J Liver Cancer.
2020 Mar;20(1):32-40. 10.17998/jlc.20.1.32.
Gut-microbiome Taxonomic Profiling as Non-invasive Biomarkers for the Early Detection of Alcoholic Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute for Liver and Digestive Diseases, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea
- KMID: 2505840
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17998/jlc.20.1.32
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a prevalent form of primary liver cancer and the fifth leading cause of worldwide cancer mortality. Though early diagnosis of HCC is important, so far lack of effective biomarkers for early diagnosis of HCC has been a problem. In this study, we searched for potential functional biomarkers of alcoholic HCC by using metagenomics approach.
Methods
Between September 2017 and April 2019, normal control (n=44), alcoholic liver cirrhosis (n=44), and alcoholic HCC (n=13) groups were prospectively enrolled and analyzed. Gut microbiota was analyzed using the 16S-based microbiome taxonomic profiling platform of EzBioCloud Apps and analyzing system.
Results
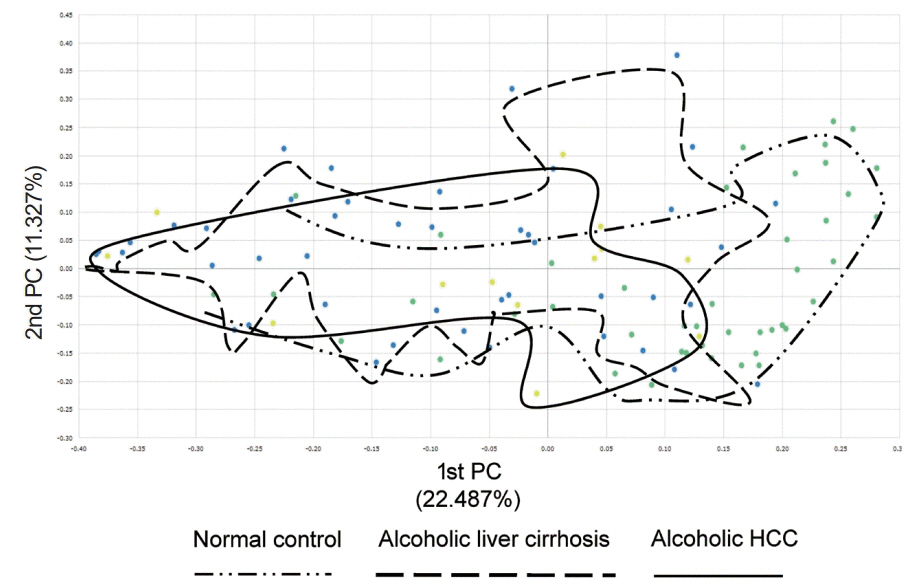
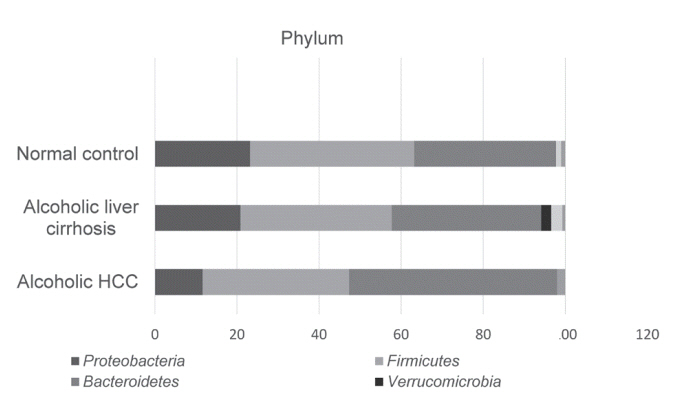
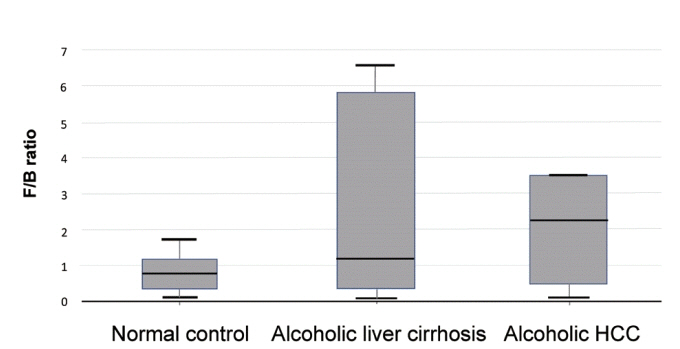
There was a statistically significant difference among groups in diversity (P<0.05). In the comparison of phylum between cirrhosis and HCC, Proteobacteria were increased and Bacteroidetes were decreased. Firmicutes were not significantly different among the three groups. In the taxonomic profiling, relative abundance of Lactobacillus in the cirrhosis and HCC groups showed richness (P<0.05). In the biomarker analysis between cirrhosis and HCC, obiquinome Fe-S protein 3, global nitrogen regulator, Vesicle-associated membrane protein 7, toxin YoeB, peroxisome-assembly ATPase, and nitrogen oxide reductase regulator were differently expressed (P<0.001).
