Ann Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg.
2020 Aug;24(3):292-300. 10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.3.292.
Hemorrhage complicating the course of severe acute pancreatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of 1General Surgery Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India
- 2Departments of Gastroenterology Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India
- 3Departments of Internal Medicine Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India
- 4Departments of Radiodiagnosis, Postgraduate Institute of Medical Education and Research, Chandigarh, India
- KMID: 2505341
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14701/ahbps.2020.24.3.292
Abstract
- Backgrounds/Aims
The course of severe acute pancreatitis (SAP) complicated by hemorrhage is associated with poor outcome.
Methods
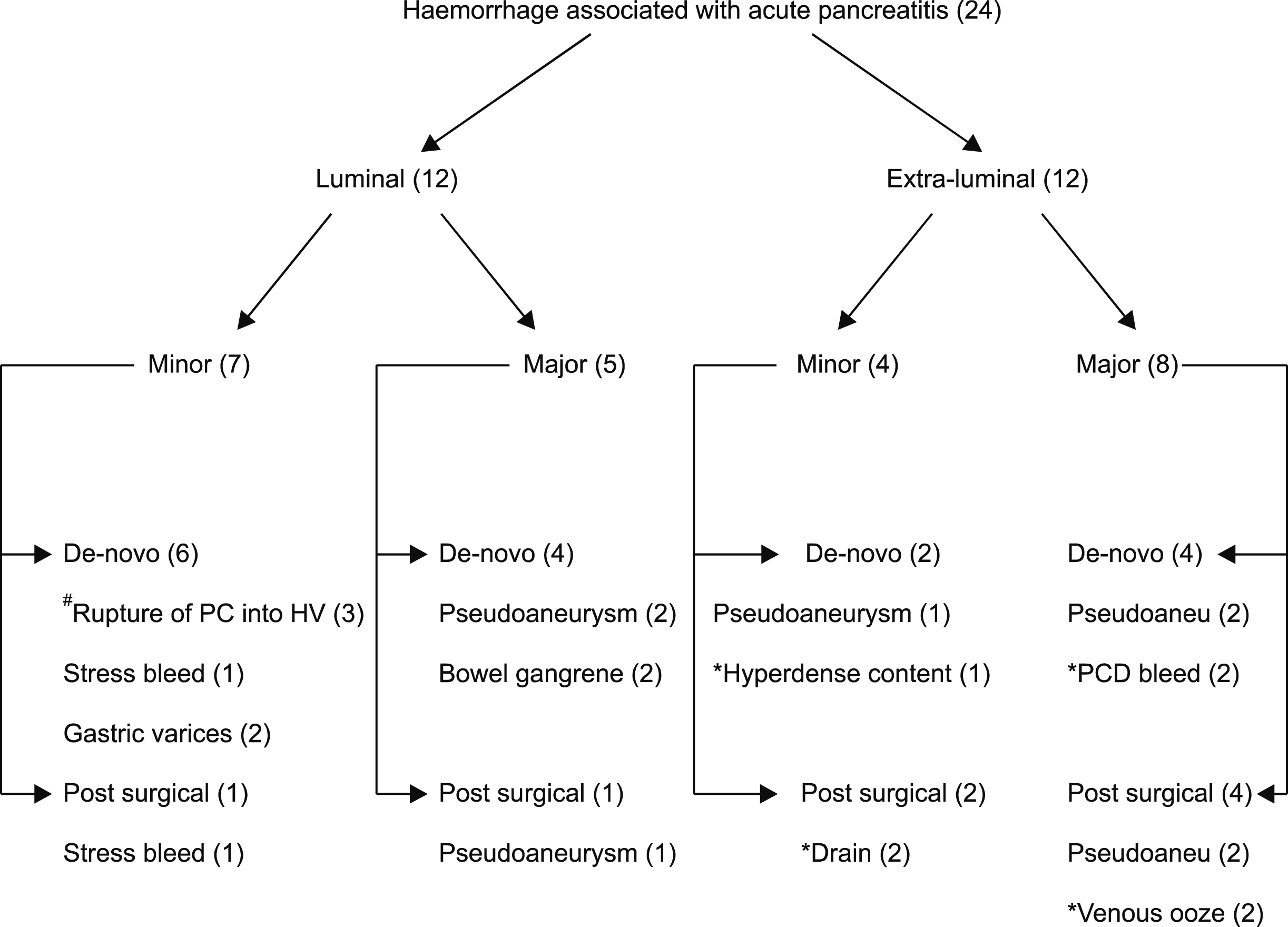
Twenty-four (13%) out of 183 cases of SAP had hemorrhagic complications- 12 intraabdominal & 12 intraluminal, 13 had major & 11 had minor and 16 had de-novo & 8 post-surgical bleeding. The mean duration of pancreatitis prior to bleeding was 27±27.2 days. Results: Predictors of haemorrhage on univariate analysis were delayed admission (0.037), more than one organ failure (p=0.008), presence of venous thrombosis (p=0.033), infective necrosis (0.001) and systemic sepsis – bacterial (0.037) & fungal (p=0.032). On multivariate analysis infected necrosis (OR=11.82) and presence of fungal sepsis (OR=3.73) were the significant factors. Patients presenting with