Neurointervention.
2020 Nov;15(3):117-125. 10.5469/neuroint.2020.00248.
Bench-Top Comparison of Three Different Types of Stents Used for Treatment of Intracranial Atherosclerotic Stenosis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurysurgery, Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- 2Department of Radiology, Jeonbuk National University Hospital, Jeonju, Korea
- 3Department of Bionanosystem Engineering, Graduate School, Jeonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea
- KMID: 2508063
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5469/neuroint.2020.00248
Abstract
- Purpose
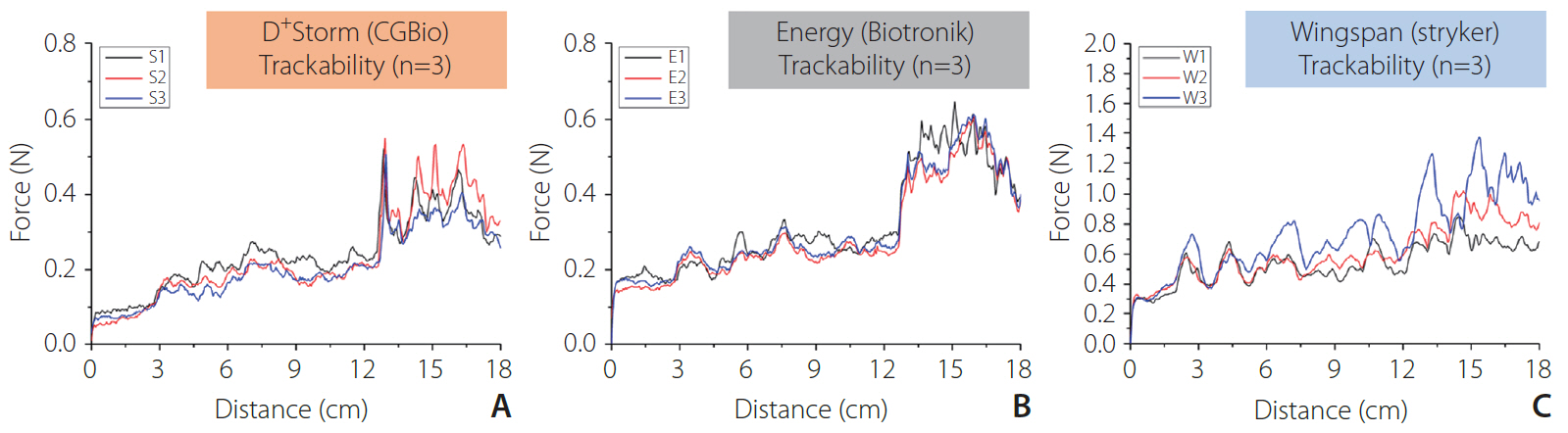
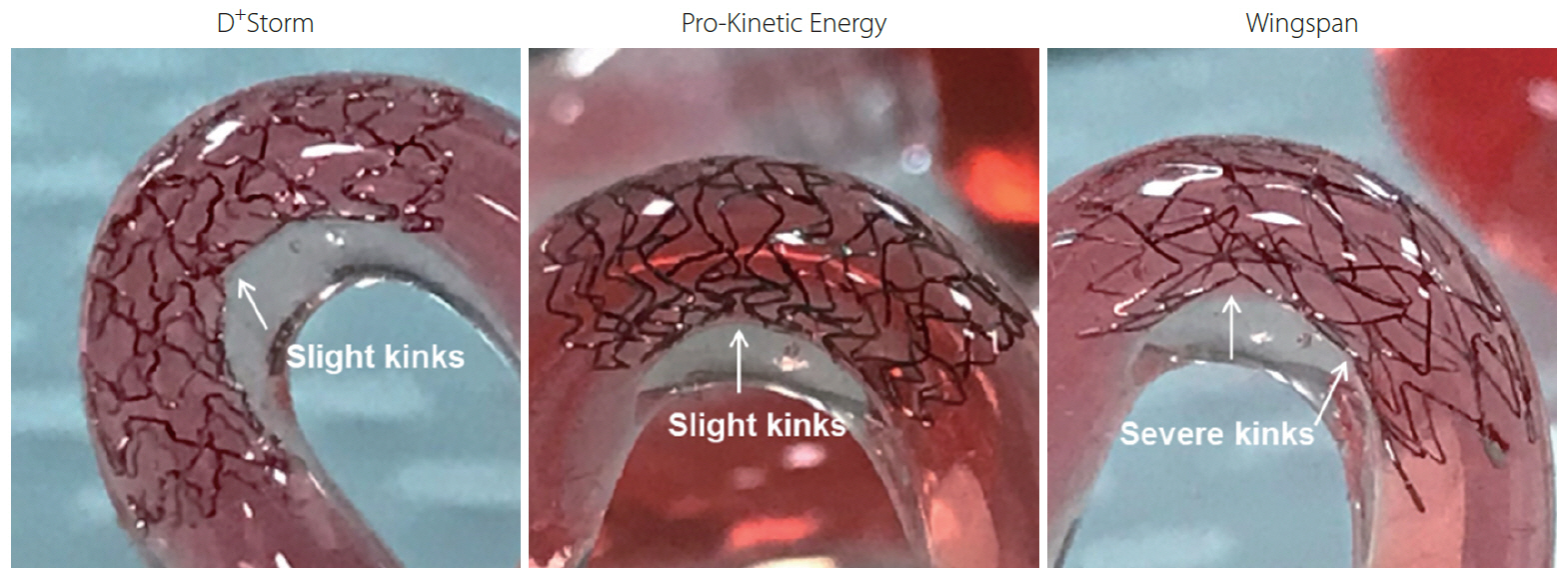
Four key bench-top tests, including trackability, conformability, wall-apposition, and bending stiffness, were performed to understand the mechanical characteristics in 3 different types of stents applicable for treatment of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: Balloon-expandable D+Storm, Pro-Kinetic Energy, and self-expandable Wingspan stents.
Materials and Methods
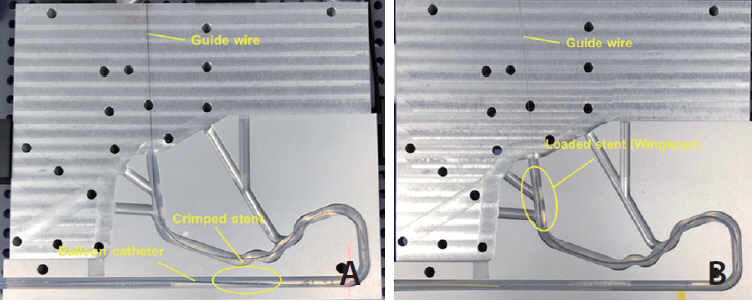
Trackability was assessed by measuring the tracking forces of each stent with its delivery systems. Conformability and wall apposition were quantified and analyzed using curved vessel models. A 3-point bending test was employed to evaluate bending stiffness.