Conclusions
Alcoholic HCC showed different expressions in the stool taxonomy and biomarker compared with that of cirrhosis and control. Therefore, new biomarkers using stool analysis for alcoholic HCC are necessary.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Wong MC, Jiang JY, Goggins WB, Liang M, Fang Y, Fung FD, et al. International incidence and mortality trends of liver cancer: a global profile. Sci Rep. 2017; 7:45846.2. Jiang W, Wu N, Wang X, Chi Y, Zhang Y, Qiu X, et al. Dysbiosis gut microbiota associated with inflammation and impaired mucosal immune function in intestine of humans with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep. 2015; 5:8096.3. Cui X, Ye L, Li J, Jin L, Wang W, Li S, et al. Metagenomic and metabolomic analyses unveil dysbiosis of gut microbiota in chronic heart failure patients. Sci Rep. 2018; 8:635.4. Kundu P, Blacher E, Elinav E, Pettersson S. Our gut microbiome: the evolving inner self. Cell. 2017; 171:1481–1493.5. Lindheim L, Bashir M, Münzker J, Trummer C, Zachhuber V, Leber B, et al. Alterations in gut microbiome composition and barrier function are associated with reproductive and metabolic defects in women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS): a pilot study. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0168390.6. Suk KT, Kim DJ. Gut microbiota: novel therapeutic target for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2019; 13:193–204.7. Hong M, Han DH, Hong J, Kim DJ, Suk KT. Are probiotics effective in targeting alcoholic liver diseases? Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2019; 11:335–347.8. Yuan J, Chen C, Cui J, Lu J, Yan C, Wei X, et al. Fatty liver disease caused by high-alcohol-producing klebsiella pneumoniae. Cell Metab. 2019; 30:675–688. e677.9. Chen J, Thomsen M, Vitetta L. Interaction of gut microbiota with dysregulation of bile acids in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and potential therapeutic implications of probiotics. J Cell Biochem. 2019; 120:2713–2720.10. Petrosino JF, Highlander S, Luna RA, Gibbs RA, Versalovic J. Metagenomic pyrosequencing and microbial identification. Clin Chem. 2009; 55:856–866.11. Miele L, Marrone G, Lauritano C, Cefalo C, Gasbarrini A, Day C, et al. Gut-liver axis and microbiota in NAFLD: insight pathophysiology for novel therapeutic target. Curr Pharm Des. 2013; 19:5314–5324.12. Schnabl B, Brenner DA. Interactions between the intestinal microbiome and liver diseases. Gastroenterology. 2014; 146:1513–1524.13. Haque TR, Barritt AS 4th. Intestinal microbiota in liver disease. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2016; 30:133–142.14. Bajaj JS. The role of microbiota in hepatic encephalopathy. Gut Microbes. 2014; 5:397–403.15. Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, et al. Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017; 67:1613–1617.16. Edgar RC. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics. 2010; 26:2460–2461.17. Yoon SH, Ha SM, Kwon S, Lim J, Kim Y, Seo H, et al. Introducing EzBioCloud: a taxonomically united database of 16S rRNA gene sequences and whole-genome assemblies. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2017; 67:1613–1617.18. Schloss PD, Westcott SL, Ryabin T, Hall JR, Hartmann M, Hollister EB, et al. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009; 75:7537–7541.19. Zakrzewski M, Proietti C, Ellis JJ, Hasan S, Brion MJ, Berger B, et al. Calypso: a user-friendly web-server for mining and visualizing microbiome-environment interactions. Bioinformatics. 2016; 33:782–783.20. Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, et al. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011; 12:R60.21. Farazi PA, DePinho RA. Hepatocellular carcinoma pathogenesis: from genes to environment. