J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2020 Mar;63(2):237-247. 10.3340/jkns.2019.0172.
Comparative Analysis of Surgical Outcomes of C1–2 Fusion Spine Surgery between Intraoperative Computed Tomography Image Based Navigation-Guided Operation and Fluoroscopy-Guided Operation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- 2Research Institute for Convergence of Biomedical Science and Technology, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- 3Department of Neurosurgery, School of Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Yangsan, Korea
- KMID: 2501710
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2019.0172
Abstract
Objective
: Fixation of the C1–2 segment is challenging because of the complex anatomy in the region and the need for a high degree of accuracy to avoid complications. Preoperative 3D-computed tomography (CT) scans can help reduce the risk of complications in the vertebral artery, spinal cord, and nerve roots. However, the patient may be susceptible to injury if the patient’s anatomy does not match the preoperative CT scans. The intraoperative 3D image-based navigation systems have reduced complications in instrument-assisted techniques due to greater accuracy. This study aimed to compare the radiologic outcomes of C1–2 fusion surgery between intraoperative CT image-guided operation and fluoroscopy-guided operation.
Methods
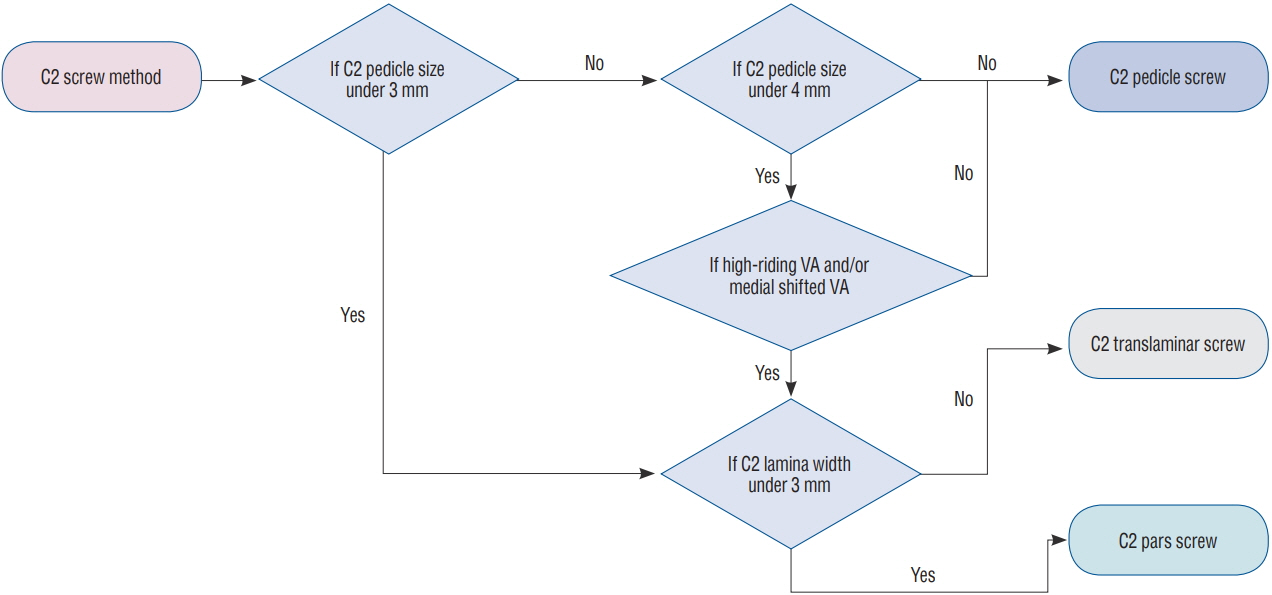
: We retrospectively reviewed the radiologic images of 34 patients who underwent C1–2 fusion spine surgery from January 2009 to November 2018 at our hospital. We assessed 17 cases each of degenerative cervical disease and trauma in a study population of 18 males and 16 females. The mean age was 54.8 years. A total of 139 screws were used and the surgical procedures included 68 screws in the C1 lateral mass, 58 screws in C2 pedicle, nine screws in C2 lamina and C2 pars screws, four lateral mass screws in sub-axial level. Of the 34 patients, 19 patients underwent screw insertion using intraoperative mobile CT. Other patients underwent atlantoaxial fusion with a standard fluoroscopy-guided device.
