Ann Rehabil Med.
2020 Oct;44(5):386-392. 10.5535/arm.19213.
Effects of Extracorporeal Shockwave Therapy on Improvements in Lymphedema, Quality of Life, and Fibrous Tissue in Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2508464
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.19213
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effects of extracorporeal shockwave therapy (ESWT) on improving lymphedema, quality of life, and fibrous tissue in patients with stage 2 lymphedema.
Methods
Breast cancer-related lymphedema patients referred to the rehabilitation center were recruited. We enrolled stage 2 lymphedema patients who had firmness of the skin at their forearm, a circumference difference of more than 2 cm between each arm, or a volume difference between upper extremities greater than 200 mL, confirmed by lymphoscintigraphy. The patients were randomly divided into the ESWT group and the control group. ESWT was performed for 3 weeks (two sessions per week); both groups received complex decongestive physical therapy. All patients were evaluated at baseline and at 3 weeks after treatment. The measurements performed included visual analog scale score, volume, circumference, QuickDASH (Quick Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder and Hand) score, bioelectrical impedance, and skin thickness.
Results
The patients in both groups (n=15 in each group) completed the 3-week therapy experiment. No significant differences were observed in demographic characteristics between groups. After the 3-week treatment period, improvement was noted in the circumference difference below the elbow, volume, ratio of extracellular water to total body water, and skin thickness in the ESWT group. A significant difference was found in all the above-mentioned areas except in circumference below the elbow in the ESWT group.
Conclusion
ESWT reduced edema and skin fibrosis without significant complications. Therefore, ESWT can be used together with complex decongestive physical therapy for treating lymphedema.
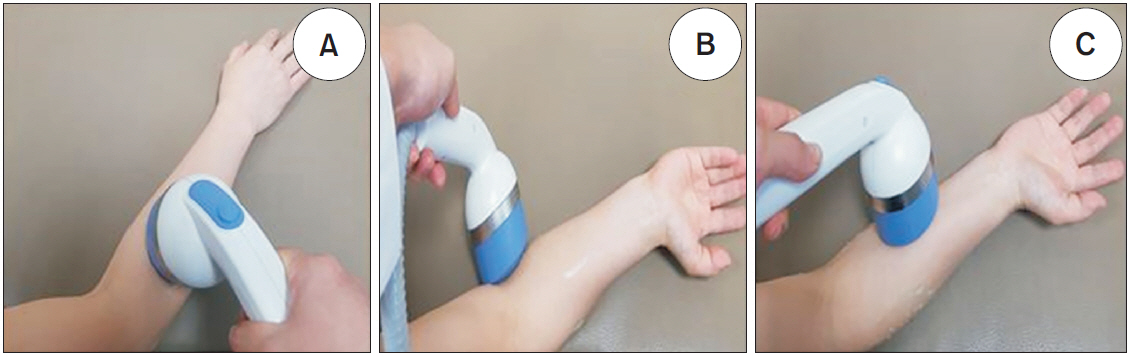
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
A Risk Factor Analysis of Axillary Web Syndrome in Patients After Breast Cancer Surgery: A Single Center Study in Korea
Sangah Jeong, Byung Joo Song, Jiyoung Rhu, Cheolki Kim, Sun Im, Geun-Young Park
Ann Rehabil Med. 2021;45(5):401-409. doi: 10.5535/arm.21092.
Reference
-
1. Warren AG, Brorson H, Borud LJ, Slavin SA. Lymphedema: a comprehensive review. Ann Plast Surg. 2007; 59:464–72.2. Hinrichs CS, Watroba NL, Rezaishiraz H, Giese W, Hurd T, Fassl KA, et al. Lymphedema secondary to postmastectomy radiation: incidence and risk factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2004; 11:573–80.
Article3. Williams AF, Vadgama A, Franks PJ, Mortimer PS. A randomized controlled crossover study of manual lymphatic drainage therapy in women with breast cancer-related lymphoedema. Eur J Cancer Care (Engl). 2002; 11:254–61.
Article4. Moattari M, Jaafari B, Talei A, Piroozi S, Tahmasebi S, Zakeri Z. The effect of combined decongestive therapy and pneumatic compression pump on lymphedema indicators in patients with breast cancer related lymphedema. Iran Red Crescent Med J. 2012; 14:210–7.5. Hwang JM, Hwang JH, Kim TW, Lee SY, Chang HJ, Chu IH. Long-term effects of complex decongestive therapy in breast cancer patients with arm lymphedema after axillary dissection. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013; 37:690–7.
