Ann Rehabil Med.
2020 Aug;44(4):301-310. 10.5535/arm.19156.
The Formula for Health and Well-Being in Individuals With Cerebral Palsy: Cross-Sectional Data on Physical Activity, Sleep, and Nutrition
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
- 2School of Rehabilitation Science, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
- 3CanChild Centre for Childhood Disability Research, Department of Pediatrics, McMaster University, Hamilton, ON, Canada
- 4Brain Center Rudolf Magnus and Center of Excellence for Rehabilitation Medicine, University Medical Center Utrecht and De Hoogstraat Rehabilitation, Utrecht, The Netherlands
- 5Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, University of Michigan-Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI, USA
- KMID: 2505390
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.19156
Abstract
Objective
To determine physical activity, sleep, and nutrition patterns in individuals with cerebral palsy (CP) and investigate the association of Gross Motor Function Classification System (GMFCS) and age with these health behaviors.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was conducted in an outpatient setting. Participants included adolescents and adults with CP (n=28; GMFCS level I–V; mean age 35.1±14.4 years). An Exercise Questionnaire or Leisure Time Physical Activity Questionnaire was used to measure physical activity in adolescents and adults, respectively. Sleep quality was measured using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI). An adapted version of the PrimeScreen questionnaire was used to assess nutrition. Linear regression analyses were performed to investigate the association between GMFCS and age with physical activity, sleep, and nutrition.
Results
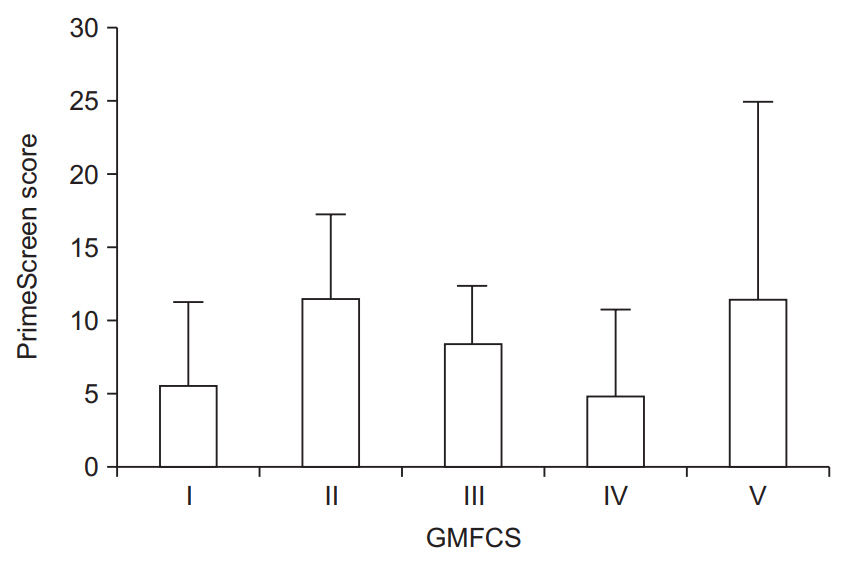
The average total physical activity was 29.2±30.0 min/day. Seventy-five percent of the participants had poor sleep quality (PSQI score >5). Seventy-one percent reported “fair” eating behaviors; none reported “excellent” eating behaviors. Neither GMFCS nor age were significantly associated with PSQI score, PrimeScreen score, or total physical activity. A negative correlation existed between sleep quantity (hr/night) and PSQI score (r=-0.66, p=0.01).
Conclusion
The triad of health components, consisting of physical activity, sleep, and nutrition, was not associated with GMFCS or age in our sample of 28 individuals with CP, suggesting that these three health behaviors should be assessed during clinical encounters of CP in adolescents and adults at all levels of the GMFCS.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Christensen D, Van Naarden Braun K, Doernberg NS, Maenner MJ, Arneson CL, Durkin MS, et al. Prevalence of cerebral palsy, co‐occurring autism spectrum disorders, and motor functioning: Autism and Developmental Disabilities Monitoring Network, USA, 2008. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2014; 56:59–65.2. Maenner MJ, Blumberg SJ, Kogan MD, Christensen D, Yeargin-Allsopp M, Schieve LA. Prevalence of cerebral palsy and intellectual disability among children identified in two U.S. National Surveys, 2011-2013. Ann Epidemiol. 2016; 26:222–6.
