J Korean Med Sci.
2020 Jul;35(28):e222. 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e222.
Comparison of Serum Uric Acid in Major Depressive Disorder and Bipolar Disorder: a Retrospective Chart Review Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1College of Medicine, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Neuropsychiatry, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Psychiatry, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Institute of Human Behavioral Medicine, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2504361
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e222
Abstract
- Background
Uric acid (UA) has been suggested as a possible biomarker of bipolar disorder (BD) in recent studies. We aimed to provide a clearer comparison of UA levels between BD and major depressive disorder (MDD).
Methods
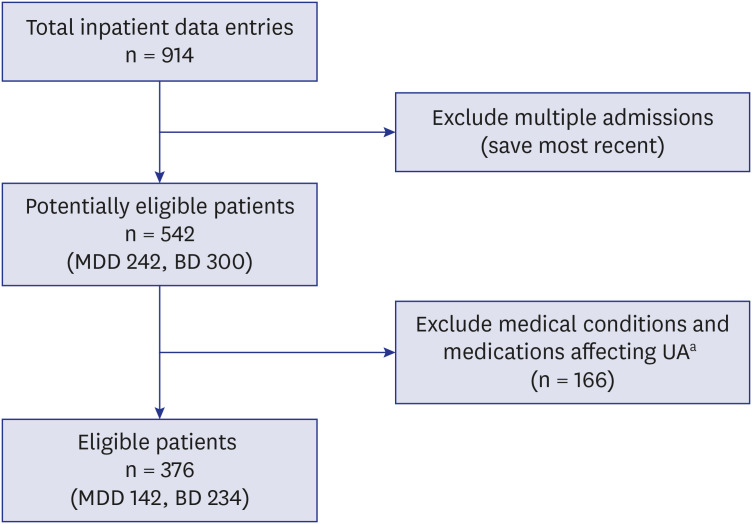
We retrospectively reviewed the medical chart records of psychiatric inpatients aged 19–60 years, whose main discharge diagnoses were either MDD or BD, with an admission between January 1, 2015 and December 31, 2018 at Seoul National University Hospital. Data such as sex, age, body mass index (BMI), medication usage, and serum UA levels were extracted. Patients with medical conditions or on medications that could influence UA levels were excluded. Age, sex, BMI, and psychiatric drug usage were considered in the comparison of serum UA between MDD and BD patients.
Results
Our sample consisted of 142 MDD patients and 234 BD patients. The BD patients had significantly higher serum UA levels compared to the MDD patients, without accounting for other confounding variables (5.75 ± 1.56 mg/dL vs. 5.29 ± 1.59 mg/dL, P = 0.006). T-test comparisons between psychiatric medication users and non-users revealed that mood stabilizers and antipsychotics may be relevant confounding factors in our sample analysis. The likelihood of BD diagnosis was significantly correlated with higher UA levels (odds ratio, 1.410; 95% confidence interval, 1.150–1.728; P = 0.001) when accounting for sex, age, and BMI in the logistic regression analysis. Also, accounting for mood stabilizers or antipsychotics, the likelihood of BD diagnosis was still significantly correlated with higher UA levels.
Conclusion
Our study confirms that BD patients are significantly more likely to show higher serum UA levels than MDD patients. The high UA levels in BD point to purinergic dysfunction as an underlying mechanism that distinguishes BD from MDD. Further research is recommended to determine whether UA is a trait or a state marker and whether UA correlates with the symptoms and severity of BD.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Muzina DJ, Kemp DE, McIntyre RS. Differentiating bipolar disorders from major depressive disorders: treatment implications. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2007; 19(4):305–312. PMID: 18058287.
Article2. Geddes JR, Miklowitz DJ. Treatment of bipolar disorder. Lancet. 2013; 381(9878):1672–1682. PMID: 23663953.
Article3. Song M, Yoon H, Choi I, Hong SD, Joung YS. Differences of clinical characteristics and phenotypes between prepubertal- and adolescent-onset bipolar disorders. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25(6):912–917. PMID: 20514314.
Article4. Joe S, Joo Y, Kim S. Experience of subjective symptoms in euthymic patients with bipolar disorder. J Korean Med Sci. 2008; 23(1):18–23. PMID: 18303193.
Article5. Sigitova E, Fišar Z, Hroudová J, Cikánková T, Raboch J. Biological hypotheses and biomarkers of bipolar disorder. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017; 71(2):77–103. PMID: 27800654.
Article6. Bartoli F, Carrà G, Clerici M. Purinergic dysfunction in bipolar disorder: any role for the antioxidant uric acid as a trait and state biomarker? Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2017; 71(6):417.
Article7. Malewska-Kasprzak MK, Permoda-Osip A, Rybakowski J. Disturbances of purinergic system in affective disorders and schizophrenia. Psychiatr Pol. 2019; 53(3):577–587. PMID: 31522198.
Article8. Ortiz R, Ulrich H, Zarate CA Jr, Machado-Vieira R. Purinergic system dysfunction in mood disorders: a key target for developing improved therapeutics. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2015; 57:117–131. PMID: 25445063.
Article9. Bartoli F, Crocamo C, Clerici M, Carrà G. Allopurinol as add-on treatment for mania symptoms in bipolar disorder: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Br J Psychiatry. 2017; 210(1):10–15. PMID: 27856422.
Article10. Jahangard L, Soroush S, Haghighi M, Ghaleiha A, Bajoghli H, Holsboer-Trachsler E, et al. In a double-blind, randomized and placebo-controlled trial, adjuvant allopurinol improved symptoms of mania in in-patients suffering from bipolar disorder. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014; 24(8):1210–1221. PMID: 24953766.
