Korean J Sports Med.
2020 Jun;38(2):78-84. 10.5763/kjsm.2020.38.2.78.
Comparison of Changes in Glucose and Lipid Parameters Associated with Three Types of Long-Distance Running
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Clinical Laboratory Science, Shinsung University, Dangjin, Korea
- 2Department of Exercise Rehabilitation Welfare, Sungshin Women’s University, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2502519
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5763/kjsm.2020.38.2.78
Abstract
- Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate biochemical markers of blood glucose and blood lipids associated with extreme long-distance running races (marathon, 100 km, 308 km).
Methods
The participants were 45 middle-aged male runners: 15 corresponding to each distance. All participants performed graded exercise tests before the races. Blood glucose, total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels were analyzed by blood collection before and after the races to identify differences between the groups and before and after the races.
Results
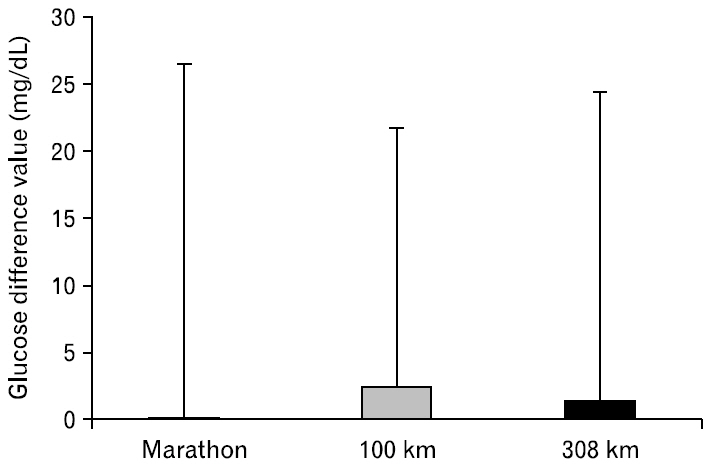
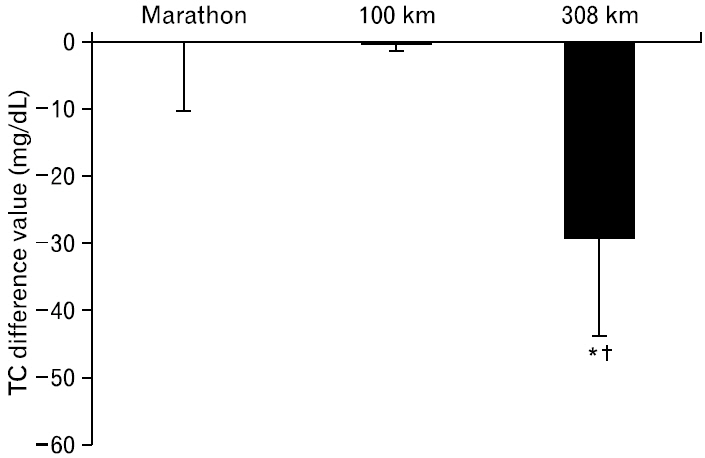
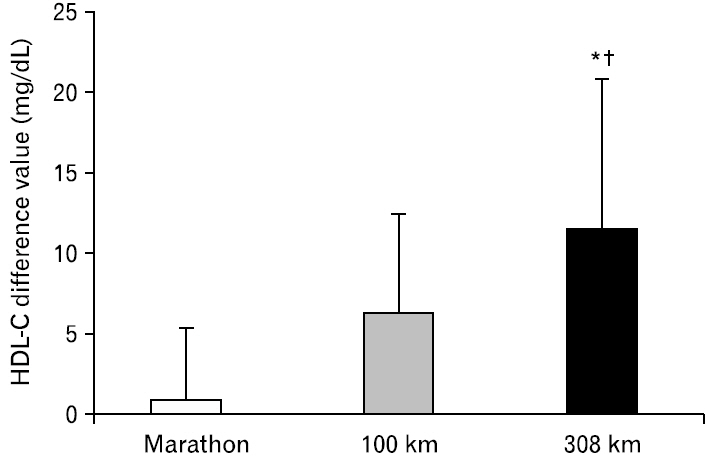
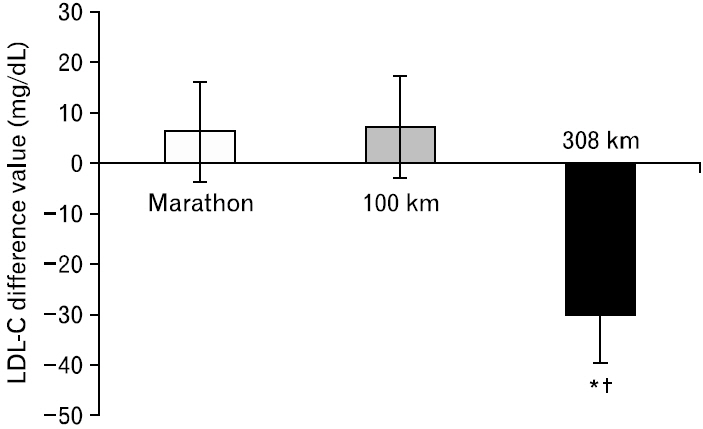
No differences were found in blood glucose levels before and after all races, as well as between the groups. TC levels decreased only after the 308-km race, and this decrease was lower than the differences after the marathon and 100-km races. TG levels decreased after all three races and were lower after the 100-km and 308-km races than that after the marathon race. HDL-C levels showed no differences after the marathon race but increased after the 100-km and 308-km races, with higher levels after the 308-km race than those after the marathon and 100-km races. LDL-C levels increased after the marathon race, but decreased after the 308-km race, with lower levels after the 308-km race than those after the marathon and 100-km races.