Article3. Hutton JL. Outcome in cerebral palsy: life-expectancy. Paediatr Child Health (Oxford). 2008; 18:419–22.
Article4. Shortland A. Muscle deficits in cerebral palsy and early loss of mobility: can we learn something from our elders? Dev Med Child Neurol. 2009; 51 Suppl 4:59–63.
Article5. McPhee PG, Brunton LK, Timmons BW, Bentley T, Gorter JW. Fatigue and its relationship with physical activity, age, and body composition in adults with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2017; 59:367–73.
Article6. Peterson MD, Ryan JM, Hurvitz EA, Mahmoudi E. Chronic conditions in adults with cerebral palsy. JAMA. 2015; 314:2303–5.
Article7. Peterson MD, Kamdar N, Hurvitz EA. Age-related trends in cardiometabolic disease among adults with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2019; 61:484–9.
Article8. Kruse M, Michelsen SI, Flachs EM, Bronnum-Hansen H, Madsen M, Uldall P. Lifetime costs of cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2009; 51:622–8.
Article9. Claridge EA, McPhee PG, Timmons BW, Martin Ginis KA, Macdonald MJ, Gorter JW. Quantification of physical activity and sedentary time in adults with cerebral palsy. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015; 47:1719–26.
Article10. Verschuren O, Gorter JW, Pritchard-Wiart L. Sleep: an underemphasized aspect of health and development in neurorehabilitation. Early Hum Dev. 2017; 113:120–8.
Article11. Verschuren O, McPhee P, Rosenbaum P, Gorter JW. The formula for health and well-being in individuals with cerebral palsy: physical activity, sleep, and nutrition. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2016; 58:989–90.
Article12. Maher CA, Williams MT, Olds T, Lane AE. Physical and sedentary activity in adolescents with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2007; 49:450–7.
Article13. Ryan JM, Crowley VE, Hensey O, Broderick JM, McGahey A, Gormley J. Habitual physical activity and cardiometabolic risk factors in adults with cerebral palsy. Res Dev Disabil. 2014; 35:1995–2002.
Article14. Maltais DB, Dumas F, Boucher N, Richards CL. Factors related to physical activity in adults with cerebral palsy may differ for walkers and nonwalkers. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2010; 89:584–97.
Article15. Berg K, Isaksson B. Body composition and nutrition of school children with cerebral palsy. Acta Paediatr Scand Suppl. 1970; Suppl 204:41–52.
Article16. Donkervoort M, Roebroeck M, Wiegerink D, van der Heijden-Maessen H, Stam H; Transition Research Group South West Netherlands. Determinants of functioning of adolescents and young adults with cerebral palsy. Disabil Rehabil. 2007; 29:453–63.
Article17. McPhee PG, MacDonald MJ, Cheng JL, Dunford EC, Gorter JW. Emerging evidence for accelerated ageing and cardiovascular disease in individuals with cerebral palsy. J Rehabil Med. 2019; 51:525–31.
Article18. Martin AA, Cotie LM, Timmons BW, Gorter JW, Macdonald MJ. Arterial structure and function in ambulatory adolescents with cerebral palsy are not different from healthy controls. Int J Pediatr. 2012; 2012:168209.
Article19. McPhee PG, Gorter JW, Cotie LM, Timmons BW, Bentley T, MacDonald MJ. Associations of non-invasive measures of arterial structure and function, and traditional indicators of cardiovascular risk in adults with cerebral palsy. Atherosclerosis. 2015; 243:462–5.
