Pediatr Infect Vaccine.
2016 Aug;23(2):137-142. 10.14776/piv.2016.23.2.137.
Severe Cytomegalovirus Infection in a Late-Preterm Infant at 2 Months of Age
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, College of Medicine, Dankook University, Cheonan, Korea. pdlks@dankook.ac.kr
- KMID: 2353394
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14776/piv.2016.23.2.137
Abstract
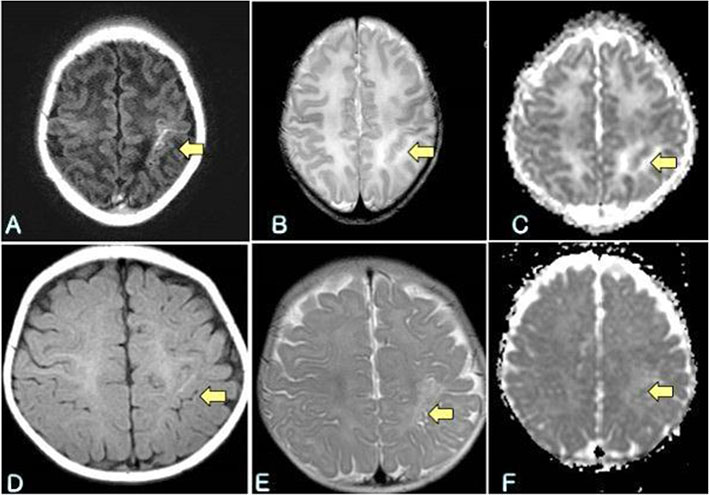
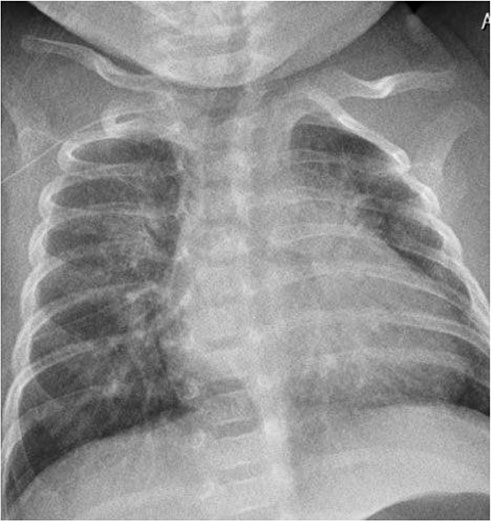
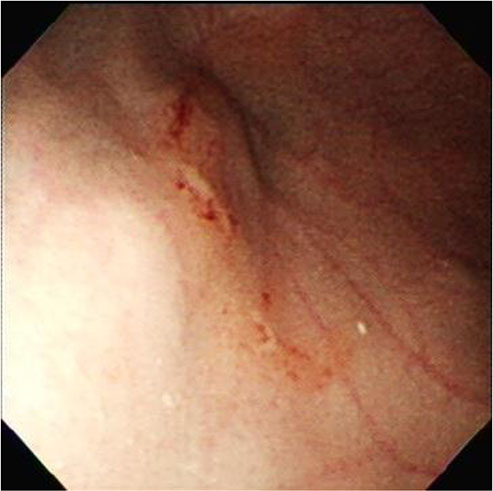
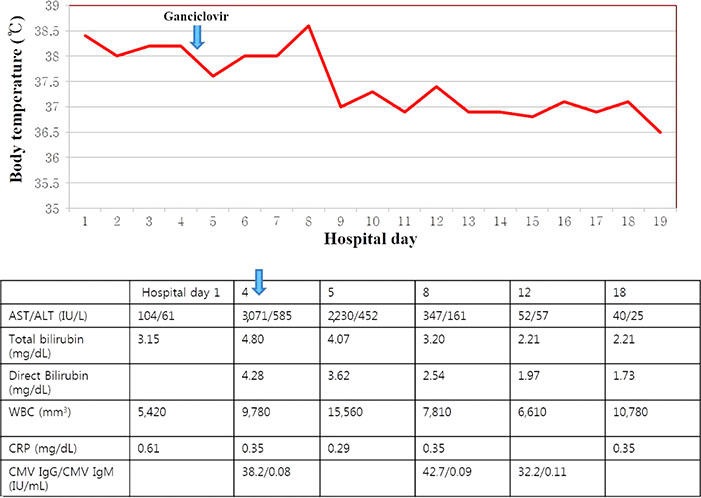
- Severe cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection involving multiorgan is very rare except in very low-birth weight infants, or in immunocompromised pediatric patients. We report an unusual case of severe CMV infection involving multiple organs including the central nervous system, liver, lung, and gastrointestinal tract in a late-preterm infant at 2 months of age.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kim CS. Congenital and perinatal cytomegalovirus infection. Korean J Pediatr. 2010; 53:14–20.