more than one organ failure and bacterial sepsis had borderline significance on multivariate analysis. Need for surgery (50% vs.12.6%), intensive care stay (7.4±7.9 vs. 5.4±5.2 days) and mortality (41.7% vs. 10.7%) were significantly higher in patients who suffered haemorrhage. Seven of the 13 with major bleeding had pseudoaneurysms-4 were embolized, 4 needed surgery including 1 embolization failure. Seven with intraabdominal bleeding required surgical intervention,2 had successful embolization and 3 had expectant management. CT severity index and surgical intervention, were significantly associated with intraabdominal bleeding. Organ failure, presence of pseudoaneurysm and surgical intervention were associated with major bleeding.
Conclusions
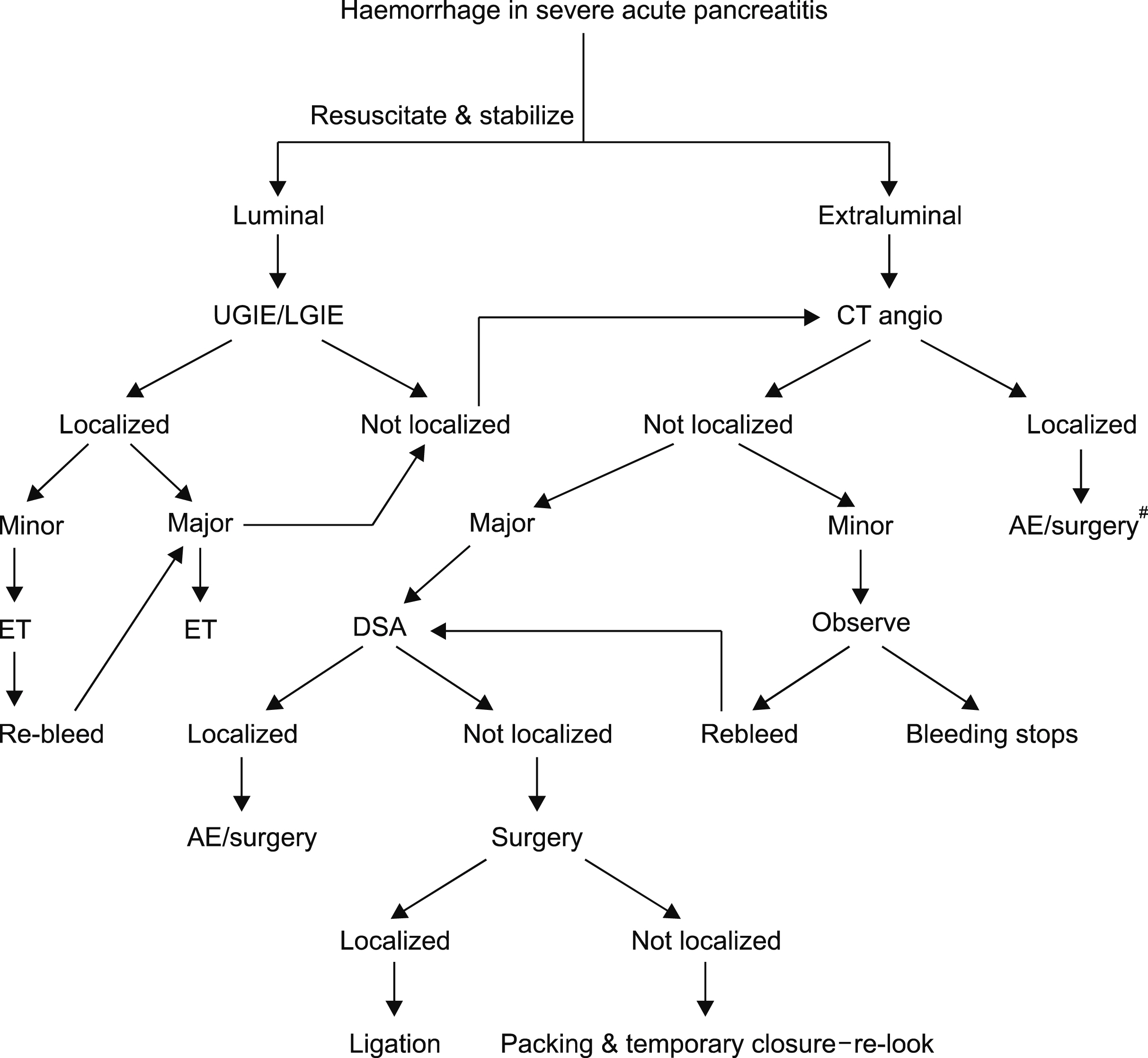
Hemorrhage in SAP was associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Infected necrosis accentuated the degradation of the vessel wall, which predispose to hemorrhage. Luminal bleeding may be indicative of erosion into the adjacent viscera by the pseudoaneurysm.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Working Group IAP/APA Acute Pancreatitis Guidelines. 2013; IAP/ APA evidence-based guidelines for the management of acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 13(4 Suppl 2):e1–e15. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2013.07.063. PMID: 24054878.2. Manrai M, Kochhar R, Gupta V, Yadav TD, Dhaka N, Kalra N, et al. 2018; Outcome of acute pancreatic and peripancreatic collections occurring in patients with acute pancreatitis. Ann Surg. 267:357–363. DOI: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000002065. PMID: 27805963.
