Arch Hand Microsurg.
2020 Jun;25(2):128-133. 10.12790/ahm.20.0001.
Subungual Ganglion Cyst Mimicking Glomus Tumor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Dongguk University Ilsan Hospital, Dongguk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2502709
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12790/ahm.20.0001
Abstract
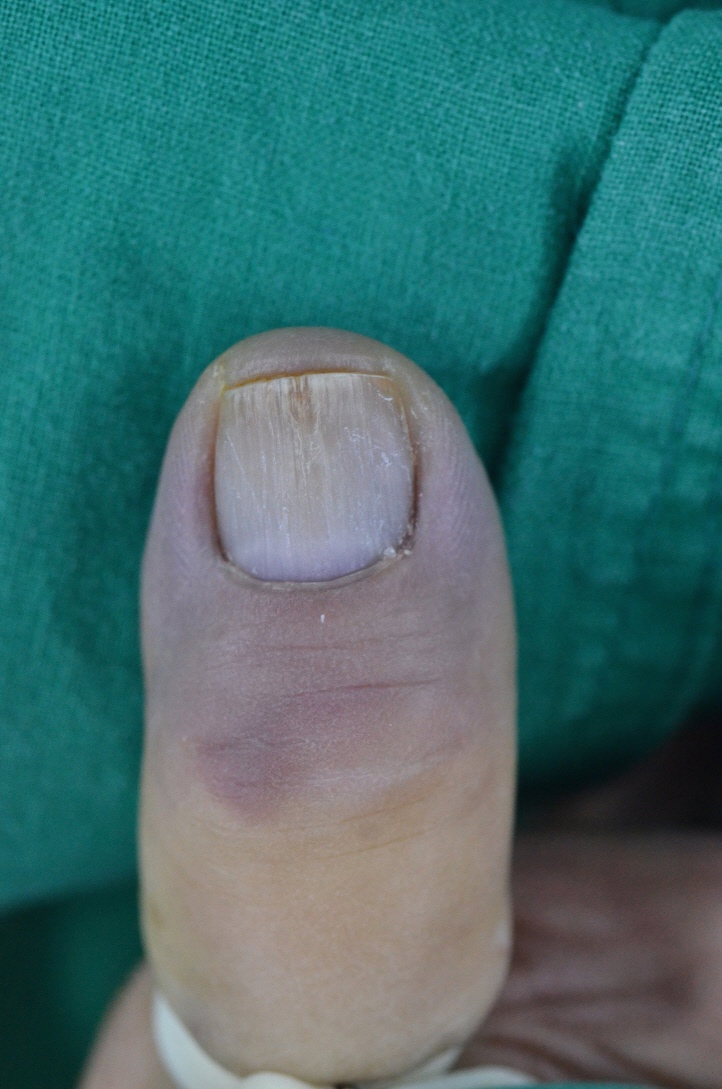
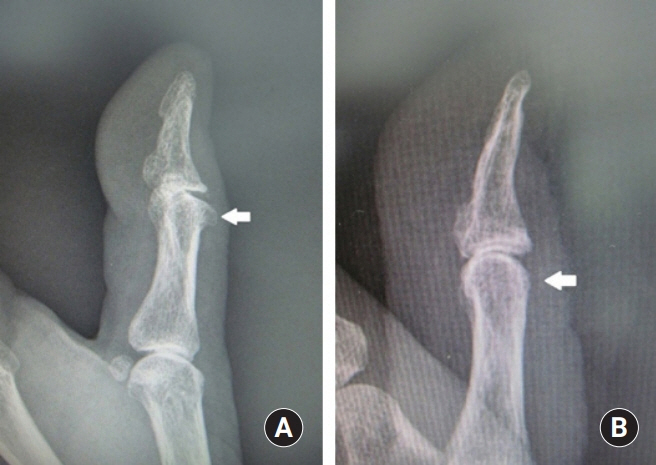
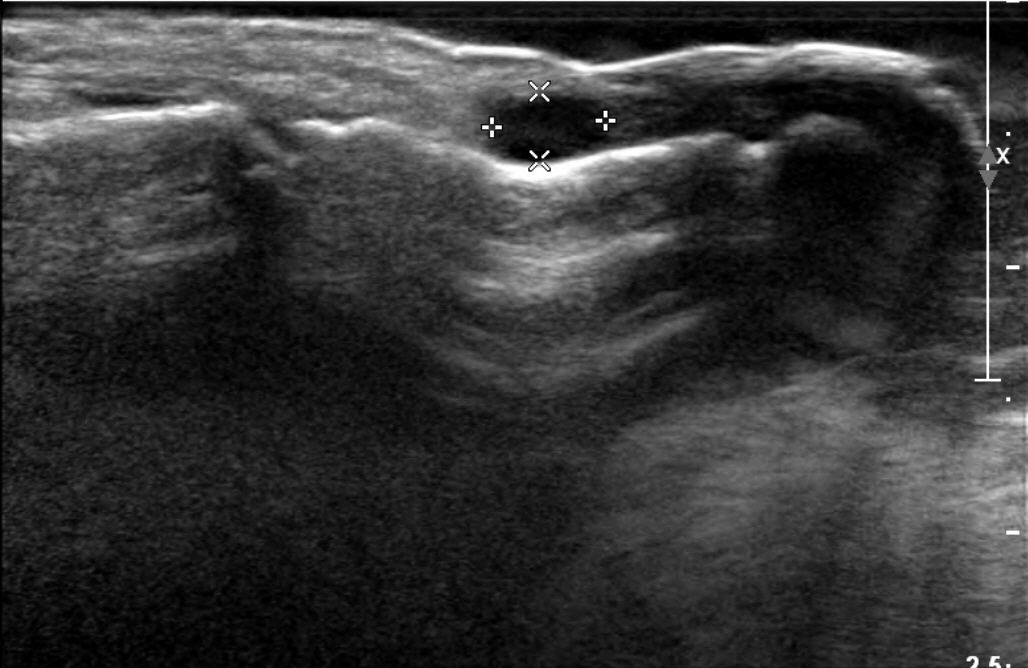
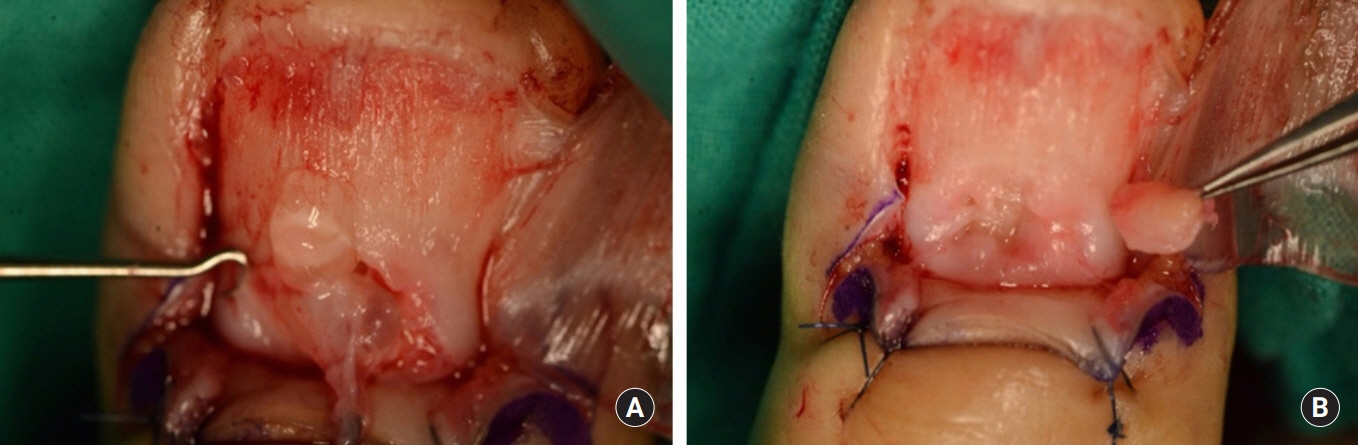
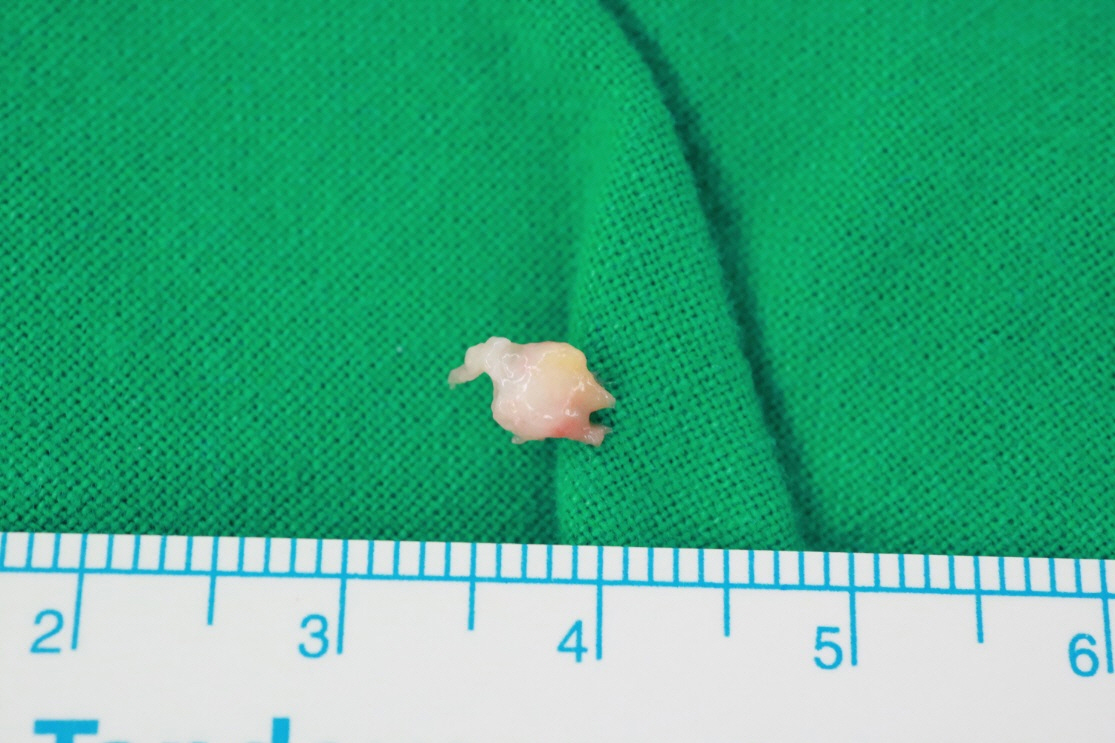
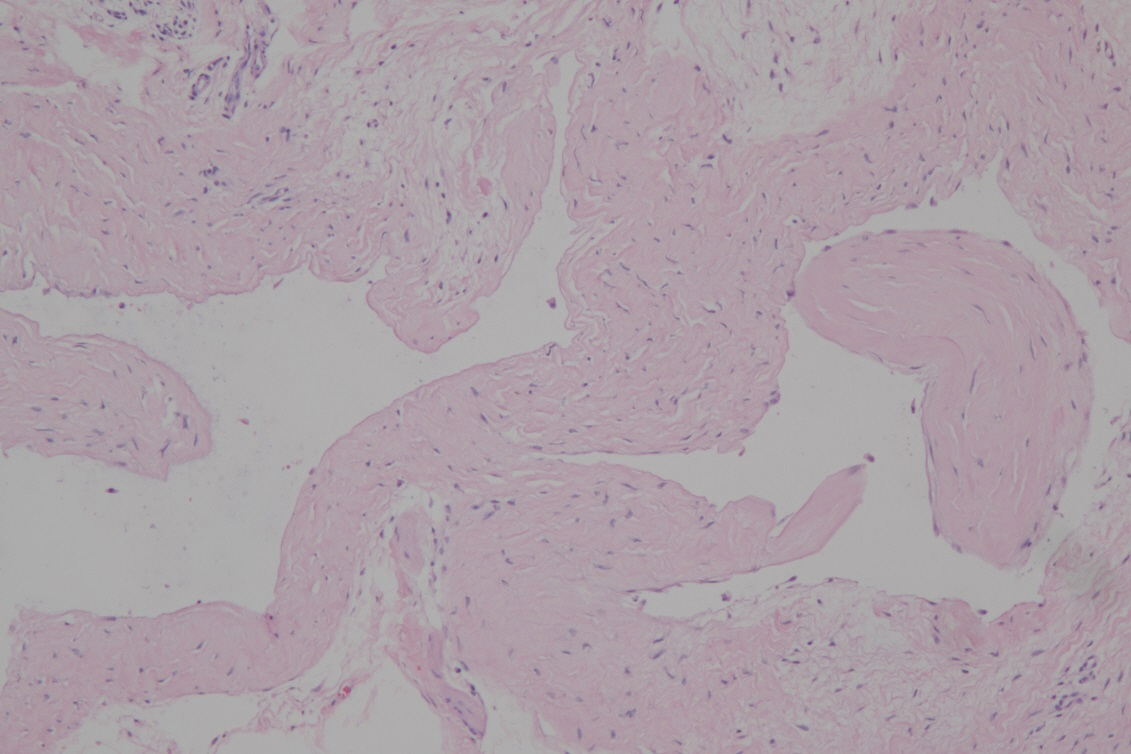
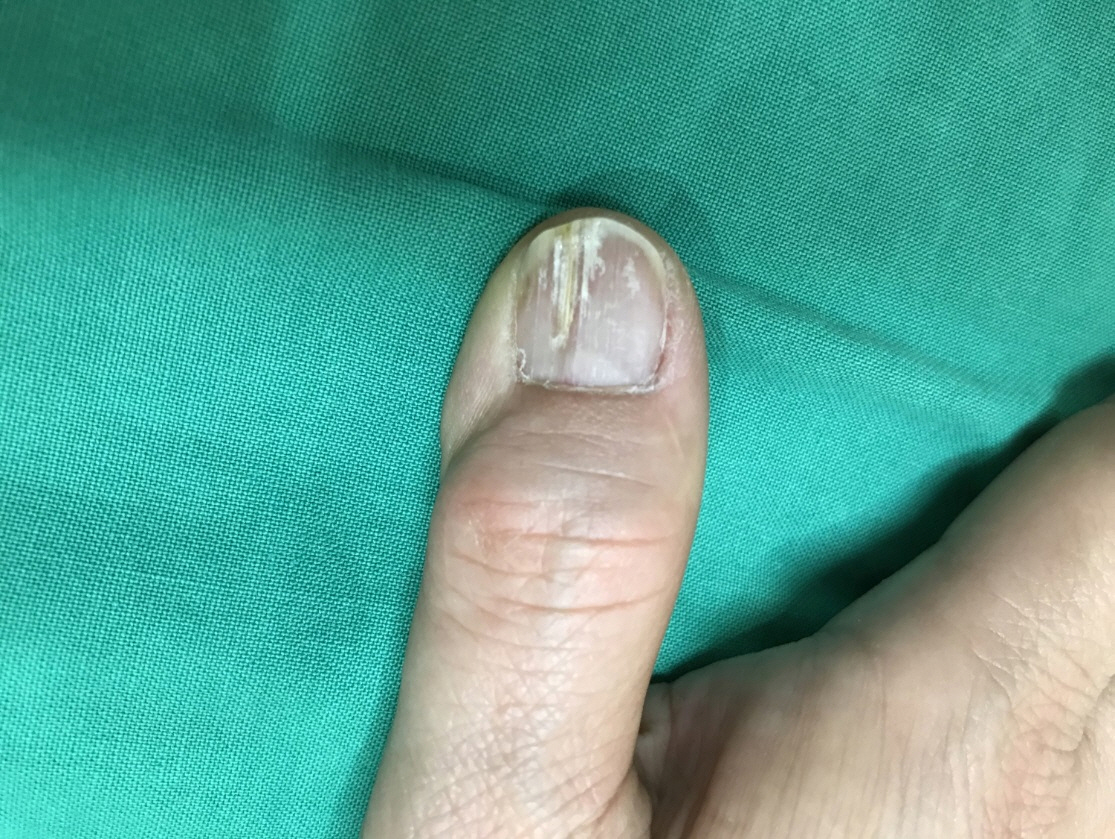