Article2. El-Sayed MF, Goldfarb DM, Fulford M, Pernica JM. Severe late-onset multisystem cytomegalovirus infection in a premature neonate previously treated for congenital infection. BMC Pediatr. 2013; 13:142.
Article3. Kim JH, Chung EJ, Park HK, Moon SJ, Choi SM, Oh SH. Postnatal cytomegalovirus infection in an extremely premature infant transmitted via breast milk: a case report. Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:1053–1058.
Article4. Byun WM, Hwang MS. Congenital cytomegalovirus infection of the brain: MR imaging and ultrasonographic findings of paraventricular cysts. J Korean Radiol Soc. 2002; 47:85–91.
Article5. Kanik-Yuksek S, Gulhan B, Tezer H, Ozkaya-Parlakay A. A perinatal cytomegalovirus infection in an immunocompetent patient with chorioretinitis. J Trop Pediatr. 2014; 60:401–403.
Article6. Nijman J, de Vries LS, Koopman-Esseboom C, Uiterwaal CS, van Loon AM, Verboon-Maciolek MA. Postnatally acquired cytomegalovirus infection in preterm infants: a prospective study on risk factors and cranial ultrasound findings. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2012; 97:F259–F263.
Article7. Mussi-Pinhata MM, Yamamoto AY, do Carmo Rego MA, Pinto PC, da Motta MS, Calixto C. Perinatal or early-postnatal cytomegalovirus infection in preterm infants under 34 weeks gestation born to CMV-seropositive mothers within a high-seroprevalence population. J Pediatr. 2004; 145:685–688.
Article8. James SH, Kimberlin DW, Whitley RJ. Antiviral therapy for herpesvirus central nervous system infections: neonatal herpes simplex virus infection, herpes simplex encephalitis, and congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Antiviral Res. 2009; 83:207–213.
Article9. Noh JH, Suh ES. A case of congenital cytomegalovirus encephalopathy with patchy, nodular lesion of periventricular area on brain magnetic resonance imaging. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2001; 9:416–420.10. Okulu E, Akin IM, Atasay B, Ciftci E, Arsan S, Turmen T. Severe postnatal cytomegalovirus infection with multisystem involvement in an extremely low birth weight infant. J Perinatol. 2012; 32:72–74.
Article11. Na SY. Cytomegalovirus infection in infantile hepatitis. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2012; 15:91–99.
Article12. Tezer H, Secmeer G, Kara A, Ceyhan M, Cengiz AB, Devrim I, et al. Cytomegalovirus hepatitis and ganciclovir treatment in immunocompetent children. Turk J Pediatr. 2008; 50:228–234.13. Hasosah MY, Kutbi SY, Al-Amri AW, Alsahafi AF, Sukkar GA, Alghamdi KJ, et al. Perinatal cytomegalovirus hepatitis in Saudi infants: a case series. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2012; 18:208–213.
Article14. Vancikova Z, Kucerova T, Pelikan L, Zikmundova L, Priglova M. Perinatal cytomegalovirus hepatitis: to treat or not to treat with ganciclovir. J Paediatr Child Health. 2004; 40:444–448.
Article15. Jang HJ, Kim AS, Hwang JB. Cytomegalovirus-associated esophageal ulcer in an immunocompetent infant: when should ganciclovir be administered? Korean J Pediatr. 2012; 55:491–493.
Article16. Hendriks G, McPartland J, El-Matary W. Gastrointestinal presentation and outcome of perinatal cytomegalovirus infection. BMJ Case Rep. 2013; 2013.
Article17. Tan BH. Cytomegalovirus treatment. Curr Treat Options Infect Dis. 2014; 6:256–270.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Cytomegalovirus Infection in a Neonate with Osteopetrosis
- Central Diabetes Insipidus Associated with Symptomatic Cytomegalovirus Infection in an Extremely Low Birth Weight Infant
- Hospital Visits from Respiratory Diseases of Early and Late Preterm Infants
- Hearing and Neurodevelopmental Out comes in Preterm Infants with Postnatal Cytomegalovirus Infection
- Obstetrical Management of Late Preterm Pregnancy