Results
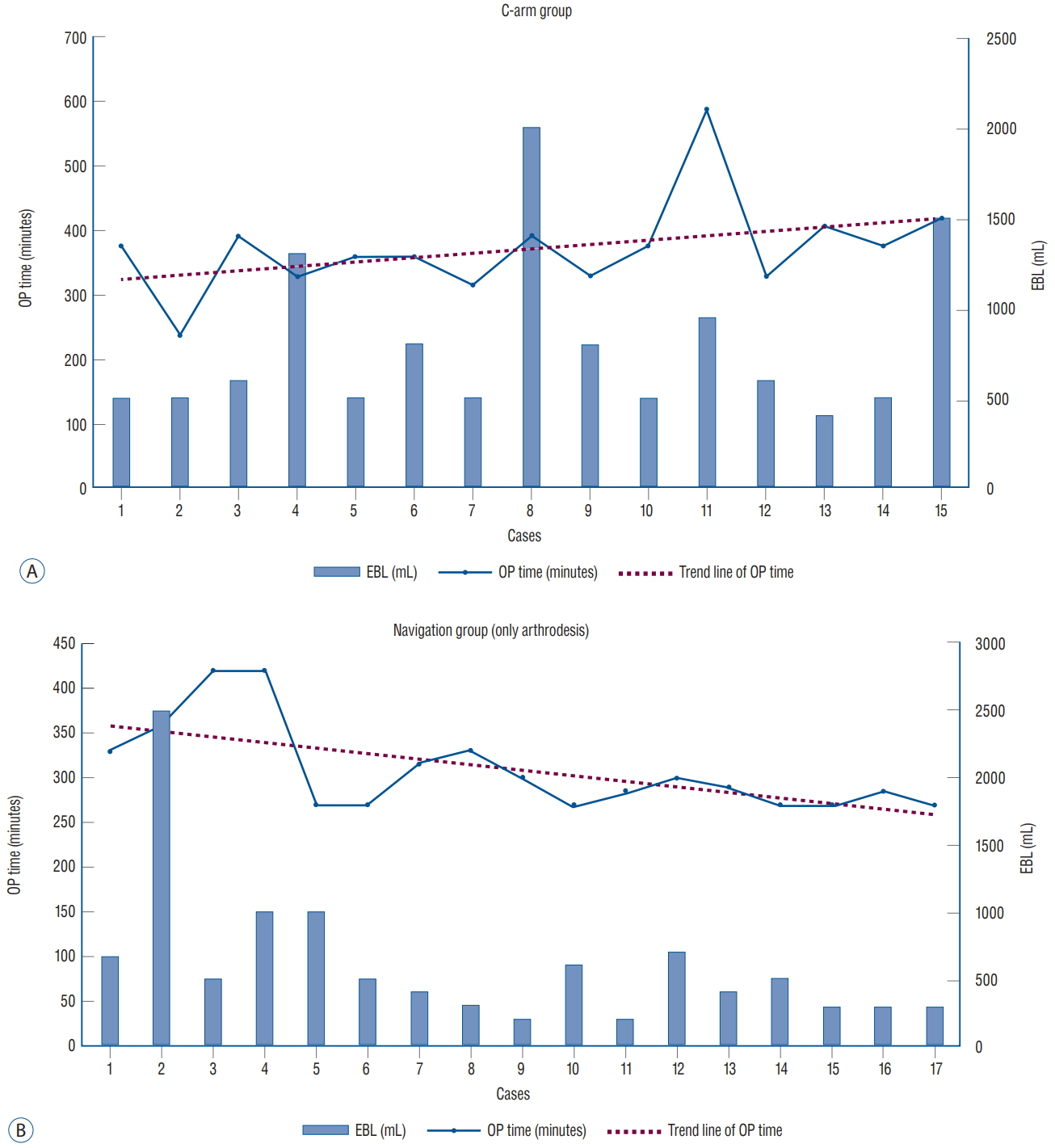
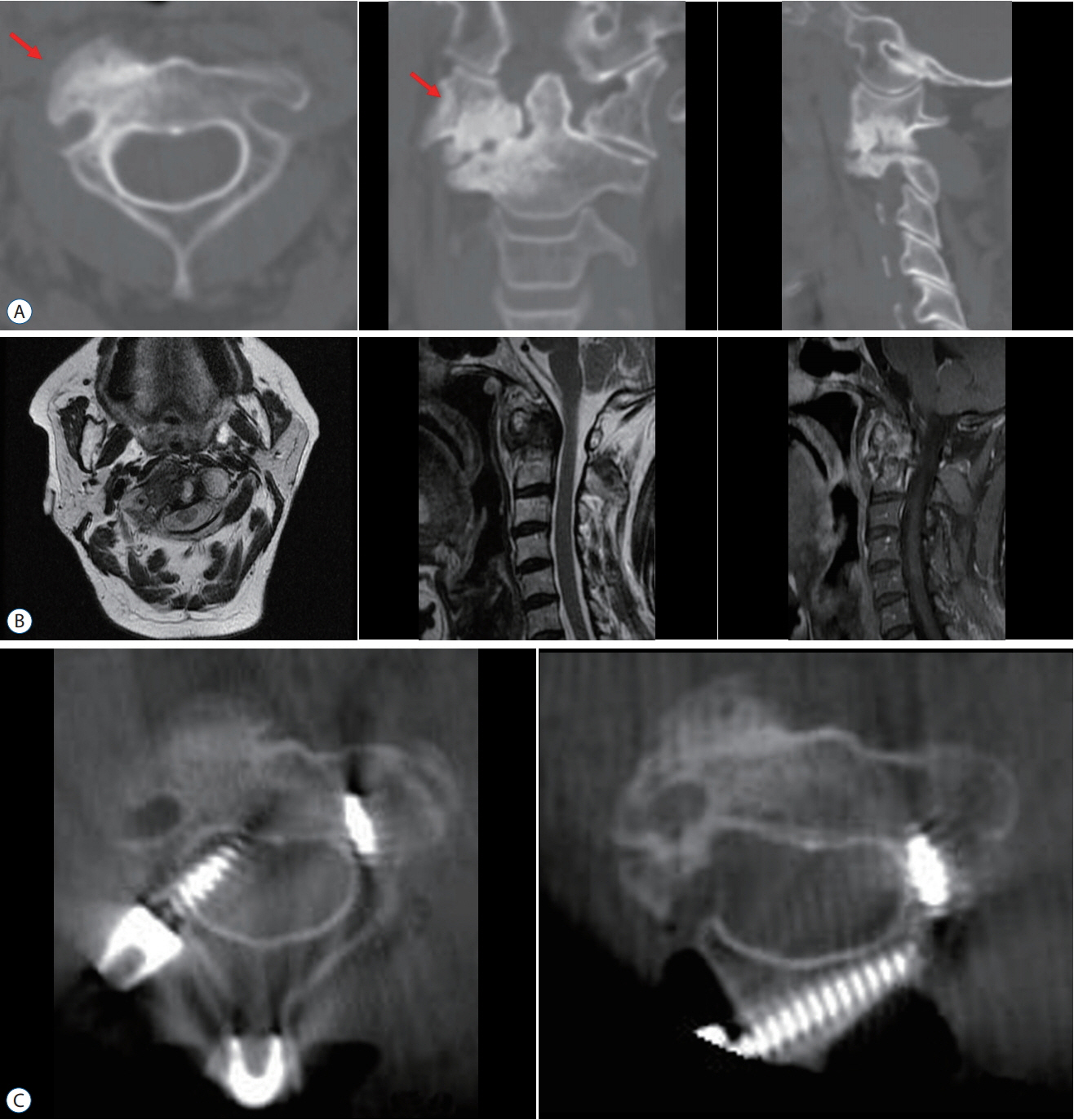
: A total of 139 screws were correctly positioned. We analyzed the positions of 135 screws except for the four screws that performed the lateral mass screws in C3 vertebra. Minor screw penetration was observed in seven cases (5.2%), and major pedicle screw penetration was observed in three cases (2.2%). In one case, the malposition of a C2 pedicle screw was confirmed, which was subsequently corrected. There were no complications regarding vertebral artery injury or onset of new neurologic deficits. The screw malposition rate was lower (5.3%) in patients who underwent intraoperative CT-based navigation than that for fluoroscopy-guided cases (10.2%). And we confirmed that the operation time can be significantly reduced by surgery using intraoperative O-arm device.
Conclusion
: Spinal navigation using intraoperative cone-beam CT scans is reliable for posterior fixation in unstable C1-2 pathologies and can be reduced the operative time.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Current Concepts in the Treatment of Traumatic C2 Vertebral Fracture : A Literature Review
Subum Lee, Junseok W Hur, Younggyu Oh, Sungjae An, Gi-Yong Yun, Jae-Min Ahn
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2024;67(1):6-13. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2023.0098.
Reference
-
References
1. Abdullah KG, Bishop FS, Lubelski D, Steinmetz MP, Benzel EC, Mroz TE. Radiation exposure to the spine surgeon in lumbar and thoracolumbar fusions with the use of an intraoperative computed tomographic 3-dimensional imaging system. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 37:E1074–E1078. 2012.
