. Nutrients. 2018; 10:261.
Article16. Yun SH, Shim JS, Kweon S, Oh K. Development of a food frequency questionnaire for the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey: data from the fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV). Korean J Nutr. 2013; 46:186–196.
Article17. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The nutrition survey guidelines book for 2013–2015 KNHANES [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2015. cited 2019 August 5. Available from: https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/sub04/sub04_02_02.do?classType=4.18. Ministry of Health and Welfare. The Korean Nutrition Society. Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015. Seoul: The Korean Nutrition Society;2015. p. 944–977.19. Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Survey guidelines for Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey [Internet]. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2014. cited 2019 September 10. Available from: https://knhanes.cdc.go.kr/knhanes/sub04/sub04_02_02.do?classType=4.20. Hari P, Nerusu K, Veeranna V, Sudhakar R, Zalawadiya S, Ramesh K, Afonso L. A gender-stratified comparative analysis of various definitions of metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular risk in a multiethnic U.S. population. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2012; 10:47–55. PMID: 21999397.
Article21. Asakura K, Uechi K, Masayasu S, Sasaki S. Sodium sources in the Japanese diet: difference between generations and sexes. Public Health Nutr. 2016; 19:2011–2023. PMID: 26573337.
Article22. Kang M, Park SY, Boushey CJ, Wilkens LR, Monroe KR, Le Marchand L, Kolonel LN, Murphy SP, Paik HY. Portion sizes from 24-hour dietary recalls differed by sex among those who selected the same portion size category on a food frequency questionnaire. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2018; 118:1711–1718. PMID: 29752189.
Article23. French SA, Tangney CC, Crane MM, Wang Y, Appelhans BM. Nutrition quality of food purchases varies by household income: the SHoPPER study. BMC Public Health. 2019; 19:231–237. PMID: 30808311.
Article24. Kim HJ, Park K. Egg consumption and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults: based on 2007–2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Korean J Community Nutr. 2011; 16:364–374.
Article25. Baek SW, Lee HO, Kim HJ, Won ES, Ha YS, Shin YK, Om AS. Relationship between intake of milk and milk products and bone health by sex and age-group in Koreans -using data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2011. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 2017; 46:513–522.26. Lee HJ, Lee KH. Health status assessment tool development based on dietary patterns in middle-aged women. Korean J Community Nutr. 2016; 21:37–52.
Article27. Lee H, Lee KH, Kim E, Kim MJ, Hwang SM. The related factors influencing on self-rated health level of middle-aged women. Korean J Community Nutr. 2012; 17:290–301.
Article28. Shiferaw B, Verrill L, Booth H, Zansky SM, Norton DM, Crim S, Henao OL. Sex-based differences in food consumption: Foodborne Diseases Active Surveillance Network (FoodNet) population survey, 2006–2007. Clin Infect Dis. 2012; 54 Suppl 5:S453–7. PMID: 22572669.
Article29. Woo J, Tong C, Yu R. Chewing difficulty should be included as a geriatric syndrome. Nutrients. 2018; 10:1997–2009.
Article30. Kim TH, Jin HJ. Current chewing difficulty according to dental prosthesis needs in Korean elderly. J Korea Acad Ind Coop Soc. 2014; 15:4353–4360.
Article31. The Korean Nutrition Society. Food Composition Databases. Seoul: The Korean Nutrition Society;2009. p. 88–95.32. Park YM, Kim MH, Yoon HH. Quality characteristics of sulgidduck added with purple sweet potato. Korean J Culinary Res. 2012; 18:54–64.33. Eom SH, Chun YG, Park CE, Kim BK, Lee SH, Park DJ. Application of freeze-thaw enzyme impregnation to produce softened root vegetable foods for elderly consumers. J Texture Stud. 2018; 49:404–414.
Article34. Iwasaki M, Taylor GW, Manz MC, Yoshihara A, Sato M, Muramatsu K, Watanabe R, Miyazaki H. Oral health status: relationship to nutrient and food intake among 80-year-old Japanese adults. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2014; 42:441–450. PMID: 25353039.
Article35. Shin KJ, Lee EJ, Lee JS. Study on demand elderly foods and food preferences among elderly people at senior welfare centers in Seoul. J East Asian Soc Dietary Life. 2016; 26:1–10.
Article36. Chun YG, Kim BK, Lee SH, Park DJ. Industry and technology trend of food development for the elderly. Food Industry Nutr. 2017; 22:6–14.37. Eom SH, Lee SH, Chun YG, Kim BK, Park DJ. Texture softening of beef and chicken by enzyme injection process. Korean J Food Sci Anim Resour. 2015; 35:486–493. PMID: 26761870.
Article38. Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs. The press release about “Focusing on fostering the five major food sectors” [Internet]. Sejong: Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs;2019. cited 2019 December 10. Available from: http://www.mafra.go.kr/mafra/293/subview.do?enc=Zm5jdDF8QEB8JTJGYmJzJTJGbWFmcmElMkY2OCUyRjMyMjE3OSUyRmFydGNsVmlldy5kbyUzRg%3D%3D.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Analysis of intake trends of kimchi, fruits and vegetables (1998–2020) and factors associated with the intake (2016–2020): based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Nutrient intakes and frequently consumed foods among Korean adults according to the intake frequency of Baechu (Chinese cabbage) kimchi: Based on the 2012~2013 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Dietary Behavior Factors for Desirable Nutrient Intakes of the Oldest-old Population in Sunchang County
- Food deserts in Korea? A GIS analysis of food consumption patterns at sub-district level in Seoul using the KNHANES 2008-2012 data
- Estimation of the Usual Food Intake Distribution Reflecting the Consumption Frequency and a Comparison of the Proportion of Non-consumers: Based on the KNHANES 2009