J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Aug;35(30):e244. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e244.
Audiologic Status of Children with Confirmed Cytomegalovirus Infection: a Case Series
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Gangnam Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Yongin Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2505189
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e244
Abstract
- Background
Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection is the most common non-genetic cause of sensorineural hearing loss (SHNL) in children. Only about 10% to 15% of children with congenital CMV are symptomatic, and most are not diagnosed at birth. About 7% to 15% of clinically asymptomatic patients may develop later complications, including SNHL, which is the most common sequela in clinically asymptomatic patients. In this study, hearing status was investigated in children with confirmed CMV infection and neonatal hearing screening (NHS) histories were reviewed to explore hearing loss caused by CMV.
Methods
The medical records of 58 children who were diagnosed with confirmed CMV infection were reviewed for clinical symptoms and signs of CMV infection. Hearing status was evaluated with age-appropriate audiological test batteries.
Results
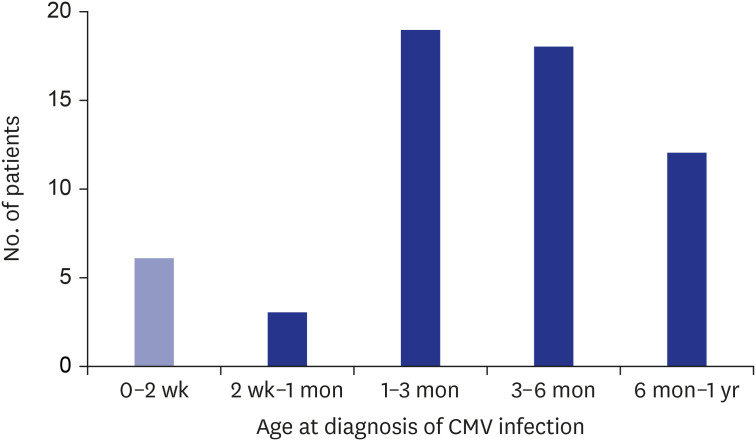
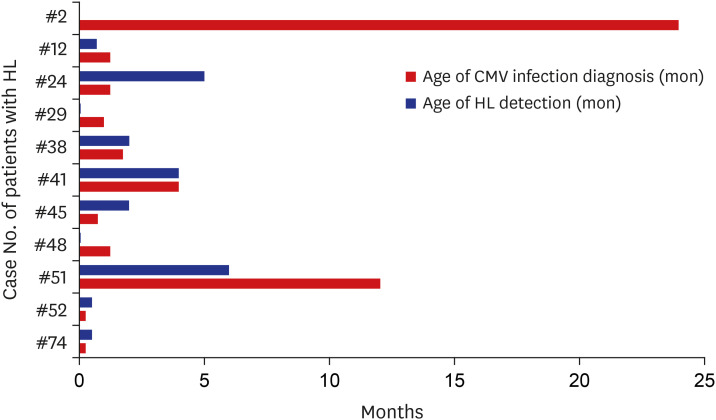
A total of 58 children (M:F = 32:26 patients; age at study: mean, 5.62 years, range, 1-10 years) were diagnosed serologically with CMV infection (14 patients, 21.1%), or diagnosed via PCR of serum (5, 7.9%) and/or PCR from urine (19, 26.8%). Hearing loss was confirmed in 11 children (19.0%), being bilateral in 6 (54.5%), and unilateral in 5 (45.5%). Note that 7 of 17 ears with hearing loss passed NHS and were diagnosed only after re-evaluation when CMV infection was identified.
Conclusion
Hearing loss is a serious complication of CMV infection in children. Our results highlight the importance of timely audiological evaluation in children with clinically symptomatic CMV infection even if they pass NHS.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kenneson A, Cannon MJ. Review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection. Rev Med Virol. 2007; 17(4):253–276. PMID: 17579921.
Article2. Dollard SC, Grosse SD, Ross DS. New estimates of the prevalence of neurological and sensory sequelae and mortality associated with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Rev Med Virol. 2007; 17(5):355–363. PMID: 17542052.
Article3. Mestas E. Congenital cytomegalovirus. Adv Neonatal Care. 2016; 16(1):60–65. PMID: 26752783.
Article4. Fowler KB, Dahle AJ, Boppana SB, Pass RF. Newborn hearing screening: will children with hearing loss caused by congenital cytomegalovirus infection be missed? J Pediatr. 1999; 135(1):60–64. PMID: 10393605.
Article5. Fowler KB, McCollister FP, Sabo DL, Shoup AG, Owen KE, Woodruff JL, et al. A targeted approach for congenital cytomegalovirus screening within newborn hearing screening. Pediatrics. 2017; 139(2):e20162128. PMID: 28049114.
Article6. Goderis J, Keymeulen A, Smets K, Van Hoecke H, De Leenheer E, Boudewyns A, et al. Hearing in children with congenital cytomegalovirus infection: results of a longitudinal study. J Pediatr. 2016; 172:110–115.e2. PMID: 26858192.
