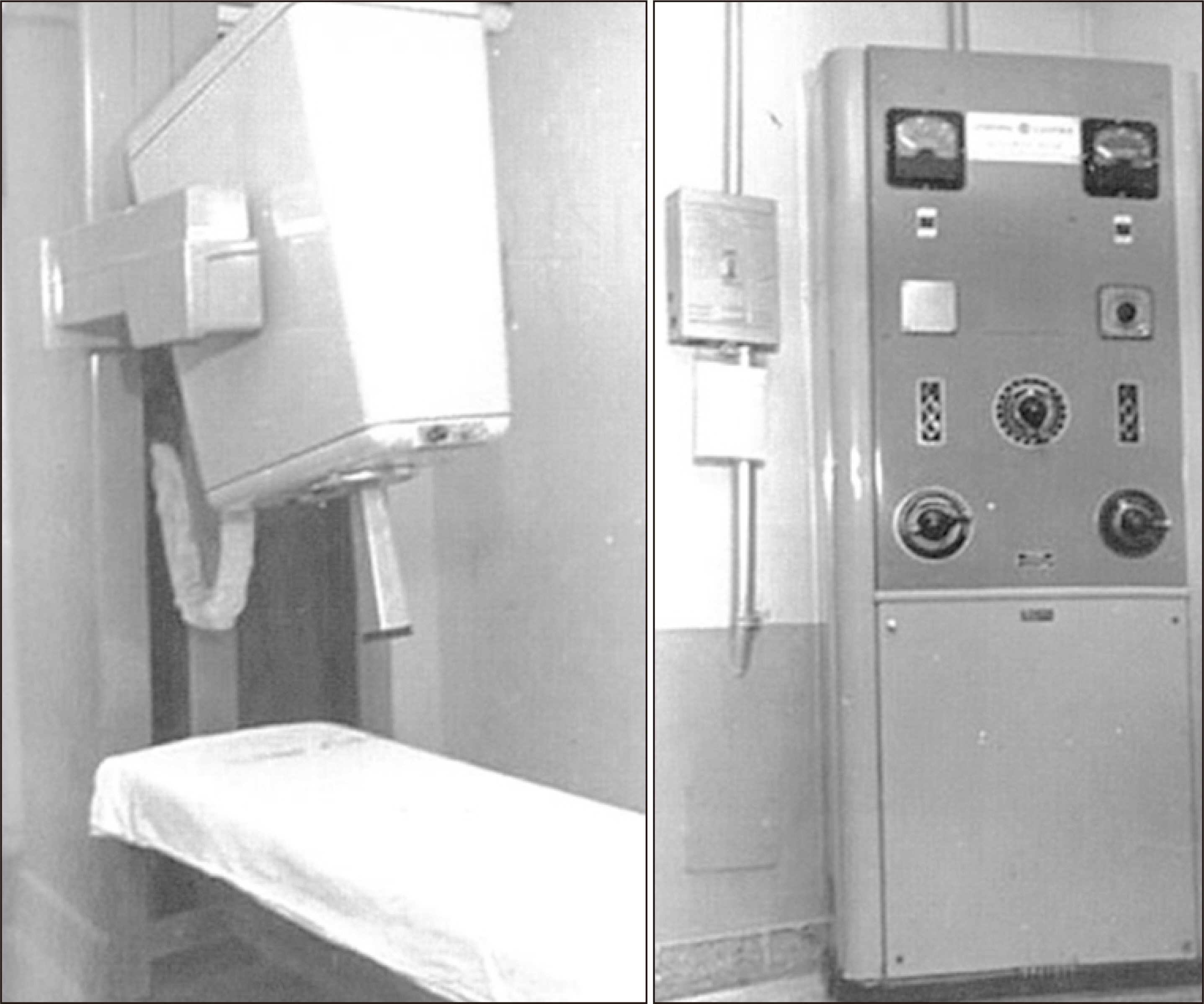
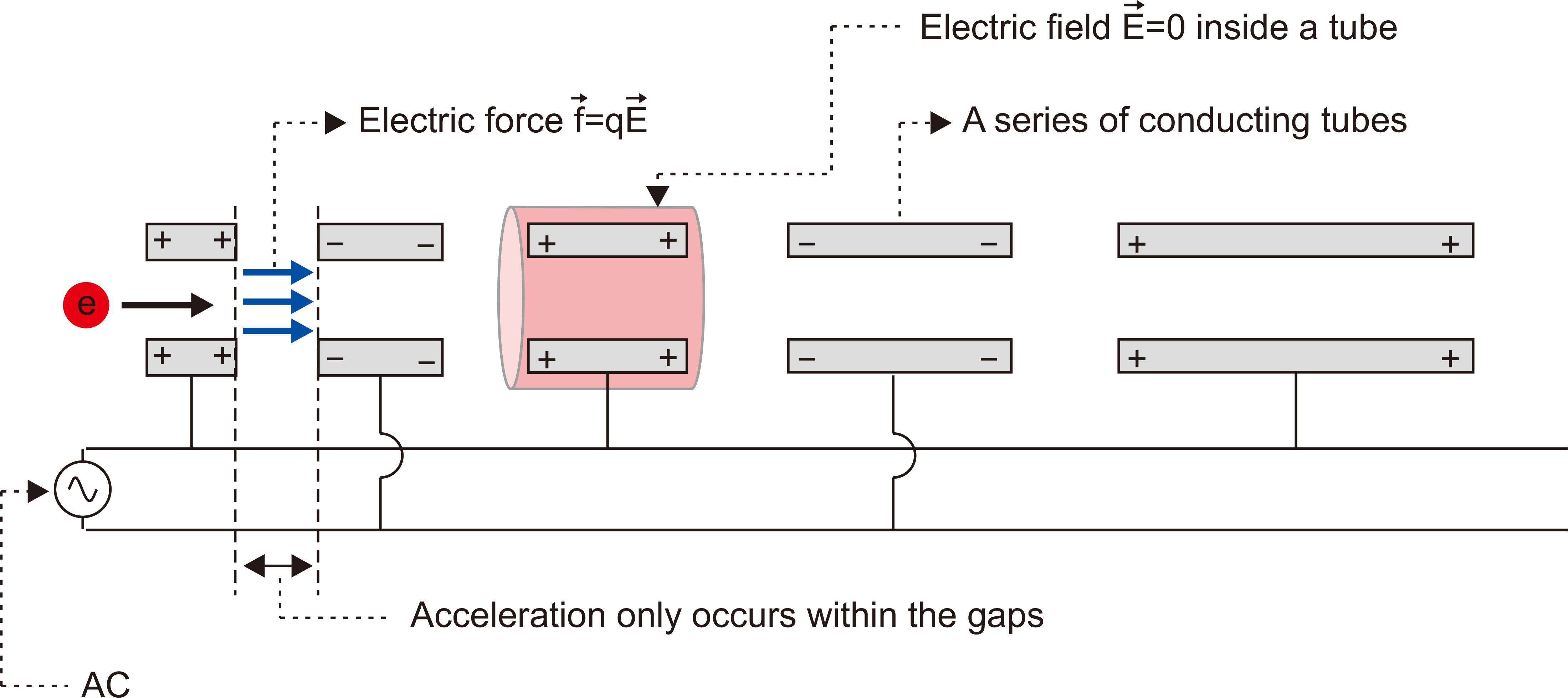
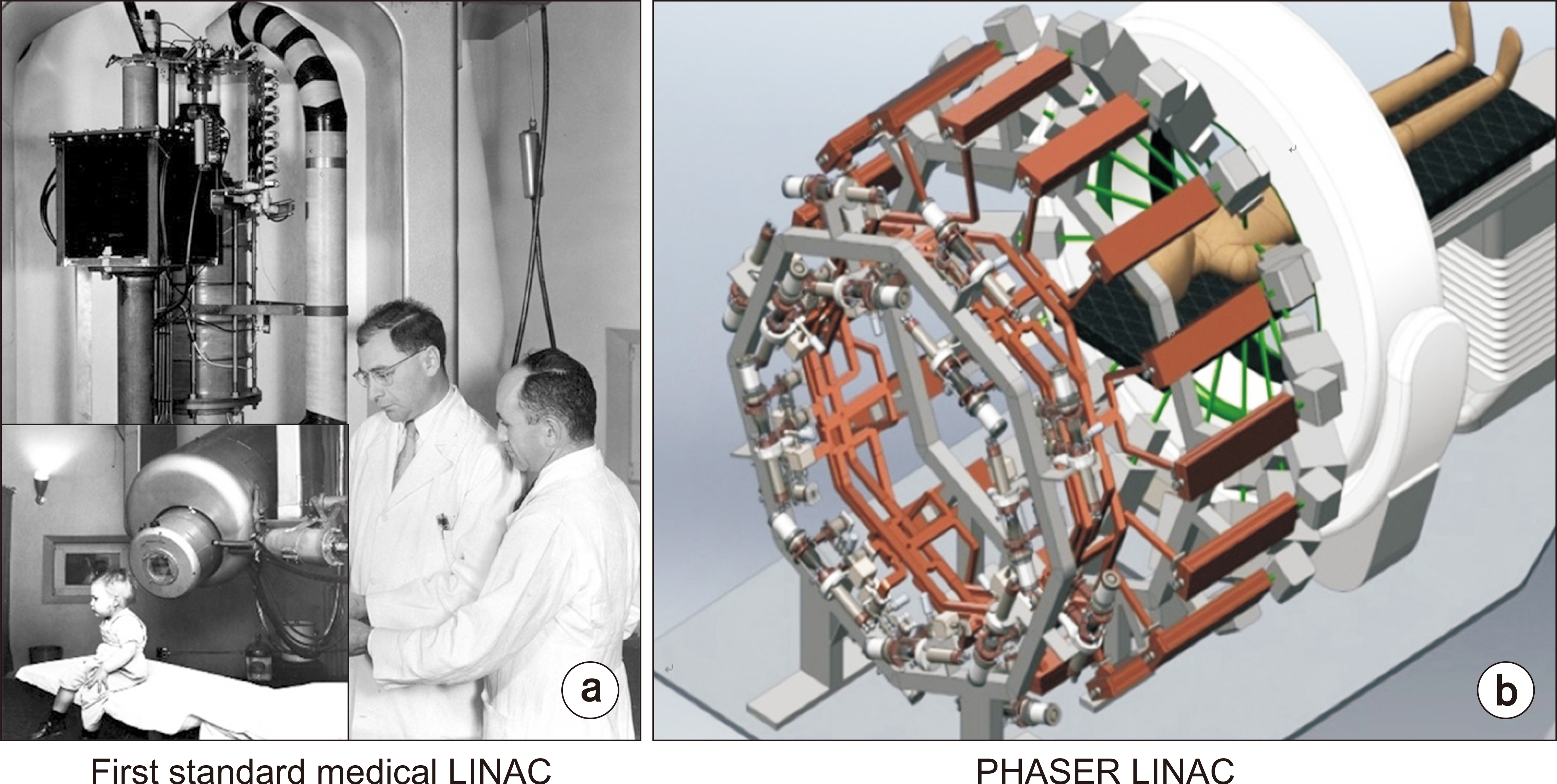
Prog Med Phys.
2020 Sep;31(3):124-134. 10.14316/pmp.2020.31.3.124.
History of Radiation Therapy Technology
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiation Oncology, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea
- 2Department of Radiation Oncology, Hanyang University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2507484
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14316/pmp.2020.31.3.124
Abstract
- Here we review the evolutionary history of radiation therapy technology through the festschrift of articles in celebration of the 30th anniversary of Korean Society of Medical Physics (KSMP). Radiation therapy technology used in clinical practice has evolved over a long period of time. Various areas of science, such as medical physics, mechanical engineering, and computer engineering, have contributed to the continual development of new devices and techniques. The scope of this review was