Results
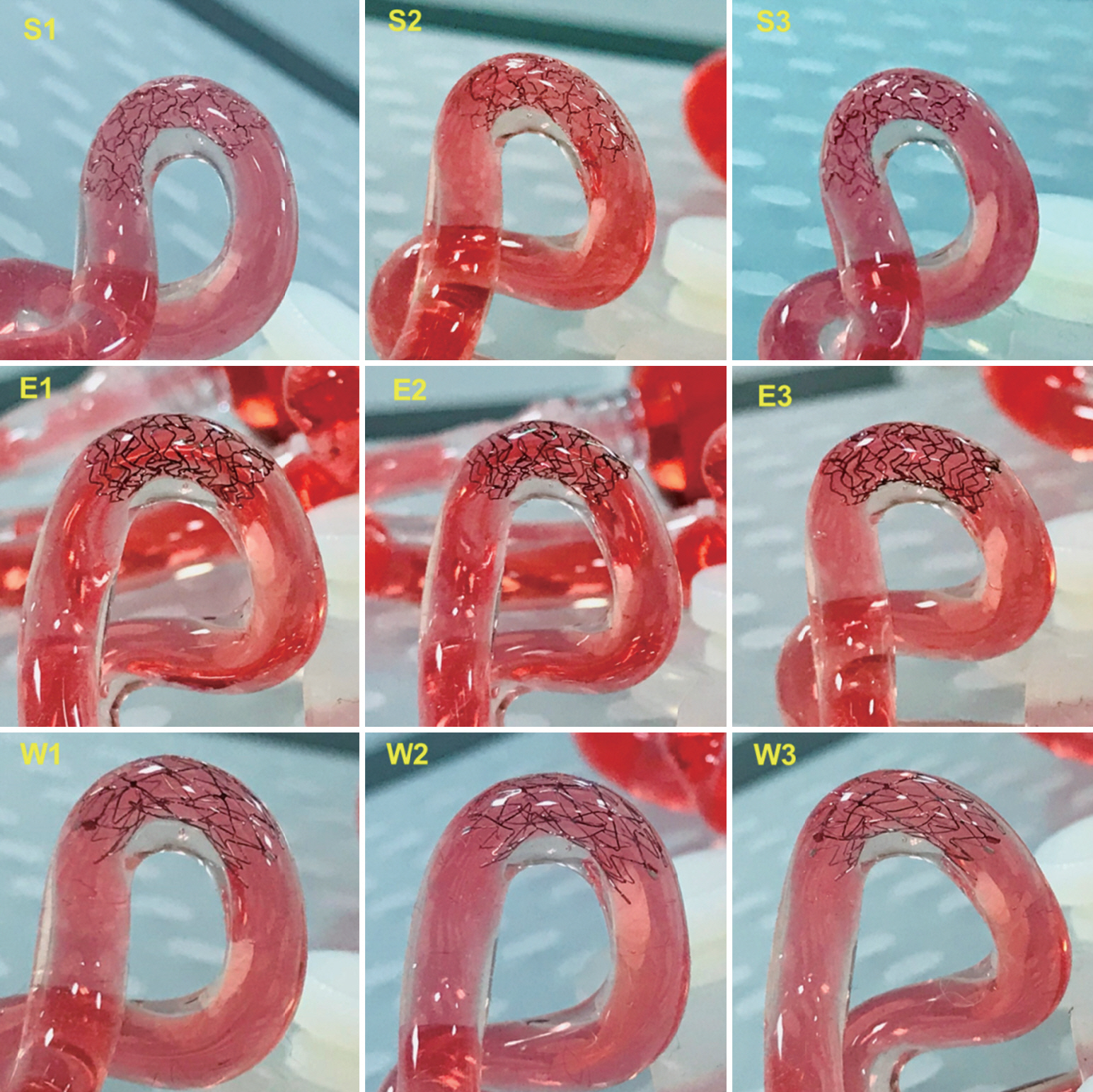
D+Storm showed the lowest tracking forces while the conformability of the Wingspan stent was superior to that of the tested stents. Pro-Kinetic Energy and D+Storm had better wall apposition in curved vessels than the Wingspan stent. Bending stiffness of the Wingspan stent was notably lower, whereas no significant differences were found between D+Storm and Energy. Pro-Kinetic Energy and D+Storm not only indicated lower gap ratios between the struts and the vessel wall but also maintained good wall apposition even in the curved model.
Conclusion
These bench-top measurements may provide clinicians with useful information in regard to selecting suitable stents for treatment of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Feigin VL. Stroke in developing countries: can the epidemic be stopped and outcomes improved? Lancet Neurol. 2007; 6:94–97.
Article2. Strong K, Mathers C, Bonita R. Preventing stroke: saving lives around the world. Lancet Neurol. 2007; 6:182–187.
Article3. Koton S, Schneider AL, Rosamond WD, Shahar E, Sang Y, Gottesman RF, et al. Stroke incidence and mortality trends in US communities, 1987 to 2011. JAMA. 2014; 312:259–268.