Article6. Finnane A, Janda M, Hayes SC. Review of the evidence of lymphedema treatment effect. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2015; 94:483–98.
Article7. Koul R, Dufan T, Russell C, Guenther W, Nugent Z, Sun X, et al. Efficacy of complete decongestive therapy and manual lymphatic drainage on treatment-related lymphedema in breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007; 67:841–6.
Article8. Tiwari P, Coriddi M, Salani R, Povoski SP. Breast and gynecologic cancer-related extremity lymphedema: a review of diagnostic modalities and management options. World J Surg Oncol. 2013; 11:237.
Article9. Yamamoto R, Yamamoto T. Effectiveness of the treatment-phase of two-phase complex decongestive physiotherapy for the treatment of extremity lymphedema. Int J Clin Oncol. 2007; 12:463–8.
Article10. Korpan MI, Crevenna R, Fialka-Moser V. Lymphedema: a therapeutic approach in the treatment and rehabilitation of cancer patients. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2011; 90(5 Suppl 1):S69–75.11. Kubo M, Li TS, Kamota T, Ohshima M, Shirasawa B, Hamano K. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy ameliorates secondary lymphedema by promoting lymphangiogenesis. J Vasc Surg. 2010; 52:429–34.
Article12. Serizawa F, Ito K, Matsubara M, Sato A, Shimokawa H, Satomi S. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy induces therapeutic lymphangiogenesis in a rat model of secondary lymphoedema. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011; 42:254–60.
Article13. Bae H, Kim HJ. Clinical outcomes of extracorporeal shock wave therapy in patients with secondary lymphedema: a pilot study. Ann Rehabil Med. 2013; 37:229–34.
Article14. Cebicci MA, Sutbeyaz ST, Goksu SS, Hocaoglu S, Oguz A, Atilabey A. Extracorporeal shock wave therapy for breast cancer-related lymphedema: a pilot study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2016; 97:1520–5.
Article15. Mutlu H, Akca Z, Teke HU, Ugur H. Evaluation of peripheral blood smear for myelodysplasia in breast cancer patients who received adjuvant antracycline. Eurasian J Med. 2011; 43:173–6.
Article16. Horan D, McMullen M. Assessment and management of the woman with lymphedema after breast cancer. J Am Acad Nurse Pract. 1998; 10:155–9.17. Vignes S, Porcher R, Arrault M, Dupuy A. Long-term management of breast cancer-related lymphedema after intensive decongestive physiotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2007; 101:285–90.
Article18. Casley-Smith JR, Casley-Smith JR. Treatment of lymphedema by complex physical therapy, with and without oral and topical benzopyrones: what should therapists and patients expect. Lymphology. 1996; 29:76–82.19. Tinazzi E, Amelio E, Marangoni E, Guerra C, Puccetti A, Codella OM, et al. Effects of shock wave therapy in the skin of patients with progressive systemic sclerosis: a pilot study. Rheumatol Int. 2011; 31:651–6.
Article20. Gupta D, Lammersfeld CA, Vashi PG, King J, Dahlk SL, Grutsch JF, et al. Bioelectrical impedance phase angle as a prognostic indicator in breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2008; 8:249.
Article21. Tuorkey MJ. Bioelectrical impedance as a diagnostic factor in the clinical practice and prognostic factor for survival in cancer patients: prediction, accuracy and reliability. J Biosens Bioelectron. 2012; 3:121.
Article22. Cornish BH, Chapman M, Hirst C, Mirolo B, Bunce IH, Ward LC, et al. Early diagnosis of lymphedema using multiple frequency bioimpedance. Lymphology. 2001; 34:2–11.23. Ward LC, Dylke E, Czerniec S, Isenring E, Kilbreath SL. Confirmation of the reference impedance ratios used for assessment of breast cancer-related lymphedema by bioelectrical impedance spectroscopy. Lymphat Res Biol. 2011; 9:47–51.
Article24. Ward LC. Bioelectrical impedance analysis: proven utility in lymphedema risk assessment and therapeutic monitoring. Lymphat Res Biol. 2006; 4:51–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Health-Related Quality of Life in Breast Cancer Patients with Lymphedema Who Survived More than One Year after Surgery
- Rapid Lymphedema Progression in Breast Cancer Patient with Previous Forearm Fracture
- Management of Lymphedema
- Comparisons of Physiological and Psychosocial Symptoms for Breast Cancer Patients with and without Lymphedema
- Feasibility of Extracorporeal Shock Wave Therapy for Complex Upper Limb Morbidity in Breast Cancer Patient