Article11. Machado-Vieira R, Soares JC, Lara DR, Luckenbaugh DA, Busnello JV, Marca G, et al. A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled 4-week study on the efficacy and safety of the purinergic agents allopurinol and dipyridamole adjunctive to lithium in acute bipolar mania. J Clin Psychiatry. 2008; 69(8):1237–1245. PMID: 18681754.
Article12. Bartoli F, Crocamo C, Mazza MG, Clerici M, Carrà G. Uric acid levels in subjects with bipolar disorder: a comparative meta-analysis. J Psychiatr Res. 2016; 81:133–139. PMID: 27442964.
Article13. Dos Santos Oliveira PM, Santos V, Coroa M, Ribeiro J, Madeira N. Serum uric acid as a predictor of bipolarity in individuals with a major depressive episode. Bipolar Disord. 2019; 21(3):235–243. PMID: 30375143.
Article14. Tatay-Manteiga A, Balanzá-Martínez V, Bristot G, Tabarés-Seisdedos R, Kapczinski F, Cauli O. Peripheral oxidative stress markers in patients with bipolar disorder during euthymia and in siblings. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2020; 20(1):77–86. PMID: 30848220.
Article15. Kim HS. Serum uric acid and metabolic syndrome: a retrospective cohort Study. J Korean Med Sci. 2019; 34(48):e324. PMID: 31833268.
Article16. Jeong J, Suh YJ. Association between serum uric acid and metabolic syndrome in Koreans. J Korean Med Sci. 2019; 34(48):e307. PMID: 31833264.
Article17. Albert U, De Cori D, Aguglia A, Barbaro F, Bogetto F, Maina G. Increased uric acid levels in bipolar disorder subjects during different phases of illness. J Affect Disord. 2015; 173:170–175. PMID: 25462413.
Article18. Wen S, Cheng M, Wang H, Yue J, Wang H, Li G, et al. Serum uric acid levels and the clinical characteristics of depression. Clin Biochem. 2012; 45(1-2):49–53. PMID: 22040815.
Article19. Bartoli F, Crocamo C, Bava M, Castagna G, Di Brita C, Riboldi I, et al. Testing the association of serum uric acid levels with behavioral and clinical characteristics in subjects with major affective disorders: a cross-sectional study. Psychiatry Res. 2018; 269:118–123. PMID: 30145291.
Article20. Wiener C, Rassier GT, Kaster MP, Jansen K, Pinheiro RT, Klamt F, et al. Gender-based differences in oxidative stress parameters do not underlie the differences in mood disorders susceptibility between sexes. Eur Psychiatry. 2014; 29(1):58–63. PMID: 23850061.
Article21. Muti M, Del Grande C, Musetti L, Marazziti D, Turri M, Cirronis M, et al. Serum uric acid levels and different phases of illness in bipolar I patients treated with lithium. Psychiatry Res. 2015; 225(3):604–608. PMID: 25547850.
Article22. Machado-Vieira R, Lara DR, Souza DO, Kapczinski F. Purinergic dysfunction in mania: an integrative model. Med Hypotheses. 2002; 58(4):297–304. PMID: 12027524.
Article23. Brown ES, Rush AJ, McEwen BS. Hippocampal remodeling and damage by corticosteroids: implications for mood disorders. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999; 21(4):474–484. PMID: 10481830.
Article24. Stehle JH, Rivkees SA, Lee JJ, Weaver DR, Deeds JD, Reppert SM. Molecular cloning and expression of the cDNA for a novel A2-adenosine receptor subtype. Mol Endocrinol. 1992; 6(3):384–393. PMID: 1584214.
Article25. Brooks SC, Linn JJ, Disney N. Serotonin, folic acid, and uric acid metabolism in the diagnosis of neuropsychiatric disorders. Biol Psychiatry. 1978; 13(6):671–684. PMID: 737255.26. Chung KH, Huang CC, Lin HC. Increased risk of gout among patients with bipolar disorder: a nationwide population-based study. Psychiatry Res. 2010; 180(2-3):147–150. PMID: 20483460.
Article27. Burnstock G. Purinergic signalling and disorders of the central nervous system. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2008; 7(7):575–590. PMID: 18591979.
Article28. Lucae S, Salyakina D, Barden N, Harvey M, Gagné B, Labbé M, et al. P2RX7, a gene coding for a purinergic ligand-gated ion channel, is associated with major depressive disorder. Hum Mol Genet. 2006; 15(16):2438–2445. PMID: 16822851.
Article29. Barden N, Harvey M, Gagné B, Shink E, Tremblay M, Raymond C, et al. Analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms in genes in the chromosome 12Q24.31 region points to P2RX7 as a susceptibility gene to bipolar affective disorder. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2006; 141B(4):374–382. PMID: 16673375.
Article30. Anumonye A, Reading HW, Knight F, Ashcroft GW. Uric-acid metabolism in manic-depressive illness and during lithium therapy. Lancet. 1968; 1(7555):1290–1293. PMID: 4172145.
Article31. Ring HA, Heller AJ, Marshall WJ, Johnson AL, Reynolds EH. Plasma uric acid in patients receiving anticonvulsant monotherapy. Epilepsy Res. 1991; 8(3):241–244. PMID: 1868823.
Article32. Yao JK, Reddy R, van Kammen DP. Reduced level of plasma antioxidant uric acid in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res. 1998; 80(1):29–39. PMID: 9727961.
Article