Article4. Gorelick PB, Wong KS, Bae HJ, Pandey DK. Large artery intracranial occlusive disease: a large worldwide burden but a relatively neglected frontier. Stroke. 2008; 39:2396–2399.5. Wong LK. Global burden of intracranial atherosclerosis. Int J Stroke. 2006; 1:158–159.
Article6. Thijs VN, Albers GW. Symptomatic intracranial atherosclerosis: outcome of patients who fail antithrombotic therapy. Neurology. 2000; 55:490–497.
Article7. Chimowitz MI, Kokkinos J, Strong J, Brown MB, Levine SR, Silliman S, et al. The warfarin-aspirin symptomatic intracranial disease study. Neurology. 1995; 45:1488–1493.
Article8. Luo J, Wang T, Gao P, Krings T, Jiao L. Endovascular treatment of intracranial atherosclerotic stenosis: current debates and future prospects. Front Neurol. 2018; 9:666.
Article9. Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Howlett-Smith H, Stern BJ, Hertzberg VS, Frankel MR, Warfarin-Aspirin Symptomatic Intracranial Disease Trial Investigators, et al. Comparison of warfarin and aspirin for symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:1305–1316.
Article10. Kasner SE, Chimowitz MI, Lynn MJ, Howlett-Smith H, Stern BJ, Hertzberg VS, et al. Predictors of ischemic stroke in the territory of a symptomatic intracranial arterial stenosis. Circulation. 2006; 113:555–563.
Article11. Turan TN, Derdeyn CP, Fiorella D, Chimowitz MI. Treatment of atherosclerotic intracranial arterial stenosis. Stroke. 2009; 40:2257–2261.