restricted to two areas; i.e., output energy production and functional development, because it is not possible to include all development processes of this technology due to space limitations. The former includes the technological transition process from the initial technique applied to the first model to the latest technique currently used in a variety of machines. The latter has had a direct effect on treatment outcomes and safety, which changed the paradigm of radiation therapy, leading to new guidelines on dose prescriptions, innovation of dose verification tools, new measurement methods and calculation systems for radiation doses, changes in the criteria for errors, and medical law changes in all countries. Various complex developments are covered in this review. To the best of our knowledge, there have been few reviews on this topic and we consider it very meaningful to provide a review in the festschrift in celebration of the 30th anniversary of the KSMP.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Dead Layer Thickness and Geometry Optimization of HPGe Detector Based on Monte Carlo Simulation
Suah Yu, Na Hye Kwon, Young Jae Jang, Byungchae Lee, Jihyun Yu, Dong-Wook Kim, Gyu-Seok Cho, Kum-Bae Kim, Geun Beom Kim, Cheol Ha Baek, Sang Hyoun Choi
Prog Med Phys. 2022;33(4):129-135. doi: 10.14316/pmp.2022.33.4.129.
Reference
-
References
1. Case JT, Buschke F. 1958. History of radiation therapy . Progress in radiation therapy. Grune & Stratton;New York: p. 13–41.2. Lederman M. 1981; The early history of radiotherapy: 1895-1939. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 7:639–648. DOI: 10.1016/0360-3016(81)90379-5. PMID: 7024222.
Article3. Holsti LR. 1995; Development of clinical radiotherapy since 1896. Acta Oncol. 34:995–1003. DOI: 10.3109/02841869509127225. PMID: 8608037.
Article4. Senn N. 1903; Case of spleno-medullary leukemia successfully treated by use of roentgen ray. Med Rec N Y. 63:281–282.5. Thames HD Jr. 1988; Early fractionation methods and the origins of the NSD concept. Acta Oncol. 27:89–103. DOI: 10.3109/02841868809090329. PMID: 3291904.