Conclusion
The 308-km race was associated with decreases in TC, TG, and LDL-C levels and an increase in HDL-C levels, indicating that exercise time may have a positive effect on lipid metabolism rather than exercise intensity.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Myers J, Prakash M, Froelicher V, Do D, Partington S, Atwood JE. 2002; Exercise capacity and mortality among men referred for exercise testing. N Engl J Med. 346:793–801. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa011858. PMID: 11893790.
Article2. West-Wright CN, Henderson KD, Sullivan-Halley J, et al. 2009; Long-term and recent recreational physical activity and survival after breast cancer: the California Teachers Study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 18:2851–9. DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-09-0538. PMID: 19843680. PMCID: PMC2783945.
Article3. Sato Y, Nagasaki M, Nakai N, Fushimi T. 2003; Physical exercise improves glucose metabolism in lifestyle-related diseases. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 228:1208–12. DOI: 10.1177/153537020322801017. PMID: 14610262.
Article4. Wiseman M. 2008; The second World Cancer Research Fund/ American Institute for Cancer Research expert report: food, nutrition, physical activity, and the prevention of cancer: a global perspective: Nutrition Society and BAPEN Medical Symposium on 'nutrition support in cancer therapy'. Proc Nutr Soc. 67:253–6. DOI: 10.1017/S002966510800712X. PMID: 18452640.5. Kim JW, Kim TU, Park TG. 2006; Effects of the marathon career on cardiac function and serum lipid in middle-aged men. Korean J Phys Educ. 45:547–57.6. Castelli WP, Cooper GR, Doyle JT, et al. 1977; Distribution of triglyceride and total, LDL and HDL cholesterol in several populations: a cooperative lipoprotein phenotyping study. J Chronic Dis. 30:147–69. DOI: 10.1016/0021-9681(77)90082-0. PMID: 191465.
Article7. Kim TH, Shin HS, Lee JK. 1998; Studies of the correlations between % body fat and physical fitness factors in girls' middle school students. Korean Soc Sports Sci. 7:199–222.8. Wu HJ, Chen KT, Shee BW, Chang HC, Huang YJ, Yang RS. 2004; Effects of 24 h ultra-marathon on biochemical and hematological parameters. World J Gastroenterol. 10:2711–4. DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i18.2711. PMID: 15309724. PMCID: PMC4572198.
Article9. Waskiewicz Z, Klapcinska B, Sadowska-Krepa E, et al. 2012; Acute metabolic responses to a 24-h ultra-marathon race in male amateur runners. Eur J Appl Physiol. 112:1679–88. DOI: 10.1007/s00421-011-2135-5. PMID: 21879351. PMCID: PMC3324692.
Article10. Gorecka M, Krzeminski K, Buraczewska M, Kozacz A, Dabrowski J, Ziemba AW. 2020; Effect of mountain ultra-marathon running on plasma angiopoietin-like protein 4 and lipid profile in healthy trained men. Eur J Appl Physiol. 120:117–25. DOI: 10.1007/s00421-019-04256-w. PMID: 31707478. PMCID: PMC6969869.
Article11. Jeukendrup AE, Saris WH, Wagenmakers AJ. 1998; Fat metabolism during exercise: a review. Part I: fatty acid mobilization and muscle metabolism. Int J Sports Med. 19:231–44. DOI: 10.1055/s-2007-971911. PMID: 9657362.
Article12. Kreider RB. 1991; Physiological considerations of ultraendurance performance. Int J Sport Nutr. 1:3–27. DOI: 10.1123/ijsn.1.1.3. PMID: 1844400.
Article13. Rapoport BI. 2010; Metabolic factors limiting performance in marathon runners. PLoS Comput Biol. 6:e1000960. DOI: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1000960. PMID: 20975938. PMCID: PMC2958805.
