Neonatal Med.
2020 May;27(2):57-64. 10.5385/nm.2020.27.2.57.
Clinical Status of Inhaled Nitric Oxide Treatment in Infants with Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn in Korea: Post-Marketing Surveillance Results
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2503160
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5385/nm.2020.27.2.57
Abstract
- Purpose
Inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) is a potent selective pulmonary vasodilator and an important treatment for newborn infants with hypoxic respiratory failure due to persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn (PPHN). The Ministry of Food and Drug Safety of Korea first approved iNO in 2009 for use as a new drug to treat hypoxic res piratory failure with PPHN. A post-marketing surveillance study (PMSS) was conducted to assess the effectiveness and safety of the iNO treatment. We evaluated the clinical status of the iNO treatment currently available in Korea by using the PMSS data.
Methods
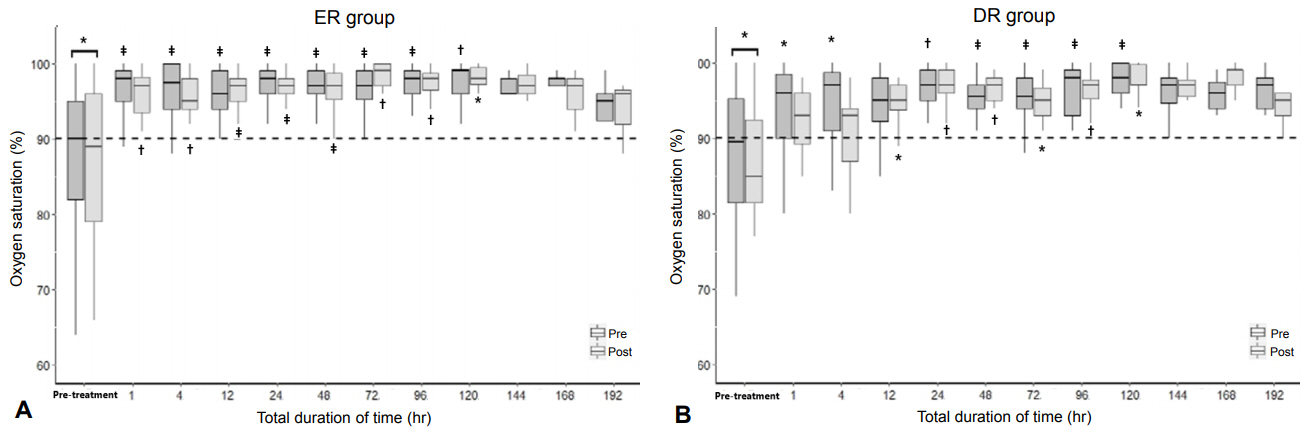
We retrospectively reviewed the PMSS data from 22 hospitals in Korea from October 2014 to September 2018. Altogether, 97 infants were enrolled and divided into early response (ER), delayed response (DR), no response (NR), and death groups according to their response to the iNO treatment.
Results
The ER group included 52 infants (53.6%); DR group, 33 (34.0%); NR group, seven (7.2%); and death group, five (5.2%). The iNO treatment was initiated within 14 days after birth at a concentration of 20 ppm. The median treatment duration was 91.5 hours (69.0 to 134.3) in all the infants. Of the infants, 43 (44.3%) received the treatment for >96 hours. Fifty-one infants (52.6%) needed >20 ppm of iNO, and 10 (10.5%) needed a maximum of 80 ppm of iNO. None of the infants had hypermethemoglobinemia or an alarm report of NO2.
Conclusion
Korean neonatologists reported that a large proportion of the infants with PPHN showed improvement in oxygenation after treatment with the approved iNO. These infants received relatively longer durations and higher concentrations of the iNO treatment than the current recommendations, without any side and adverse effect.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pepke-Zaba J, Higenbottam TW, Dinh-Xuan AT, Stone D, Wallwork J. Inhaled nitric oxide as a cause of selective pulmonary vasodilatation in pulmonary hypertension. Lancet. 1991; 338:1173–4.2. Roberts JD, Polaner DM, Lang P, Zapol WM. Inhaled nitric oxide in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Lancet. 1992; 340:818–9.3. Kinsella JP, Neish SR, Shaffer E, Abman SH. Low-dose inhalation nitric oxide in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Lancet. 1992; 340:819–20.4. Kinsella JP. Inhaled nitric oxide in the term newborn. Early Hum Dev. 2008; 84:709–16.5. DiBlasi RM, Myers TR, Hess DR. Evidence-based clinical practice guideline: inhaled nitric oxide for neonates with acute hypoxic respiratory failure. Respir Care. 2010; 55:1717–45.6. Peliowski A; Canadian Paediatric Society; Fetus and Newborn Committee. Inhaled nitric oxide use in newborns. Paediatr Child Health. 2012; 17:95–100.7. Neonatal Inhaled Nitric Oxide Study Group. Inhaled nitric oxide in full-term and nearly full-term infants with hypoxic respiratory failure. N Engl J Med. 1997; 336:597–604.8. Clark RH, Kueser TJ, Walker MW, Southgate WM, Huckaby JL, Perez JA, et al. Low-dose nitric oxide therapy for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Clinical Inhaled Nitric Oxide Research Group. N Engl J Med. 2000; 342:469–74.9. Barrington KJ, Finer N, Pennaforte T, Altit G. Nitric oxide for respiratory failure in infants born at or near term. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017; 1:CD000399.10. Lee EH, Choi BM. Clinical application of inhaled nitric oxide therapy in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Neonatal Med. 2015; 22:61–70.11. Davidson D, Barefield ES, Kattwinkel J, Dudell G, Damask M, Straube R, et al. Inhaled nitric oxide for the early treatment of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the term newborn: a randomized, double-masked, placebo-controlled, dose-response, multicenter study. The I-NO/PPHN Study Group. Pediatrics. 1998; 101(3 Pt 1):325–34.12. Rhine WD, Suzuki S, Potenziano JL, Escalante S, Togari H. An analysis of time to improvement in oxygenation in Japanese preterm and late preterm or term neonates with hypoxic respiratory failure and pulmonary hypertension. Clin Ther. 2019; 41:910–9.13. Goldman AP, Tasker RC, Haworth SG, Sigston PE, Macrae DJ. Four patterns of response to inhaled nitric oxide for persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Pediatrics. 1996; 98(4 Pt 1):706–13.14. Guthrie SO, Walsh WF, Auten K, Clark RH. Initial dosing of inhaled nitric oxide in infants with hypoxic respiratory failure. J Perinatol. 2004; 24:290–4.15. Ahn SY. Prognosis and side effects of inhaled nitric oxide treatment in persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Neonatal Med. 2015; 22:71–7.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The Therapeutic Effect of Inhaled Iloprost in Newborn Infants with Severe Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension Refractory to Inhaled Nitric Oxide
- Prognosis and Side Effects of Inhaled Nitric Oxide Treatment in Persistent Pulmonary Hypertension of the Newborn
- A case of persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn: Treatment with inhaled iloprost
- Clinical Indications for Inhaled Nitric Oxide Therapy in Neonates
- Inhaled Nitric Oxide as a Therapy for Pulmonary Hypertension after Operations for Congenital Heart Diseases