Article6. Quimby EH. 1945; The history of dosimetry in roentgen therapy. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther. 54:688–703. PMID: 21011622.7. Buschek F. 1969. Radiation therapy: the past, the present, the future. Paper presented at: Fifty-first Annual Meeting of the American Radium Society. 1969 Apr 27-30; Pennsylvania, USA. p. 236.8. Kim KE. 2009. Past Footprints. The Department of Radiation Oncology, Yonsei University College of Medicine;Seoul: p. 46–53.9. Webb S, Evans PM. 2006; Innovative techniques in radiation therapy: editorial, overview, and crystal ball gaze to the future. Semin Radiat Oncol. 16:193–198. DOI: 10.1016/j.semradonc.2006.04.001. PMID: 17010901.
Article10. Brahme A, Roos JE, Lax I. 1982; Solution of an integral equation encountered in rotation therapy. Phys Med Biol. 27:1221–1229. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/27/10/002. PMID: 7146095.
Article11. Palta JR, Mackie R, Chen Z. 2003. Intensity-modulated radiation therapy- the state of the art. Medical Physics Publishing;Madison: p. 1–23.12. Royal College of Radiologists. 2002. Development and implementation of conformal radiotherapy in the United Kingdom. Royal College of Radiologist;London:13. Sternick ES. 1997. The theory and practice of intensity modulated radiation therapy. Advanced Medical Publishing;Madison:14. Cho B. 2018; Intensity-modulated radiation therapy: a review with a physics perspective. Radiat Oncol J. 36:1–10. DOI: 10.3857/roj.2018.00122. PMID: 29621869. PMCID: PMC6074066.
Article15. Thwaites DI, Tuohy JB. 2006; Back to the future: the history and development of the clinical linear accelerator. Phys Med Biol. 51:R343–R362. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/51/13/R20. PMID: 16790912.
Article16. Miller CW. 1955. An 8 MeV linear accelerator for x-ray therapy. Metropolitan-Vickers Electrical Co.;Manchester: DOI: 10.1049/jiee-2.1954.0094.17. Miller CW. 1956. Linear accelerators in clinical service. Metropolitan-Vickers Electrical Co.;Manchester:18. Karzmark CJ, Pering NC. 1973; Electron linear accelerators for radiation therapy: history, principles and contemporary developments. Phys Med Biol. 18:321–354. DOI: 10.1088/0031-9155/18/3/001. PMID: 4610600.
Article19. Hansen WW. 1938; A type of electrical resonator. J Appl Phys. 9:654–663. DOI: 10.1063/1.1710371.
Article20. Boot H, Randall JT. 1976; Historical notes on the cavity magnetron. IEEE Trans Electron Devices. 23:724–729. DOI: 10.1109/T-ED.1976.18476.
Article21. Varian RH, Varian SF. 1939; A high frequency oscillator and amplifier. J Appl Phys. 10:321. DOI: 10.1063/1.1707311.
Article22. Knapp EA, Knapp BC, Potter JM. 1986; Standing wave high energy linear accelerator structures. Rev Sci Instrum. 39:979–991. DOI: 10.1063/1.1683583.
Article23. Maxim PG, Tantawi SG, Loo BW Jr. 2019; PHASER: A platform for clinical translation of FLASH cancer radiotherapy. Radiother Oncol. 139:28–33. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.05.005. PMID: 31178058.
Article24. Vozenin MC, Baumann M, Coppes RP, Bourhis J. 2019; FLASH radiotherapy international workshop. Radiother Oncol. 139:1–3. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.07.020. PMID: 31445836.
Article25. Vozenin MC, De Fornel P, Petersson K, Favaudon V, Jaccard M, Germond JF, et al. 2019; The advantage of FLASH radiotherapy confirmed in mini-pig and cat-cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res. 25:35–42. DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-3375. PMID: 29875213.
Article26. Favaudon V, Caplier L, Monceau V, Pouzoulet F, Sayarath M, Fouillade C, et al. 2014; Ultrahigh dose-rate FLASH irradiation increases the differential response between normal and tumor tissue in mice. Sci Transl Med. 6:245ra93. DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3008973. PMID: 25031268.
Article27. Beyreuther E, Brand M, Hans S, Hideghéty K, Karsch L, Leßmann E, et al. 2019; Feasibility of proton FLASH effect tested by zebrafish embryo irradiation. Radiother Oncol. 139:46–50. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.06.024. PMID: 31266652.
Article28. Skouboe S, Ravkilde T, Bertholet J, Hansen R, Worm ES, Muurholm CG, et al. 2019; First clinical real-time motion-including tumor dose reconstruction during radiotherapy delivery. Radiother Oncol. 139:66–71. DOI: 10.1016/j.radonc.2019.07.007. PMID: 31431367.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Proton Therapy Review: Proton Therapy from a Medical
- Advancing radiation therapy through smartwatch technology to monitor anxiety
- A rare case of abdominal adenoid basal cell carcinoma in a patient with a history of radiation therapy
- Conventional Radiation Therapy for Intracranial Meningiomas: Experience of 7 Cases
- Role of Radiation Therapy for Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Focused on Stereotactic Ablative Radiation Therapy in Stage I