J Korean Foot Ankle Soc.
2020 Jun;24(2):81-86. 10.14193/jkfas.2020.24.2.81.
Efficacy of Temporal Fixation Using Threaded Trans-Calcaneal Pin in Patients with Ankle Fracture-Dislocation or Tibia Pilon Fractures
- Affiliations
-
- 1Departments of Orthopaedic Surgery, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea
- 2Departments of Radiology, Inje University Busan Paik Hospital, Busan, Korea
- KMID: 2502914
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14193/jkfas.2020.24.2.81
Abstract
- Purpose
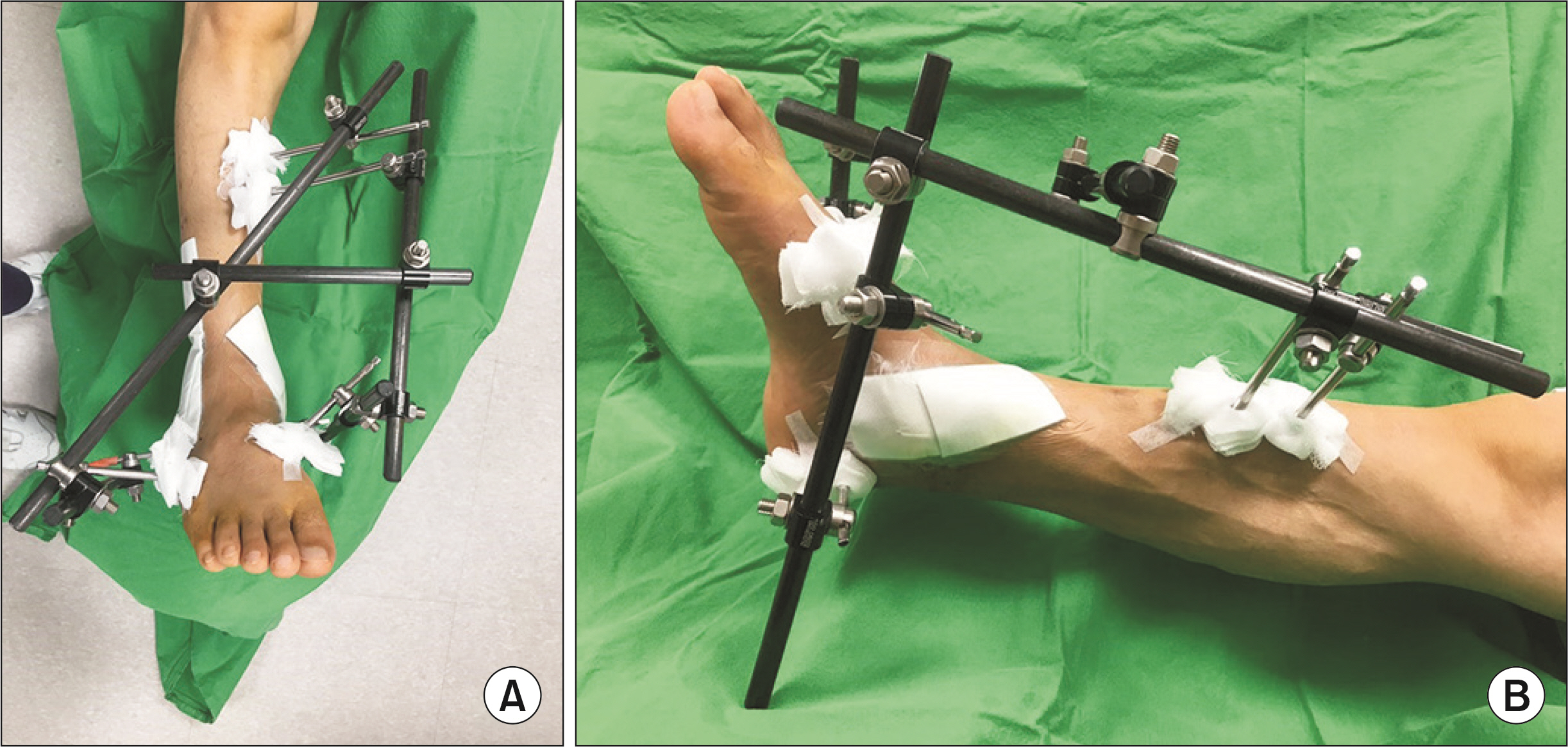
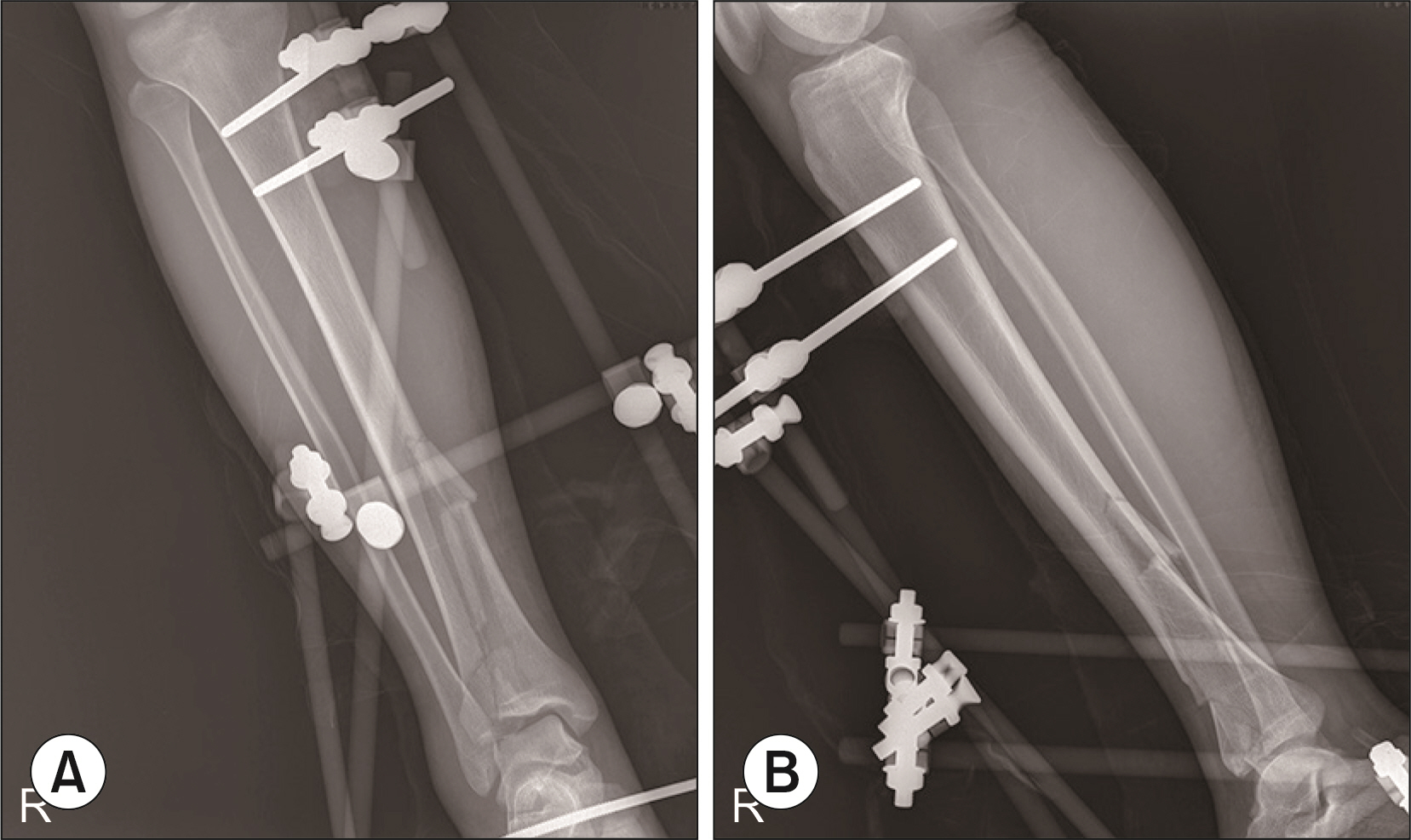
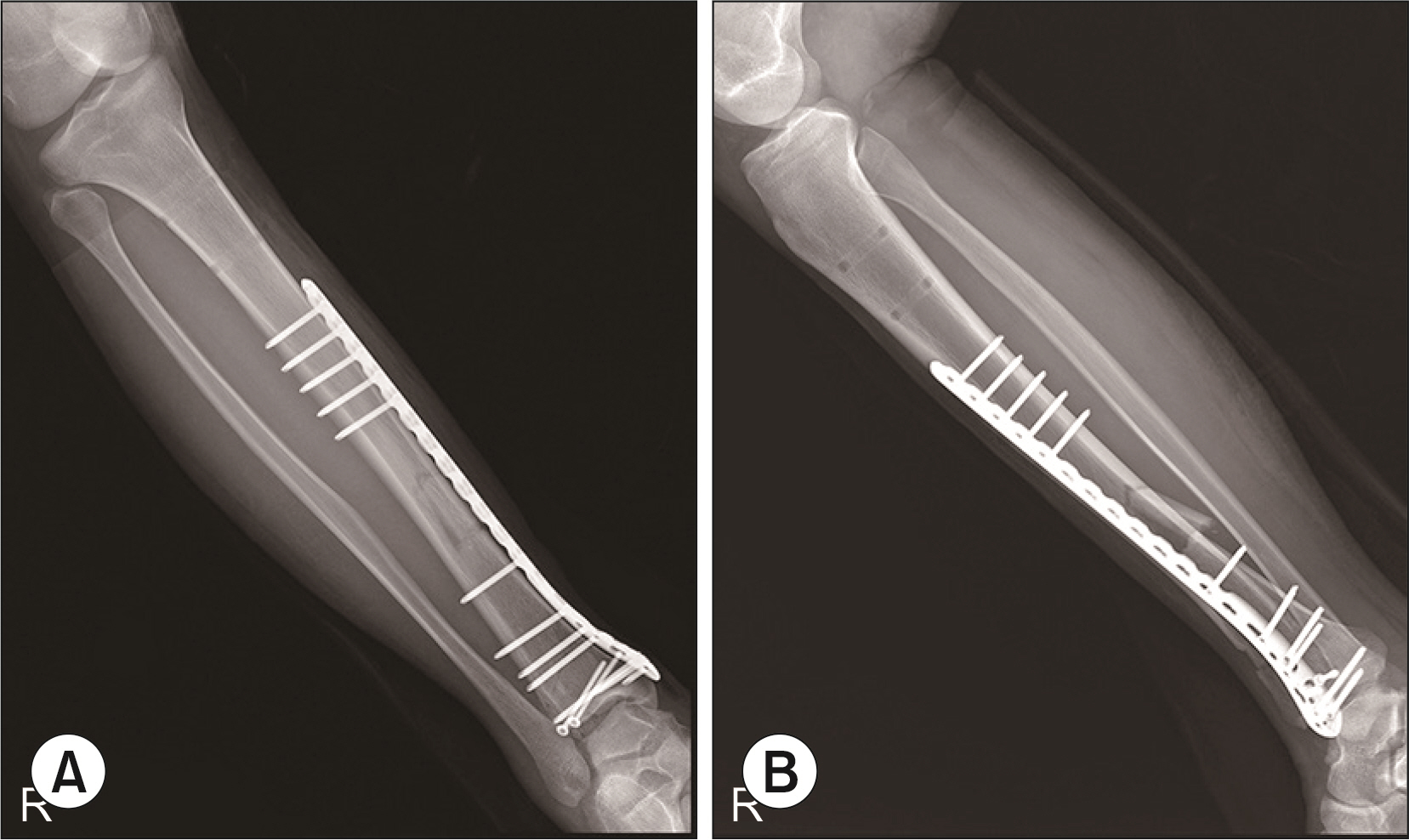
Ankle fractures with dislocations and pilon fractures at the distal tibia are usually associated with soft tissue damage caused by high-energy damage. Recently, a two-stage operation to perform internal fixation after the application of external fixation devices for stabilizing soft tissues has been accepted as the treatment of choice. This paper reports the clinical result of these injuries treated with threaded trans-calcaneal pin external fixation devices.