Article2. Costa F, Ortolina A, Attuati L, Cardia A, Tomei M, Riva M, et al. Management of C1-2 traumatic fractures using an intraoperative 3D imaging-based navigation system. J Neurosurg Spine. 22:128–133. 2015.
Article3. Gertzbein SD, Robbins SE. Accuracy of pedicular screw placement in vivo. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 15:11–14. 1990.
Article4. Goel A, Laheri V. Plate and screw fixation for atlanto-axial subluxation. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 129:47–53. 1994.
Article5. Harms J, Melcher RP. Posterior C1-C2 fusion with polyaxial screw and rod fixation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 26:2467–2471. 2001.
Article6. Hitti FL, Hudgins ED, Chen HI, Malhotra NR, Zager EL, Schuster JM. Intraoperative navigation is associated with reduced blood loss during C1-C2 posterior cervical fixation. World Neurosurg. 107:574–578. 2017.
Article7. Hlubek RJ, Bohl MA, Cole TS, Morgan CD, Xu DS, Chang SW, et al. Safety and accuracy of freehand versus navigated C2 pars or pedicle screw placement. Spine J. 18:1374–1381. 2018.
Article8. Hur JW, Kim JS, Ryu KS, Shin MH. Accuracy and safety in screw placement in the high cervical spine: retrospective analysis of O-arm-based navigation-assisted C1 lateral mass and C2 pedicle screws. Clin Spine Surg. 32:193–199. 2019.9. Jacobs C, Roessler PP, Scheidt S, Plöger MM, Jacobs C, Disch AC, et al. When does intraoperative 3D-imaging play a role in transpedicular C2 screw placement? Injury. 48:2522–2528. 2017.
Article10. Lee SH, Park DH, Kim SD, Huh DS, Kim KT. Analysis of 3-dimensional course of the intra-axial vertebral artery for C2 pedicle screw trajectory: a computed tomographic study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:E1010–E1014. 2014.11. Mandel IM, Kambach BJ, Petersilge CA, Johnstone B, Yoo JU. Morphologic considerations of C2 isthmus dimensions for the placement of transarticular screws. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 25:1542–1547. 2000.
Article12. Neo M, Sakamoto T, Fujibayashi S, Nakamura T. The clinical risk of vertebral artery injury from cervical pedicle screws inserted in degenerative vertebrae. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30:2800–2805. 2005.
Article13. Smith JD, Jack MM, Harn NR, Bertsch JR, Arnold PM. Screw placement accuracy and outcomes following O-arm-navigated atlantoaxial fusion: a feasibility study. Global Spine J. 6:344–349. 2016.
Article14. Wakao N, Takeuchi M, Nishimura M, Riew KD, Kamiya M, Hirasawa A, et al. Vertebral artery variations and osseous anomaly at the C1-2 level diagnosed by 3D CT angiography in normal subjects. Neuroradiology. 56:843–849. 2014.
Article15. Yeom JS, Buchowski JM, Kim HJ, Chang BS, Lee CK, Riew KD. Risk of vertebral artery injury: comparison between C1-C2 transarticular and C2 pedicle screws. Spine J. 13:775–785. 2013.
Article16. Yukawa Y, Kato F, Ito K, Horie Y, Hida T, Nakashima H, et al. Placement and complications of cervical pedicle screws in 144 cervical trauma patients using pedicle axis view techniques by fluoroscope. Eur Spine J. 18:1293–1299. 2009.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparative Analysis of Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion at a Single Level: Free-Hand Versus Navigation-Guided Approaches
- Atlantoaxial Stabilization Using C1 Lateral Mass and C2 Pedicle/Translaminar Screw Fixation by Intraoperative C1- and C2-Direct-Captured Navigation with Preoperative Computed Tomography Images
- Comparative Prospective Study Reporting Intraoperative Parameters, Pedicle Screw Perforation, and Radiation Exposure in Navigation-Guided versus Non-navigated Fluoroscopy-Assisted Minimal Invasive Transforaminal Lumbar Interbody Fusion
- Accuracy and Safety in Pedicle Screw Placement in the Thoracic and Lumbar Spines : Comparison Study between Conventional C-Arm Fluoroscopy and Navigation Coupled with O-Arm(R) Guided Methods
- The Clinical Experience of Computed Tomographic-Guided Navigation System in C1-2 Spine Instrumentation Surgery