Article14. Suzuki K, Nakaji S, Yamada M, et al. 2003; Impact of a competitive marathon race on systemic cytokine and neutrophil responses. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 35:348–55. DOI: 10.1249/01.MSS.0000048861.57899.04. PMID: 12569227.
Article15. Trivax JE, Franklin BA, Goldstein JA, et al. 2010; Acute cardiac effects of marathon running. J Appl Physiol (1985). 108:1148–53. DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.01151.2009. PMID: 20150567.
Article16. Dill DB, Costill DL. 1974; Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol. 37:247–8. DOI: 10.1152/jappl.1974.37.2.247. PMID: 4850854.
Article17. Yoon YH. 2004; The effect of Taekwondo competition on serum metabolites. Korea Sport Res. 15:1651–58.18. Shin KA, Kim YJ. 2012; Comparison of the muscle damage and liver function in ultra-marathon race (100 km) by sections. J Exp Biomed Sci. 18:276–82.19. Shin KA, Kim YJ. 2017; Acute variation of hematological parameters during 622 km ultra-marathon. Biomed Sci Lett. 23:208–14. DOI: 10.15616/BSL.2017.23.3.208.
Article20. Klapcinska B, Waskiewicz Z, Chrapusta SJ, Sadowska-Krepa E, Czuba M, Langfort J. 2013; Metabolic responses to a 48-h ultra-marathon run in middle-aged male amateur runners. Eur J Appl Physiol. 113:2781–93. DOI: 10.1007/s00421-013-2714-8. PMID: 24002469. PMCID: PMC3824198.
Article21. Upton SJ, Hagan RD, Lease B, Rosentswieg J, Gettman LR, Duncan JJ. 1984; Comparative physiological profiles among young and middle-aged female distance runners. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 16:67–71. DOI: 10.1249/00005768-198401000-00014. PMID: 6708782.
Article22. Keul J, Kohler B, von Glutz G, Luthi U, Berg A, Howald H. 1981; Biochemical changes in a 100 km run: carbohydrates, lipids, and hormones in serum. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 47:181–9. DOI: 10.1007/BF00421670. PMID: 7026231.
Article23. Fallon KE, Sivyer G, Sivyer K, Dare A. 1999; The biochemistry of runners in a 1600 km ultramarathon. Br J Sports Med. 33:264–9. DOI: 10.1136/bjsm.33.4.264. PMID: 10450482. PMCID: PMC1756186.
Article24. Kratz A, Lewandrowski KB, Siegel AJ, et al. 2002; Effect of marathon running on hematologic and biochemical laboratory parameters, including cardiac markers. Am J Clin Pathol. 118:856–63. DOI: 10.1309/14TY-2TDJ-1X0Y-1V6V. PMID: 12472278.
Article25. Vukovich MD, Costill DL, Hickey MS, Trappe SW, Cole KJ, Fink WJ. 1993; Effect of fat emulsion infusion and fat feeding on muscle glycogen utilization during cycle exercise. J Appl Physiol (1985). 75:1513–8. DOI: 10.1152/jappl.1993.75.4.1513. PMID: 8282597.
Article26. Lippi G, Schena F, Montagnana M, Salvagno GL, Banfi G, Guidi GC. 2011; Significant variation of traditional markers of liver injury after a half-marathon run. Eur J Intern Med. 22:e36–8. DOI: 10.1016/j.ejim.2011.02.007. PMID: 21925040.
Article27. Shin KA, Kim YJ. 2018; Effect of extreme long-distance running on hepatic metabolism and renal function in middle-aged men. Biomed Sci Lett. 24:411–7. DOI: 10.15616/BSL.2018.24.4.411.
Article28. Fahlman MM, Boardley D, Lambert CP, Flynn MG. 2002; Effects of endurance training and resistance training on plasma lipoprotein profiles in elderly women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 57:B54–60. DOI: 10.1093/gerona/57.2.B54. PMID: 11818424.
Article29. Arakawa K, Hosono A, Shibata K, et al. 2016; Changes in blood biochemical markers before, during, and after a 2-day ultramarathon. Open Access J Sports Med. 7:43–50. DOI: 10.2147/OAJSM.S97468. PMID: 27186145. PMCID: PMC4847591.
Article30. Burke LM. 2007; Nutrition strategies for the marathon: fuel for training and racing. Sports Med. 37:344–7. DOI: 10.2165/00007256-200737040-00018. PMID: 17465604.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Intensive Long Distance Running as a Possible Cause of Multiple Splanchnic Arterial Aneurysms: A Case Report
- Surgical Resection of Intermetatarsal Coalition of the Fourth and Fifth Founded in Long Distance Running
- Topographical Relationship of the Superficial Temporal Vessels and the Auriculotemporal Nerve
- Types of Patients during a Marathon Course: Two International Scale of Marathon Runnings
- The effect of regular physical exercise on glucose uptake in soleus and intravenous glucose tolerance in streptozotocin diabetic rats