Article3. Mallick B, Dhaka N, Sharma V, Malik S, Sinha SK, Dutta U, et al. 2019; Impact of timing of presentation of acute pancreatitis to a tertiary care centre on the outcome. Pancreatology. 19:143–148. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2018.10.005. PMID: 30366676.
Article4. Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, Gooszen HG, Johnson CD, Sarr MG, et al. 2013; Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut. 62:102–111. DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-302779. PMID: 23100216.
Article5. Evans RP, Mourad MM, Pall G, Fisher SG, Bramhall SR. 2017; Pancreatitis: preventing catastrophic haemorrhage. World J Gastroenterol. 23:5460–5468. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i30.5460. PMID: 28852306. PMCID: PMC5558110.
Article6. Andersson E, Ansari D, Andersson R. 2010; Major haemorrhagic complications of acute pancreatitis. Br J Surg. 97:1379–1384. DOI: 10.1002/bjs.7113. PMID: 20564308.
Article7. Sharma PK, Madan K, Garg PK. 2008; Hemorrhage in acute pancreatitis: should gastrointestinal bleeding be considered an organ failure? Pancreas. 36:141–145. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0b013e318158466e. PMID: 18376304.8. Flati G, Andrén-Sandberg A, La Pinta M, Porowska B, Carboni M. 2003; Potentially fatal bleeding in acute pancreatitis: pathophysiology, prevention, and treatment. Pancreas. 26:8–14. DOI: 10.1097/00006676-200301000-00002. PMID: 12499910.
