Anat Cell Biol.
2020 Jun;53(2):137-142. 10.5115/acb.20.039.
The distribution pattern of the dorsal cutaneous nerves of the foot and its clinical implications
- Affiliations
-
- 1PhD Degree Program in Anatomy, Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- 2Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- 3Department of Orthopedics, Faculty of Medicine, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- 4Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Nara Medical University, Kashihara, Japan
- 5Excellence Center in Osteology Research and Training Center, Chiang Mai University, Chiang Mai, Thailand
- KMID: 2503443
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5115/acb.20.039
Abstract
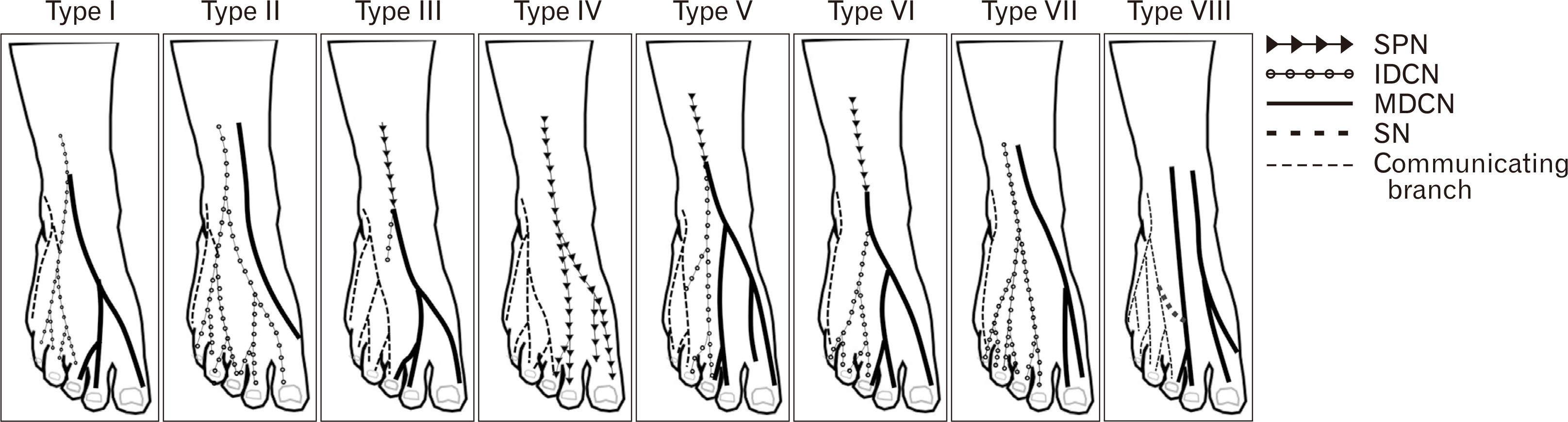
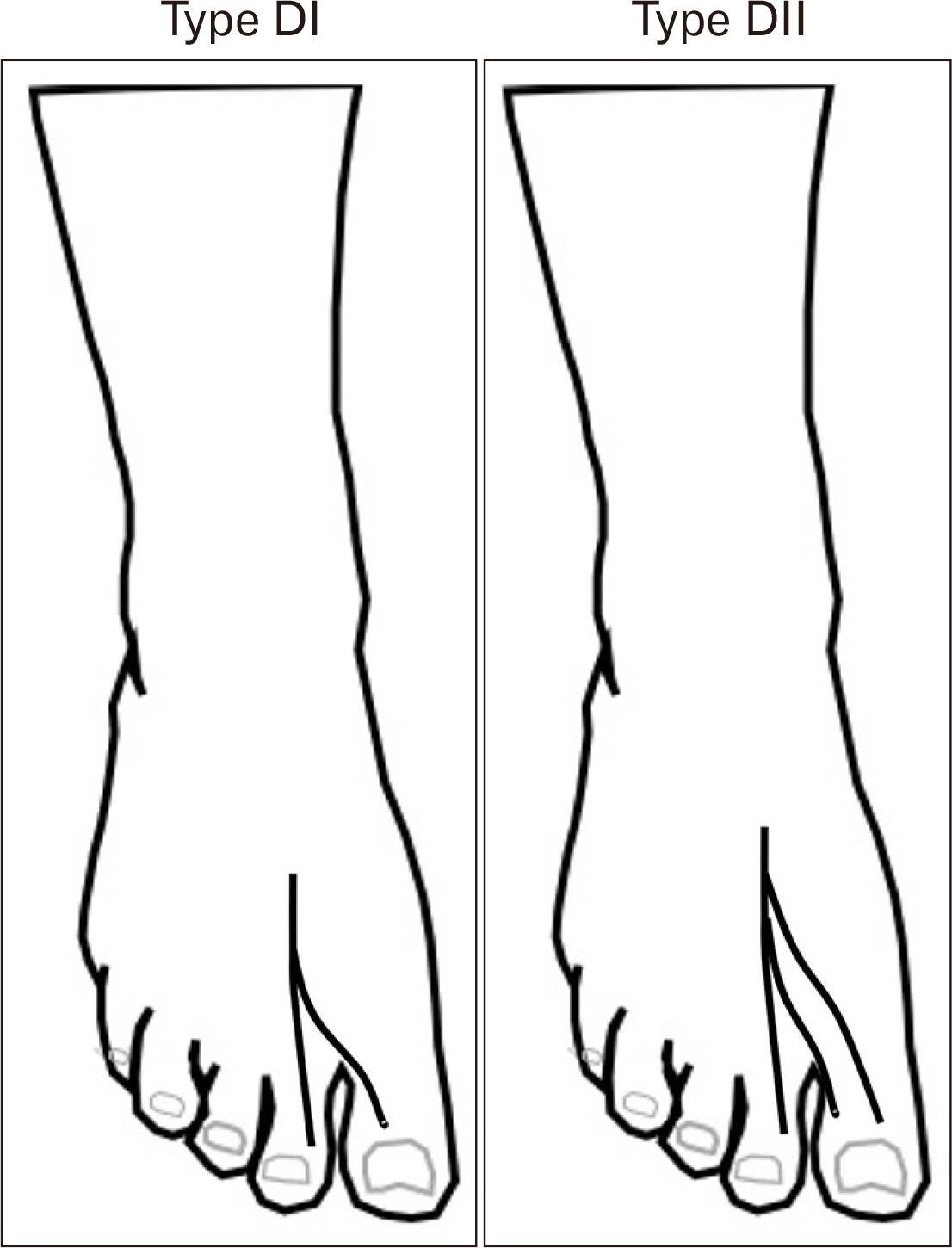
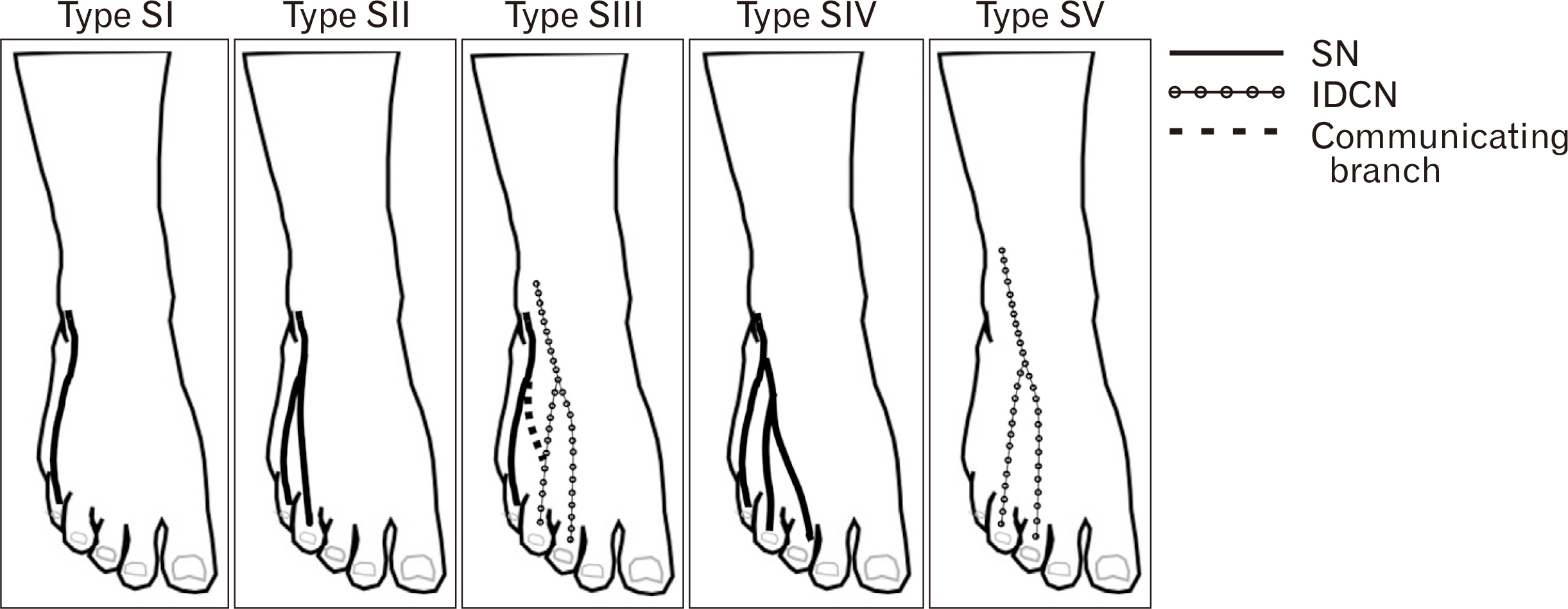
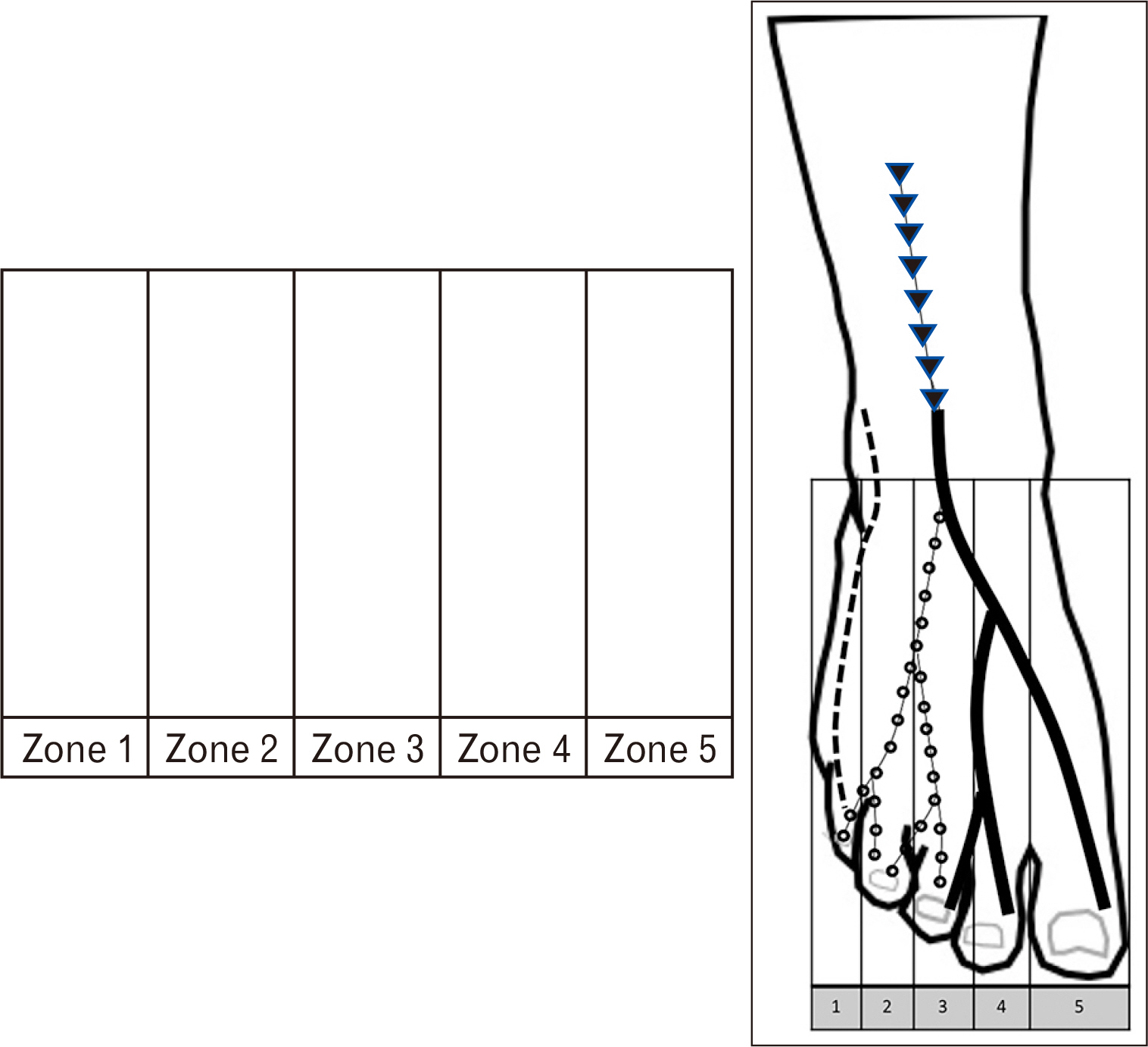