Materials and Methods
Thirty-three patients diagnosed with ankle fractures with dislocations or tibial pilon fractures without open wounds. They underwent surgical treatment with threaded trans-calcaneal pin external fixation from January 2008 to February were enrolled in this study. This study evaluated the visual analogue scale (VAS), foot function index (FFI), and Olerud & Molander score as well as whether complications occurred.
Results
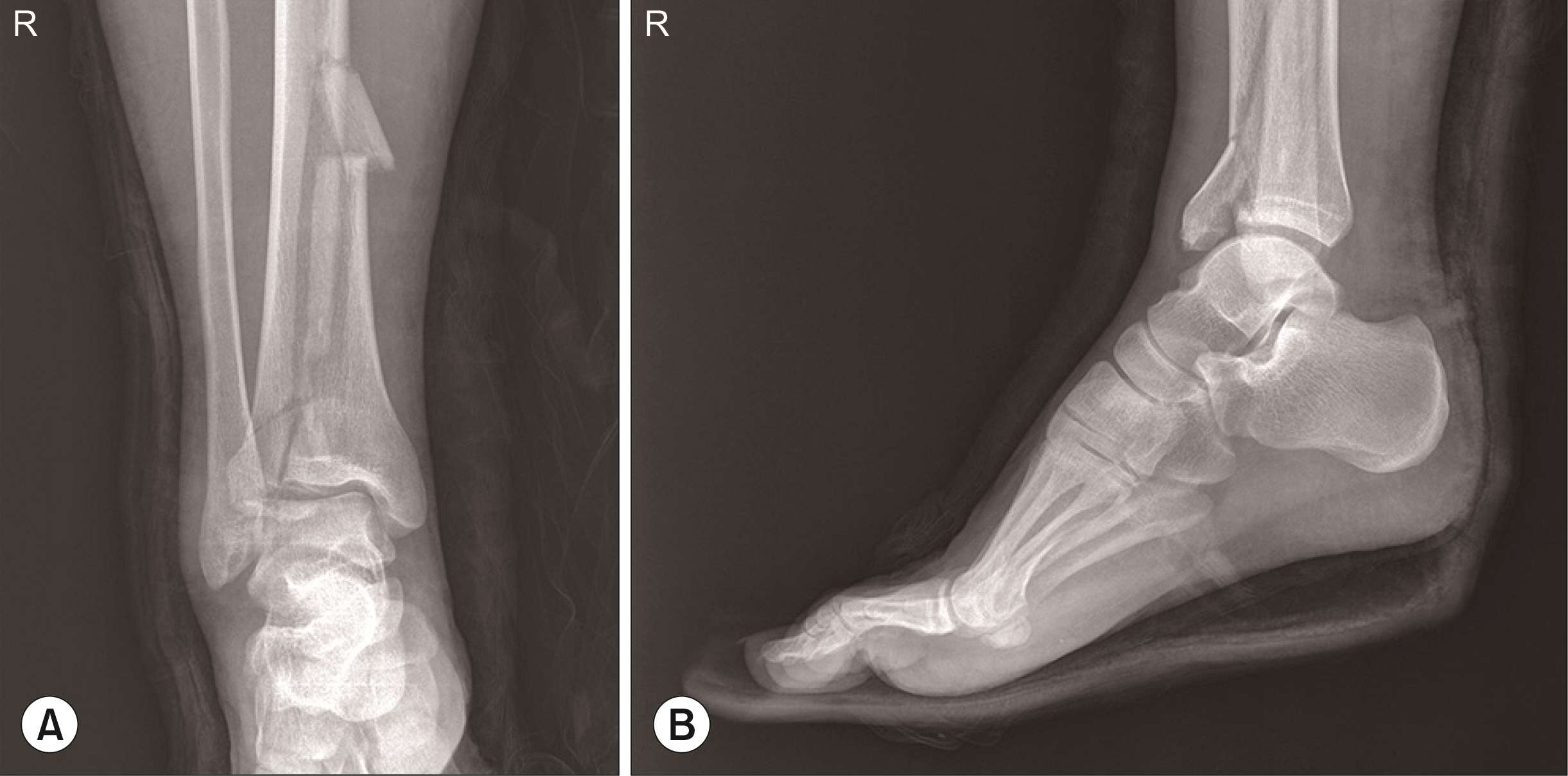
The average VAS showed a meaningful decrease (p<0.001) from 7.4 before surgery to 2.6 after application of the external fixation device, and 1.4 at 12 months after surgery. The FFI also decreased significantly from 84.3 preoperatively to 20.3 at 12 months postoperatively (p<0.001). The Olerud & Molander score averaged 71.4 points, showing good clinical results. Complete bone union was observed in all patients. One patient each underwent debridement due to wound necrosis and infection in the pin insertion site. At the final follow-up, seven patients had posttraumatic ankle joint arthritis, according to a radiological examination.