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006; 6:674–687.22. Ghouri YA, Mian I, Rowe JH. Review of hepatocellular carcinoma: epidemiology, etiology, and carcinogenesis. J Carcinog. 2017; 16:1.23. Zhang DY, Friedman SL. Fibrosis-dependent mechanisms of hepatocarcinogenesis. Hepatology. 2012; 56:769–775.24. Shlomai A, de Jong YP, Rice CM. Virus associated malignancies: the role of viral hepatitis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 2014; 26:78–88.25. Yu LX, Schwabe RF. The gut microbiome and liver cancer: mechanisms and clinical translation. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017; 14:527–539.26. Chitapanarux T, Phornphutkul K. Risk factors for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma in Thailand. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2015; 3:182–188.27. Llovet JM. Updated treatment approach to hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2005; 40:225–235.28. Alkofer B, Lepennec V, Chiche L. Hepatocellular cancer in the noncirrhotic liver. J Visc Surg. 2011; 148:3–11.29. Ciocan D, Voican CS, Wrzosek L, Hugot C, Rainteau D, Humbert L, et al. Bile acid homeostasis and intestinal dysbiosis in alcoholic hepatitis. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018; 48:961–974.30. Arpaia N, Campbell C, Fan X, Dikiy S, van der Veeken J, deRoos P, et al. Metabolites produced by commensal bacteria promote peripheral regulatory T-cell generation. Nature. 2013; 504:451–455.31. Kverka M, Zakostelska Z, Klimesova K, Sokol D, Hudcovic T, Hrncir T, et al. Oral administration of parabacteroides distasonis antigens attenuates experimental murine colitis through modulation of immunity and microbiota composition. Clin Exp Immunol. 2011; 163:250–259.32. Round JL, Mazmanian SK. Inducible Foxp3+ regulatory T-cell development by a commensal bacterium of the intestinal microbiota. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010; 107:12204–12209.33. Iida N, Dzutsev A, Stewart CA, Smith L, Bouladoux N, Weingarten RA, et al. Commensal bacteria control cancer response to therapy by modulating the tumor microenvironment. Science. 2013; 342:967–970.34. Li J, Sung CY, Lee N, Ni Y, Pihlajamäki J, Panagiotou G, et al. Probiotics modulated gut microbiota suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma growth in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016; 113:E1306–E1315.35. Rao RK, Seth A, Sheth P. Recent Advances in Alcoholic Liver Disease I. Role of intestinal permeability and endotoxemia in alcoholic liver disease. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004; 286:G881–G884.36. Suraweera DB, Weeratunga AN, Hu RW, Pandol SJ, Hu R. Alcoholic hepatitis: The pivotal role of Kupffer cells. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015; 6:90–98.37. Trebicka J, Krag A, Gansweid S, Appenrodt B, Schiedermaier P, Sauerbruch T, et al. Endotoxin and tumor necrosis factor-receptor levels in portal and hepatic vein of patients with alcoholic liver cirrhosis receiving elective transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 23:1218–1225.38. Wheeler MD. Endotoxin and Kupffer cell activation in alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Res Health. 2003; 27:300–306.39. Gao B. Hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory cytokines in alcoholic liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 27 Suppl 2:89–93.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Tumor Biomarkers in the Surveillance of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- The role of the gut microbiome and diet in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- Early Life Events and Development of Gut Microbiota in Infancy
- Screening and surveillance of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hepatocellular Carcinoma