Article12. Lylyk P, Cohen JE, Ceratto R, Ferrario A, Miranda C. Angioplasty and stent placement in intracranial atherosclerotic stenoses and dissections. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2002; 23:430–436.13. Mori T, Kazita K, Mori K. Cerebral angioplasty and stenting for intracranial vertebral atherosclerotic stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:787–789.14. SSYLVIA Study Investigators. Stenting of symptomatic atherosclerotic lesions in the vertebral or intracranial arteries (SSYLVIA): study results. Stroke. 2004; 35:1388–1392.15. Kimura T, Yokoi H, Nakagawa Y, Tamura T, Kaburagi S, Sawada Y, et al. Three-year follow-up after implantation of metallic coronary-artery stents. N Engl J Med. 1996; 334:561–566.
Article16. Vajda Z, Miloslavski E, Güthe T, Schmid E, Schul C, Albes G, et al. Treatment of intracranial atherosclerotic arterial stenoses with a balloon-expandable cobalt chromium stent (Coroflex Blue): procedural safety, efficacy, and midterm patency. Neuroradiology. 2010; 52:645–651.
Article17. Bose A, Hartmann M, Henkes H, Liu HM, Teng MM, Szikora I, et al. A novel, self-expanding, nitinol stent in medically refractory intracranial atherosclerotic stenoses: the Wingspan study. Stroke. 2007; 38:1531–1537.18. Zaidat OO, Klucznik R, Alexander MJ, Chaloupka J, Lutsep H, Barnwell S, NIH Multi-center Wingspan Intracranial Stent Registry Study Group, et al. The NIH registry on use of the Wingspan stent for symptomatic 70-99% intracranial arterial stenosis. Neurology. 2008; 70:1518–1524.
Article19. Albuquerque FC, Levy EI, Turk AS, Niemann DB, Aagaard-Kienitz B, Pride GL Jr, et al. Angiographic patterns of Wingspan in-stent restenosis. Neurosurgery. 2008; 63:23–27. discussion 27-28.
Article20. Miao Z, Zhang Y, Shuai J, Jiang C, Zhu Q, Chen K, Study Group of Registry Study of Stenting for Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis in China, et al. Thirty-day outcome of a multicenter registry study of stenting for symptomatic intracranial artery stenosis in China. Stroke. 2015; 46:2822–2829.
Article21. Liu L, Zhao X, Mo D, Ma N, Gao F, Miao Z. Stenting for symptomatic intracranial vertebrobasilar artery stenosis: 30-day results in a high-volume stroke center. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2016; 143:132–138.
Article22. Rohde S, Seckinger J, Hähnel S, Ringleb PA, Bendszus M, Hartmann M. Stent design lowers angiographic but not clinical adverse events in stenting of symptomatic intracranial stenosis - results of a single center study with 100 consecutive patients. Int J Stroke. 2013; 8:87–94.
Article23. Wang Q, Fang G, Zhao Y, Wang G, Cai T. Computational and experimental investigation into mechanical performances of Poly-L-Lactide Acid (PLLA) coronary stents. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2017; 65:415–427.
Article24. du Mesnil de Rochemont R, Yan B, Zanella FE, Rüfenacht DA, Berkefeld J. Conformability of balloon-expandable stents to the carotid siphon: an in vitro study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:324–326.25. Gao B, Baharoglu MI, Cohen AD, Malek AM. Stent-assisted coiling of intracranial bifurcation aneurysms leads to immediate and delayed intracranial vascular angle remodeling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012; 33:649–654.
Article26. Siqueira DA, Abizaid AA, Costa Jde R, Feres F, Mattos LA, Staico R, et al. Late incomplete apposition after drug-eluting stent implantation: incidence and potential for adverse clinical outcomes. Eur Heart J. 2007; 28:1304–1309.
Article27. Heller RS, Malek AM. Parent vessel size and curvature strongly influence risk of incomplete stent apposition in enterprise intracranial aneurysm stent coiling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 32:1714–1720.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Guideline for Intracranial Stenting of Symptomatic Intracranial Artery Stenosis: Preliminary Report
- Bench-top Comparison of Physical Properties of 4 Commercially-Available Self-Expanding Intracranial Stents
- Angioplasty, Stenting and Other Potential Treatments of Atherosclerotic Stenosis of the Intracranial Arteries: Past, Present and Future
- Stenting of Symptomatic Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis: Case Report
- Intracranial Stent Implantation for Drug Resistant Atherosclerotic Stenosis: Results of 52 Cases