- Subungual masses accompanying nail deformity are of common occurrence and uniquely confirmed by histopathologic examination postoperatively. Although glomus tumor is most frequently diagnosed with its specific clinical triad, other rarer diagnoses have also been reported. Though ganglion cysts are predominantly found around the distal phalangeal joint as a mucous cyst and myxoid cyst, they might also appear as a subungual mass accompanied by nail deformity thereby mimicking the glomus tumor. A 54-year-old woman visited our outpatient clinic with nail deformity and pain on the tip of the right thumb. She had a history of nail root injury on her right thumb which occurred 3 months back at a nail shop. Physical examination revealed a convex point with tenderness on the right thumbnail. Doppler ultrasonography revealed the presence of 0.43×0.26×0.53 cm3 sized non-specific cystic lesion with hypoechogenicity and no abnormal vascularity. Complete excision of the cyst was performed and histopathology revealed a ganglion cyst. Subungual ganglion cyst is rarely occurred and known to be usually asymptomatic. Herein, we report a case of ganglion cyst of subungual area which was mistakenly diagnosed as a glomus tumor preoperatively.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Morey VM, Garg B, Kotwal PP. Glomus tumours of the hand: review of literature. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2016; 7:286–91.
Article2. Chiang YP, Hsu CY, Lien WC, Chang YJ. Ultrasonographic appearance of subungual glomus tumors. J Clin Ultrasound. 2014; 42:336–40.
Article3. de Berker D, Goettman S, Baran R. Subungual myxoid cysts: clinical manifestations and response to therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2002; 46:394–8.
Article4. Dooley TP, Kindt KE, Baratz ME. Subungual tumors. Hand (N Y). 2012; 7:252–8.
Article5. Willard KJ, Cappel MA, Kozin SH, Abzug JM. Benign subungual tumors. J Hand Surg Am. 2012; 37:1276–86.
Article6. Whitehouse HJ, Urwin R, Stables G. Traumatic subungual neuroma. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2018; 43:65–6.
Article7. Brown RE, Zook EG, Russell RC, Kucan JO, Smoot EC. Fingernail deformities secondary to ganglions of the distal interphalangeal joint (mucous cysts). Plast Reconstr Surg. 1991; 87:718–25.
Article8. Ham KW, Yun IS, Tark KC. Glomus tumors: symptom variations and magnetic resonance imaging for diagnosis. Arch Plast Surg. 2013; 40:392–6.
Article9. Giard MC, Pineda C. Ganglion cyst versus synovial cyst? Ultrasound characteristics through a review of the literature. Rheumatol Int. 2015; 35:597–605.
Article10. Tomoda T, Ono T, Ohyama K, Kojo Y. Subungual myxoid cyst producing an ulcer in the nail plate. J Dermatol. 1982; 9:451–4.
Article11. Guero S, Guichard S, Fraitag SR. Ligamentary structure of the base of the nail. Surg Radiol Anat. 1994; 16:47–52.
Article