Korean J Schizophr Res.
2020 Oct;23(2):65-70. 10.16946/kjsr.2020.23.2.65.
Comparison of Polygenic Risk for Schizophrenia between European and Korean Populations
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Psychiatry, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- 2Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Center for Clinical Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2508354
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.16946/kjsr.2020.23.2.65
Abstract
Objectives
This study aimed to explore whether common genetic variants that confer the risk of schizophrenia have similar effects between Korean and European ancestries using the polygenic risk score (PRS) analysis.
Methods
Study subjects included 713 Korean patients with schizophrenia and 497 healthy controls. The Korea Biobank array was used for genotyping. Summary statistics of the most recent genome-wide association study (GWAS) of the European population were used as baseline data to calculate PRS. Logistic regression was conducted to determine the association between calculated PRS of European patients with schizophrenia and clinical diagnosis of schizophrenia in the Korean population.
Results
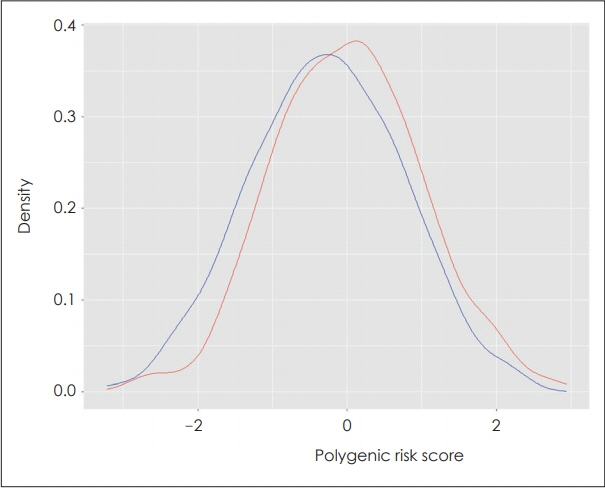
Schizophrenia PRS was significantly higher in patients with schizophrenia than in healthy controls. The PRS at the pvalue threshold of 0.5 best explained the variance of schizophrenia (R2=0.028, p=4.4×10-6). The association was significant after adjusting for age and sex (odds ratio=1.34, 95% confidence interval=1.19-1.51, p=1.1×10−6). The pattern of the association remained similar across different p-value thresholds (0.01-1).
Conclusion
Schizophrenia PRS calculated using the European GWAS data showed a significant association with the clinical diagnosis of schizophrenia in the Korean population. Results suggest overlapping genetic risk variants between the two populations.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Stilo SA, Murray RM. The epidemiology of schizophrenia: replacing dogma with knowledge. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2010; 12:305–315.
Article2. Flint J, Munafò M. Schizophrenia: genesis of a complex disease. Nature. 2014; 511:412–413.3. Cardno AG, Gottesman II. Twin studies of schizophrenia: from bowand-arrow concordances to star wars Mx and functional genomics. Am J Med Genet. 2000; 97:12–17.
Article4. Sullivan PF, Kendler KS, Neale MC. Schizophrenia as a complex trait: evidence from a meta-analysis of twin studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2003; 60:1187–1192.5. Burmeister M, McInnis MG, Zöllner S. Psychiatric genetics: progress amid controversy. Nat Rev Genet. 2008; 9:527–540.
Article6. van Os J, Kapur S. Schizophrenia. Lancet. 2009; 374:635–645.
Article7. Allen NC, Bagade S, McQueen MB, Ioannidis JP, Kavvoura FK, Khoury MJ, et al. Systematic meta-analyses and field synopsis of genetic association studies in schizophrenia: the SzGene database. Nat Genet. 2008; 40:827.
Article8. Collins AL, Kim Y, Sklar P, O’Donovan MC, Sullivan PF, Consortium IS. Hypothesis-driven candidate genes for schizophrenia compared to genome-wide association results. Psychol Med. 2012; 42:607.
Article9. Purcell SM, Wray NR, Stone JL, Visscher PM, O’Donovan MC, Sullivan PF, et al. Common polygenic variation contributes to risk of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Nature. 2009; 460:748–752.
Article10. Schizophrenia Working Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Biological insights from 108 schizophrenia-associated genetic loci. Nature. 2014; 511:421–427.
Article11. Dickson SP, Wang K, Krantz I, Hakonarson H, Goldstein DB. Rare variants create synthetic genome-wide associations. PLoS Biol. 2010; 8:e1000294.
Article12. Li Z, Chen J, Yu H, He L, Xu Y, Zhang D, et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies 30 new susceptibility loci for schizophrenia. Nat Genet. 2017; 49:1576–1583.
Article13. Yue WH, Wang HF, Sun LD, Tang FL, Liu ZH, Zhang HX, et al. Genome-wide association study identifies a susceptibility locus for schizophrenia in Han Chinese at 11p11. 2. Nat Genet. 2011; 43:1228–1231.14. Martin AR, Gignoux CR, Walters RK, Wojcik GL, Neale BM, Gravel S, et al. Human Demographic History Impacts Genetic Risk Prediction across Diverse Populations. Am J Hum Genet. 2017; 100:635–649.
Article15. Wray NR, Goddard ME, Visscher PM. Prediction of individual genetic risk to disease from genome-wide association studies. Genome Res. 2007; 17:1520–1528.
Article16. Visscher PM, Wray NR, Zhang Q, Sklar P, McCarthy MI, Brown MA, et al. 10 years of GWAS discovery: biology, function, and translation. Am J Hum Genet. 2017; 101:5–22.