Article7. Riga M, Korres G, Chouridis P, Naxakis S, Danielides V. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection inducing non-congenital sensorineural hearing loss during childhood; a systematic review. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2018; 115:156–164. PMID: 30368378.
Article8. Manicklal S, Emery VC, Lazzarotto T, Boppana SB, Gupta RK. The “silent” global burden of congenital cytomegalovirus. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2013; 26(1):86–102. PMID: 23297260.
Article9. Watkin PM, Baldwin M. Identifying deafness in early childhood: requirements after the newborn hearing screen. Arch Dis Child. 2011; 96(1):62–66. PMID: 21047829.
Article10. Dobbie AM. Evaluation and management of cytomegalovirus-associated congenital hearing loss. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2017; 25(5):390–395. PMID: 28857892.
Article11. Foulon I, Naessens A, Faron G, Foulon W, Jansen AC, Gordts F. Hearing thresholds in children with a congenital CMV infection: a prospective study. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2012; 76(5):712–717. PMID: 22386305.
Article12. Williamson WD, Demmler GJ, Percy AK, Catlin FI. Progressive hearing loss in infants with asymptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatrics. 1992; 90(6):862–866. PMID: 1331946.13. Dahle AJ, Fowler KB, Wright JD, Boppana SB, Britt WJ, Pass RF. Longitudinal investigation of hearing disorders in children with congenital cytomegalovirus. J Am Acad Audiol. 2000; 11(5):283–290. PMID: 10821506.14. Madden C, Wiley S, Schleiss M, Benton C, Meinzen-Derr J, Greinwald J, et al. Audiometric, clinical and educational outcomes in a pediatric symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) population with sensorineural hearing loss. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2005; 69(9):1191–1198. PMID: 16061110.
Article15. Sabroske E, Svoboda MD, Ng YT. Passing the newborn hearing screen does not always exclude acquired hearing loss due to congenital infection. Pediatr Neurol. 2018; 83:60–61. PMID: 29622487.
Article16. Haesen S, Shaw D. Clinical characteristics, audiological and neurodevelopmental outcomes of newborns with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Swiss Med Wkly. 2018; 148:w14628. PMID: 29767827.
Article17. Seo S, Cho Y, Park J. Serologic screening of pregnant Korean women for primary human cytomegalovirus infection using IgG avidity test. Korean J Lab Med. 2009; 29(6):557–562. PMID: 20046088.
Article18. Sohn YM, Park KI, Lee C, Han DG, Lee WY. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection in Korean population with very high prevalence of maternal immunity. J Korean Med Sci. 1992; 7(1):47–51. PMID: 1329845.
Article19. Kim BJ, Han JJ, Shin SH, Kim HS, Yang HR, Choi EH, et al. Characterization of detailed audiological features of cytomegalovirus infection: a composite cohort study from groups with distinct demographics. BioMed Res Int. 2018; 2018:7087586. PMID: 30228987.
Article20. Ronchi A, Shimamura M, Malhotra PS, Sánchez PJ. Encouraging postnatal cytomegalovirus (CMV) screening: the time is NOW for universal screening! Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2017; 15(5):417–419. PMID: 28277819.
Article21. Lu CY, Tsao PN, Ke YY, Lin YH, Lin YH, Hung CC, et al. Concurrent hearing, genetic, and cytomegalovirus screening in newborns, Taiwan. J Pediatr. 2018; 199:144–150.e1. PMID: 29681450.
Article22. Kim J, Lee YK, Ko SY, Shin SM. Diagnostic clues for congenital cytomegalovirus infection: association with newborn hearing screening tests. Neonatal Med. 2019; 26(2):96–101.
Article23. Vancor E, Shapiro ED, Loyal J. Results of a targeted screening program for congenital cytomegalovirus infection in infants who fail newborn hearing screening. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2019; 8(1):55–59. PMID: 29373759.
Article24. Kimberlin DW, Lin CY, Sánchez PJ, Demmler GJ, Dankner W, Shelton M, et al. Effect of ganciclovir therapy on hearing in symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease involving the central nervous system: a randomized, controlled trial. J Pediatr. 2003; 143(1):16–25. PMID: 12915819.
Article25. Schleiss MR. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: update on management strategies. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2008; 10(3):186–192. PMID: 18579022.
Article26. Kimberlin DW, Jester PM, Sánchez PJ, Ahmed A, Arav-Boger R, Michaels MG, et al. Valganciclovir for symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus disease. N Engl J Med. 2015; 372(10):933–943. PMID: 25738669.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cytomegalovirus Colitis
- Treatment of Cytomegalov irus-associated IgA Nephropathy by Deflazacort and Intrav enous Immunoglobulin
- Two cases of congenital cytomegalovirus infection
- Severe Cytomegalovirus Infection in a Late-Preterm Infant at 2 Months of Age
- A Case of Inherited Thymic Dysplasia Associated with Disseminated Cytomegalovirus Infection