Article9. Wei AL, Guo Q, Wang MJ, Hu WM, Zhang ZD. 2016; Early complications after interventions in patients with acute pancreatitis. World J Gastroenterol. 22:2828–2836. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i9.2828. PMID: 26973421. PMCID: PMC4778005.
Article10. Ammori BJ, Madan M, Alexander DJ. 1998; Haemorrhagic complications of pancreatitis: presentation, diagnosis and management. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 80:316–325. PMID: 9849330. PMCID: PMC2503105.11. Balthazar EJ, Fisher LA. 2001; Hemorrhagic complications of pancreatitis: radiologic evaluation with emphasis on CT imaging. Pancreatology. 1:306–313. DOI: 10.1159/000055829. PMID: 12120209.
Article12. Labarca E, Zubia F, Maraví-Poma E, Martinez F. EPAMI Group. 2018; Early predictors of abdominal hemorrhage among critically ill patients with pancreatitis: a prospective cohort study. Pancreas. 47:1027–1032. DOI: 10.1097/MPA.0000000000001135. PMID: 30045171.13. Gupta V, Irrinki S, Sakaray YR, Moond V, Yadav TD, Kochhar R, et al. 2018; Treatment strategies for bleeding from gastroduodenal artery pseudoaneurysms complicating the course of chronic pancreatitis-a case series of 10 patients. Indian J Gastroenterol. 37:457–463. DOI: 10.1007/s12664-018-0897-y. PMID: 30374751.
Article14. Bergert H, Hinterseher I, Kersting S, Leonhardt J, Bloomenthal A, Saeger HD. 2005; Management and outcome of hemorrhage due to arterial pseudoaneurysms in pancreatitis. Surgery. 137:323–328. DOI: 10.1016/j.surg.2004.10.009. PMID: 15746787.
Article15. Mendelson RM, Anderson J, Marshall M, Ramsay D. 2005; Vascular complications of pancreatitis. ANZ J Surg. 75:1073–1079. DOI: 10.1111/j.1445-2197.2005.03607.x. PMID: 16398814.
Article16. Udd M, Leppäniemi AK, Bidel S, Keto P, Roth WD, Haapiainen RK. 2007; Treatment of bleeding pseudoaneurysms in patients with chronic pancreatitis. World J Surg. 31:504–510. DOI: 10.1007/s00268-006-0209-z. PMID: 17322972.
Article17. Balthazar EJ. 2002; Complications of acute pancreatitis: clinical and CT evaluation. Radiol Clin North Am. 40:1211–1227. DOI: 10.1016/S0033-8389(02)00043-X. PMID: 12479707.18. Balachandra S, Siriwardena AK. 2005; Systematic appraisal of the management of the major vascular complications of pancreatitis. Am J Surg. 190:489–495. DOI: 10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.03.009. PMID: 16105542.
Article19. Tang MY, Chen TW, Bollen TL, Wang YX, Xue HD, Jin ZY, et al. 2018; MR imaging of hemorrhage associated with acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 18:363–369. DOI: 10.1016/j.pan.2018.03.004. PMID: 29615311.
Article20. Shen X, Sun J, Zhang J, Ke L, Tong Z, Li G, et al. 2015; Risk factors and outcome for massive intra-abdominal bleeding among patients with infected necrotizing pancreatitis. Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e1172. DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001172. PMID: 26181564. PMCID: PMC4617064.
Article21. Law NM, Freeman ML. 2003; Emergency complications of acute and chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 32:1169–1194. ix. DOI: 10.1016/S0889-8553(03)00089-X. PMID: 14696302.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Multiple Bleeding Pseudoaneurysms Complicating Acute Pancreatitis
- Acute Pancreatitis Complicating Spontaneous Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection: Case Report and Review of the Literature
- Assessment of Severity and Fluid Administration in Acute Pancreatitis
- Medical Management of Acute Pancreatitis and Complications
- Splenic Artery Pseudoaneurysm Complicating Chronic Pancreatitis: A Case Report