Article20. Palisano RJ, Rosenbaum P, Bartlett D, Livingston MH. Content validity of the expanded and revised Gross Motor Function Classification System. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2008; 50:744–50.
Article21. Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe. Surveillance of cerebral palsy in Europe: a collaboration of cerebral palsy surveys and registers. Surveillance of Cerebral Palsy in Europe (SCPE). Dev Med Child Neurol. 2000; 42:816–24.22. Martin Ginis KA, Phang SH, Latimer AE, Arbour-Nicitopoulos KP. Reliability and validity tests of the leisure time physical activity questionnaire for people with spinal cord injury. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012; 93:677–82.
Article23. Latimer AE, Ginis KA, Craven BC, Hicks AL. The physical activity recall assessment for people with spinal cord injury: validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2006; 38:208–16.24. Brunton LK, Bartlett DJ. Description of exercise participation of adolescents with cerebral palsy across a 4-year period. Pediatr Phys Ther. 2010; 22:180–7.
Article25. Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989; 28:193–213.
Article26. Rifas-Shiman SL, Willett WC, Lobb R, Kotch J, Dart C, Gillman MW. PrimeScreen, a brief dietary screening tool: reproducibility and comparability with both a longer food frequency questionnaire and biomarkers. Public Health Nutr. 2001; 4:249–54.
Article27. Nooijen CF, Slaman J, Stam HJ, Roebroeck ME, Berg-Emons RJ; Learn2Move Research Group. Inactive and sedentary lifestyles amongst ambulatory adolescents and young adults with cerebral palsy. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2014; 11:49.
Article28. World Health Organization. Physical activity [Internet]. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization;2017. [cited 2020 Jun 15]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/physical-activity.29. Verschuren O, Peterson MD, Balemans AC, Hurvitz EA. Exercise and physical activity recommendations for people with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2016; 58:798–808.
Article30. Mukherjee S, Patel SR, Kales SN, Ayas NT, Strohl KP, Gozal D, et al. An official American Thoracic Society statement: the importance of healthy sleep. Recommendations and future priorities. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2015; 191:1450–8.
Article31. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Short sleep duration among US adults [Internet]. Atlanta, GA: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2017. [cited 2020 Jun 15]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/sleep/data_statistics.html.32. Binay Safer V, Ozbudak Demir S, Ozkan E, Demircioglu Guneri F. Effects of botulinum toxin serotype A on sleep problems in children with cerebral palsy and on mothers sleep quality and depression. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2016; 21:331–7.33. McCarty SF, Gaebler-Spira D, Harvey RL. Improvement of sleep apnea in a patient with cerebral palsy. Am J Phys Med Rehabil. 2001; 80:540–2.
Article34. Sellers D, Mandy A, Pennington L, Hankins M, Morris C. Development and reliability of a system to classify the eating and drinking ability of people with cerebral palsy. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2014; 56:245–51.
Article35. van de Mortel TF. Faking it: social desirability response bias in self-report research. Aust J Adv Nurs. 2008; 25(4):40–8.36. Whitney DG, Miller F, Pohlig RT, Modlesky CM. BMI does not capture the high fat mass index and low fatfree mass index in children with cerebral palsy and proposed statistical models that improve this accuracy. Int J Obes. 2019; 43:82–90.
Article37. Ryan JM, Crowley VE, Hensey O, McGahey A, Gormley J. Waist circumference provides an indication of numerous cardiometabolic risk factors in adults with cerebral palsy. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014; 95:1540–6.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Current Status of Cerebral Palsy Patients in Handicapped Residential Facility
- Factors Influencing Parenting Stress in Mothers of Children with Cerebral Palsy
- A Study on the Body Composition, Physical Activity Level, Basal Metabolic Rate, and Daily Energy Expenditure of Elderly in Busan
- Current Physical Therapy Status for the Children with Cerebral Palsy in Korea
- Association of Sleep, Dietary Behaviors and Physical Activity with Quality of Life among Shiftwork Nurses