Article17. Rammos A, Gonzalez LAN, Weinberger DR, Mitchell KJ, Nicodemus KK. The role of polygenic risk score gene-set analysis in the context of the omnigenic model of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2019; 44:1562–1569.
Article18. Morales J, Welter D, Bowler EH, Cerezo M, Harris LW, McMahon AC, et al. A standardized framework for representation of ancestry data in genomics studies, with application to the NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog. Genome Biol. 2018; 19:21.
Article19. Popejoy AB, Fullerton SM. Genomics is failing on diversity. Nature. 2016; 538:161–164.
Article20. Ikeda M, Takahashi A, Kamatani Y, Momozawa Y, Saito T, Kondo K, et al. Genome-wide association study detected novel susceptibility genes for schizophrenia and shared trans-populations/diseases genetic effect. Schizophr Bull. 2019; 45:824–834.
Article21. Martin AR, Kanai M, Kamatani Y, Okada Y, Neale BM, Daly MJ. Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nat Genet. 2019; 51:584–591.
Article22. Lam M, Chen CY, Li Z, Martin AR, Bryois J, Ma X, et al. Comparative genetic architectures of schizophrenia in East Asian and European populations. Nat Genet. 2019; 51:1670–1678.
Article23. American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition, text revision (DSM-IV-TR). Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association;2000.24. Moon S, Kim YJ, Han S, Hwang MY, Shin DM, Park MY, et al. The Korea Biobank Array: design and identification of coding variants associated with blood biochemical traits. Sci Rep. 2019; 9:1382.
Article25. Choi SW, O’Reilly PF. PRSice-2: Polygenic Risk Score software for biobank-scale data. Gigascience. 2019; 8:giz082.
Article26. Duncan L, Shen H, Gelaye B, Meijsen J, Ressler K, Feldman M, et al. Analysis of polygenic risk score usage and performance in diverse human populations. Nat Commun. 2019; 10:3328.
Article27. Marnetto D, Pärna K, Läll K, Molinaro L, Montinaro F, Haller T, et al. Ancestry deconvolution and partial polygenic score can improve susceptibility predictions in recently admixed individuals. Nat Commun. 2020; 11:1–9.
Article28. Talarico F, Santoro M, Ota VK, Gadelha A, Pellegrino R, Hakonarson H, et al. Implications of an admixed Brazilian population in schizophrenia polygenic risk score. Schizophr Res. 2019; 204:404.
Article29. Wimberley T, Gasse C, Meier SM, Agerbo E, MacCabe JH, Horsdal HT. Polygenic risk score for schizophrenia and treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 2017; 43:1064–1069.
Article30. Zhang JP, Robinson D, Yu J, Gallego J, Fleischhacker WW, Kahn RS, et al. Schizophrenia polygenic risk score as a predictor of antipsychotic efficacy in first-episode psychosis. Am J Psychiatry. 2019; 176:21–28.
Article31. Jonas KG, Lencz T, Li K, Malhotra AK, Perlman G, Fochtmann LJ, et al. Schizophrenia polygenic risk score and 20-year course of illness in psychotic disorders. Transl Psychiatry. 2019; 9:300.
Article32. Musliner KL, Krebs MD, Albiñana C, Vilhjalmsson B, Agerbo E, Zandi PP, et al. Polygenic risk and progression to bipolar or psychotic disorders among individuals diagnosed with unipolar depression in early life. Am J Psychiatry. 2020; appiajp202019111195.
Article33. Perkins DO, Olde Loohuis L, Barbee J, Ford J, Jeffries CD, Addington J, et al. Polygenic risk score contribution to psychosis prediction in a target population of persons at clinical high risk. Am J Psychiatry. 2020; 177:155–163.
Article34. Curtis D. Polygenic risk score for schizophrenia is more strongly associated with ancestry than with schizophrenia. Psychiatr Genet. 2018; 28:85–89.
Article35. Fabbri C, Serretti A. Role of 108 schizophrenia-associated loci in modulating psychopathological dimensions in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2017; 174:757–764.
Article36. Mistry S, Harrison JR, Smith DJ, Escott-Price V, Zammit S. The use of polygenic risk scores to identify phenotypes associated with genetic risk of bipolar disorder and depression: a systematic review. J Affect Disord. 2018; 234:148–155.
Article37. Vassos E, Di Forti M, Coleman J, Iyegbe C, Prata D, Euesden J, et al. An examination of polygenic score risk prediction in individuals with first-episode psychosis. Biol Psychiatry. 2017; 81:470–477.
Article38. Gasse C, Wimberley T, Wang Y, Mors O, Børglum A, Als TD, et al. Schizophrenia polygenic risk scores, urbanicity and treatmentresistant schizophrenia. Schizophr Res. 2019; 212:79–85.
Article39. Toulopoulou T, Zhang X, Cherny S, Dickinson D, Berman KF, Straub RE, et al. Polygenic risk score increases schizophrenia liability through cognition-relevant pathways. Brain. 2019; 142:471–485.
Article40. Zhang JP, Robinson D, Yu J, Gallego J, Fleischhacker WW, Kahn RS, et al. Schizophrenia polygenic risk score as a predictor of antipsychotic efficacy in first-episode psychosis. Am J Psychiatry. 2019; 176:21–28.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Polygenic Risk Scores for Bipolar Disorder in Korean Populations in Comparison to European Populations
- Polygenic risk score for genetic evaluation of prostate cancer risk in Asian populations: A narrative review
- Polygenic Risk Score and Precision Medicine in Diabetes
- Recapitulation of previously reported associations for type 2 diabetes and metabolic traits in the 126K East Asians
- Neuroimaging Findings in Subjects at High Risk for Developing Schizophrenia