- Iatrogenic injury to subcutaneous nerves on the dorsum of the foot is an established risk factor during the surgical procedures resulting in postoperative pain, sensation loss and painful neuroma. Previous studies have reported on the distribution pattern of the superficial peroneal, deep peroneal and sural nerves (SNs) and their branches with various classifications about specific populations. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the distribution pattern and classification of the nerves on the dorsum of the foot and analyze the location of these nerves into five zones with clinical implications. Fifty-four lower limbs of fresh frozen cadavers were used in the present study. The anatomical patterns of the superficial peroneal, deep peroneal, SN and their branches were classified into eight, two and five patterns respectively. Type VI pattern, a classic distribution pattern of the superficial peroneal nerve was the most frequent type with a prevalence of 13 limbs (25.00%). In Zone 5, where the arthroscopic portal placements for the first metatarsophalangeal joint arthrodesis, 29 limbs (55.77%) showed three nerve branches located in this zone. The results of the present study provide anatomical knowledge that may help the surgeon to choose the appropriate treatment for their patients and reducing the rate of complications in surgery.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kenzora JE. 1986; Sensory nerve neuromas--leading to failed foot surgery. Foot Ankle. 7:110–7. DOI: 10.1177/107110078600700209. PMID: 3770595.
Article2. Miller RA, Hartman G. 1996; Origin and course of the dorsomedial cutaneous nerve to the great toe. Foot Ankle Int. 17:620–2. DOI: 10.1177/107110079601701006. PMID: 8908488.
Article3. Blair JM, Botte MJ. 1994; Surgical anatomy of the superficial peroneal nerve in the ankle and foot. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (305):229–38. DOI: 10.1097/00003086-199408000-00028.
Article4. Canella C, Demondion X, Guillin R, Boutry N, Peltier J, Cotten A. 2009; Anatomic study of the superficial peroneal nerve using sonography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 193:174–9. DOI: 10.2214/AJR.08.1898. PMID: 19542411.
Article5. Üçeyler N, Schäfer KA, Mackenrodt D, Sommer C, Müllges W. 2016; High-resolution ultrasonography of the superficial peroneal motor and sural sensory nerves may be a non-invasive approach to the diagnosis of vasculitic neuropathy. Front Neurol. 7:48. DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2016.00048. PMID: 27064457. PMCID: PMC4812111.
Article6. Heo Y, Jung TJ, Yang M, Kuk Y, Kim YD, Won HS. 2019; Aug. 20. Distribution patterns of the cutaneous nerves on the dorsum of the foot and their clinical significance. Clin Anat. [Epub]. http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/ca.23453. DOI: 10.1002/ca.23453. PMID: 31429988.