Conclusion
Manual reduction and external fixation using a threaded trans-calcaneal pin is a suitable surgical technique that is easy to perform and shows good clinical outcomes in stabilizing soft tissue damage in fractures and dislocations of ankle fracture or tibia pilon fractures in foot and ankle injury.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Davidovitch RI, Elkhechen RJ, Romo S, Walsh M, Egol KA. 2011; Open reduction with internal fixation versus limited internal fixation and external fixation for high grade pilon fractures (OTA type 43C). Foot Ankle Int. 32:955–61. doi: 10.3113/FAI.2011.0955. DOI: 10.3113/FAI.2011.0955. PMID: 22224324.
Article2. Babis GC, Vayanos ED, Papaioannou N, Pantazopoulos T. 1997; Results of surgical treatment of tibial plafond fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. (341):99–105. DOI: 10.1097/00003086-199708000-00016. PMID: 9269161.
Article3. Pollak AN, McCarthy ML, Bess RS, Agel J, Swiontkowski MF. 2003; Outcomes after treatment of high-energy tibial plafond fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 85:1893–900. doi: 10.2106/00004623-200310000-00005. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-200310000-00005. PMID: 14563795.
Article4. Pugh KJ, Wolinsky PR, McAndrew MP, Johnson KD. 1999; Tibial pilon fractures: a comparison of treatment methods. J Trauma. 47:937–41. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199911000-00022. DOI: 10.1097/00005373-199911000-00022. PMID: 10568726.
Article5. Wang C, Li Y, Huang L, Wang M. 2010; Comparison of two-staged ORIF and limited internal fixation with external fixator for closed tibial plafond fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 130:1289–97. doi: 10.1007/s00402-010-1075-6. DOI: 10.1007/s00402-010-1075-6. PMID: 20182880.
Article6. Koulouvaris P, Stafylas K, Mitsionis G, Vekris M, Mavrodontidis A, Xenakis T. 2007; Long-term results of various therapy concepts in severe pilon fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 127:313–20. doi: 10.1007/s00402-007-0306-y. DOI: 10.1007/s00402-007-0306-y. PMID: 17354011.
Article7. Han SB, Shin YS. 2013; The treatment principles and latest knowledge of external fixator in the treatment of fractures. J Korean Fract Soc. 26:156–63. doi: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.156. DOI: 10.12671/jkfs.2013.26.2.156.
Article8. Marsh JL, Bonar S, Nepola JV, Decoster TA, Hurwitz SR. 1995; Use of an articulated external fixator for fractures of the tibial plafond. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 77:1498–509. doi: 10.2106/00004623-199510000-00004. DOI: 10.2106/00004623-199510000-00004. PMID: 7593058.
Article9. Rammelt S, Endres T, Grass R, Zwipp H. 2004; The role of external fixation in acute ankle trauma. Foot Ankle Clin. 9:455–74. vii–viii. doi: 10.1016/j.fcl.2004.05.001. DOI: 10.1016/j.fcl.2004.05.001. PMID: 15324785.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Fibular Fixation in Comminuted Distal Tibial Fractures Affecting Ankle Joint
- Comparison of Biomechanical Stability of the Ilizarov External Fixation Methods for Treatment of Tibial Pilon Fractures
- Operative Results in AO Type C3 of Tibial Pilon Fracture: Limited Internal Fixation and Hybrid External Fixation
- External Fixation and Limited Internal Fixation in AO Type C Pilon Fracture: Report of Five Cases
- Clinical Evaluation for the Tibial Pilon Fractures