Article7. Aktan Ikiz ZA, Uçerler H, Bilge O. 2005; The anatomic features of the sural nerve with an emphasis on its clinical importance. Foot Ankle Int. 26:560–7. DOI: 10.1177/107110070502600712. PMID: 16045849.8. Kosinski C. 1926; The course, mutual relations and distribution of the cutaneous nerves of the Metazonal region of leg and foot. J Anat. 60(Pt 3):274–97.9. Solomon LB, Ferris L, Tedman R, Henneberg M. 2001; Surgical anatomy of the sural and superficial fibular nerves with an emphasis on the approach to the lateral malleolus. J Anat. 199(Pt 6):717–23. DOI: 10.1046/j.1469-7580.2001.19960717.x. PMID: 11787825. PMCID: PMC1468389.
Article10. Moore KL, Dalley AF, Agur AMR. 2006. Clinically oriented anatomy. 5th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;Philadelphia: p. 1–300.11. Loveday DT, Nogaro MC, Calder JD, Carmichael J. 2013; Is there an anatomical marker for the deep peroneal nerve in midfoot surgical approaches? Clin Anat. 26:400–2. DOI: 10.1002/ca.22173. PMID: 23378070.
Article12. Causeret A, Ract I, Jouan J, Dreano T, Ropars M, Guillin R. 2018; A review of main anatomical and sonographic features of subcutaneous nerve injuries related to orthopedic surgery. Skeletal Radiol. 47:1051–68. DOI: 10.1007/s00256-018-2917-5. PMID: 29549379.
Article13. Mahakkanukrauh P, Chomsung R. 2002; Anatomical variations of the sural nerve. Clin Anat. 15:263–6. DOI: 10.1002/ca.10016. PMID: 12112352.
Article14. Madhavi C, Isaac B, Antoniswamy B, Holla SJ. 2005; Anatomical variations of the cutaneous innervation patterns of the sural nerve on the dorsum of the foot. Clin Anat. 18:206–9. DOI: 10.1002/ca.20094. PMID: 15768411.
Article15. Eid EM, Hegazy AM. 2011; Anatomical variations of the human sural nerve and its role in clinical and surgical procedures. Clin Anat. 24:237–45. DOI: 10.1002/ca.21068. PMID: 20949489.
Article16. Jeon SK, Paik DJ, Hwang YI. 2017; Variations in sural nerve formation pattern and distribution on the dorsum of the foot. Clin Anat. 30:525–32. DOI: 10.1002/ca.22873. PMID: 28281304.
Article17. Kelikian AS, Sarrafian SK. 2012. Sarrafian's anatomy of the foot and ankle: descriptive, topographic, functional. 3rd ed. Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;Philadelphia: p. 1–736.18. Nayak VS, Bhat N, Nayak SS, Sumalatha S. 2019; Anatomical variations in the cutaneous innervation on the dorsum of the foot. Anat Cell Biol. 52:34–7. DOI: 10.5115/acb.2019.52.1.34. PMID: 30984449. PMCID: PMC6449594.
Article19. Siclari A, Piras M. 2015; Hallux metatarsophalangeal arthroscopy: indications and techniques. Foot Ankle Clin. 20:109–22. DOI: 10.1016/j.fcl.2014.10.012. PMID: 25726487.20. Vaseenon T, Phisitkul P. 2010; Arthroscopic debridement for first metatarsophalangeal joint arthrodesis with a 2-versus 3-portal technique: a cadaveric study. Arthroscopy. 26:1363–7. DOI: 10.1016/j.arthro.2010.02.015. PMID: 20887934.21. Malagelada F, Vega J, Guelfi M, Kerkhoffs G, Karlsson J, Dalmau-Pastor M. 2020; Anatomic lectures on structures at risk prior to cadaveric courses reduce injury to the superficial peroneal nerve, the commonest complication in ankle arthroscopy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 28:79–85. DOI: 10.1007/s00167-019-05373-x. PMID: 30729253.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Distribution Patterns of the Cutaneous Nerves on Dorsum of the Hands in the Korean
- Anatomical variations in the cutaneous innervation on the dorsum of the foot
- Morphology of the cutaneous vein in the dorsal foot and the ankle
- Superficial Peroneal Nerve Conduction Study
- Hinged multiperforator-based extended dorsalis pedis adipofascial flap for dorsal foot defects