Radiographic and Clinical Outcomes Following Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy : Minimum 2-Year Follow-Up Data
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Spine Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
- KMID: 2501697
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2018.0170
Abstract
Objective
: The purpose of this study was to report the results of pedicle subtraction osteotomy (PSO) for fixed sagittal imbalance with a minimum 2-year follow-up. Besides, authors evaluated the effect of adjunctive multi-level posterior column osteotomy (PCO) on achievement of additional lumbar lordosis (LL) during PSO.
Methods
: A total of 31 consecutive patients undergoing PSO for fixed sagittal imbalance were enrolled and analyzed. Correction angle of osteotomized vertebra (PSO angle) and other radiographic parameters including pelvic incidence (PI), thoracic kyphosis, LL, and sagittal vertical axis (SVA) were evaluated. Clinical outcomes and surgical complications were also assessed.
Results
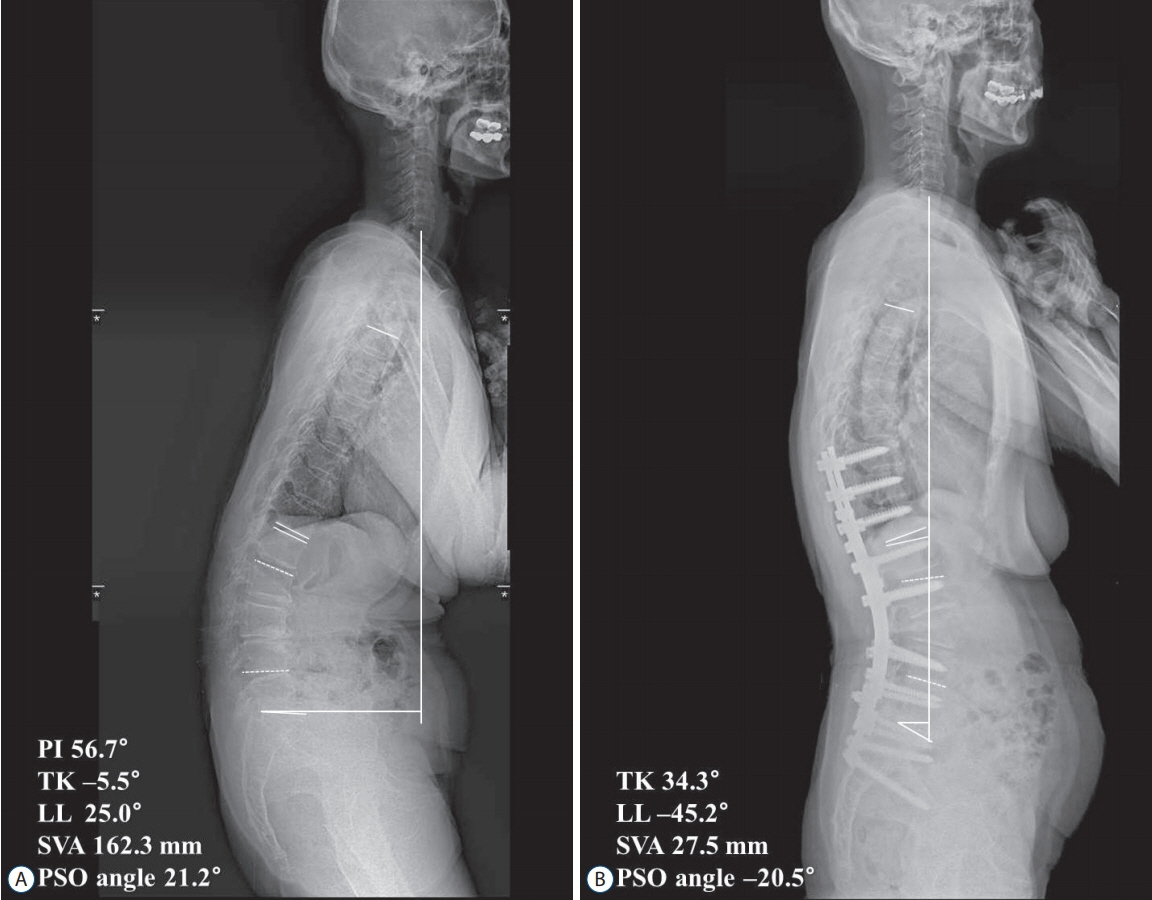
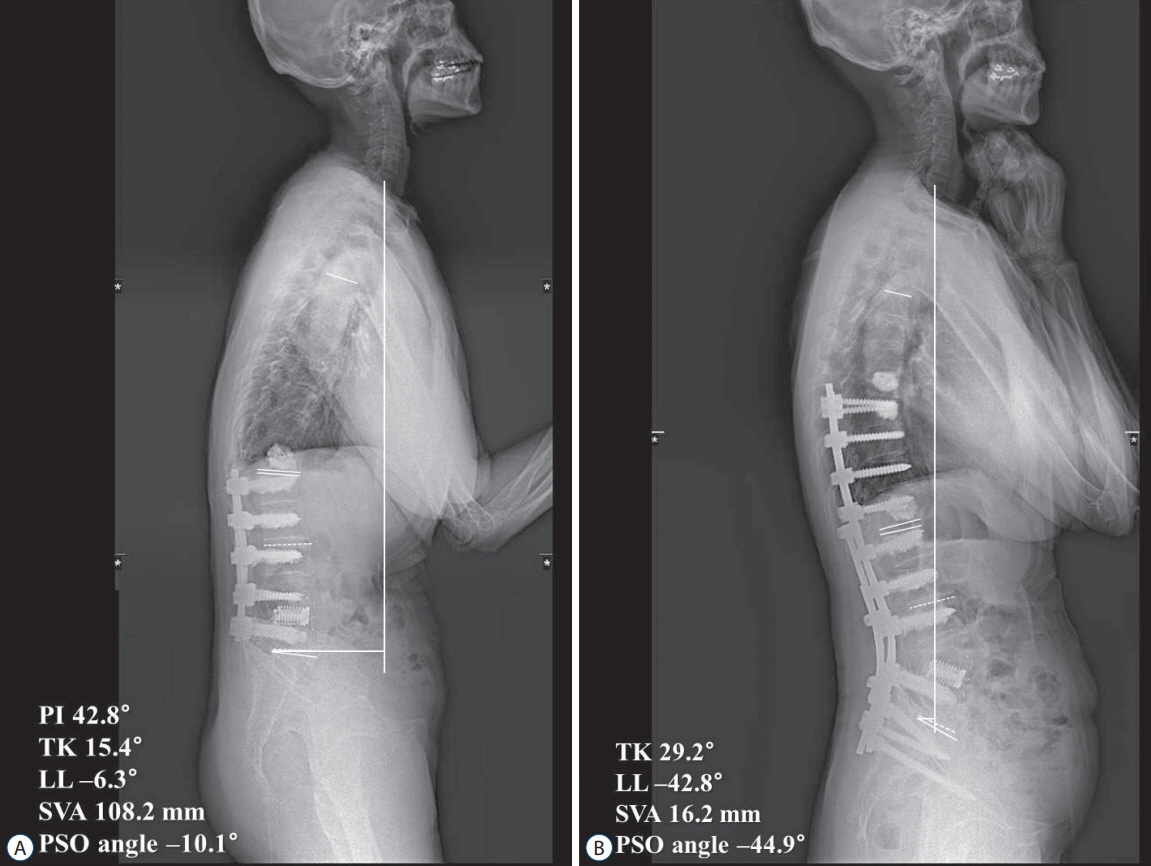
: The mean age was 66.0±9.3 years with a mean follow-up period of 33.2±10.5 months. The mean number of fused segments was 9.6±3.5. The mean operative time and surgical bleeding were 475.9±160.5 minutes and 1406.1±932.1 mL, respectively. The preoperative SRS-22 score was 2.3±0.7 and improved to 3.2±0.8 at the final follow-up. The mean PI was 54.5±9.5°. LL was changed from 7.0±28.9° to -50.2±13.2°. The PSO angle was 33.7±13.5° (15.6±20.1° preoperatively, -16.1±19.4° postoperatively). The difference of correction angle of LL (57.3°) was greater about 23.6° than which of PSO angle (33.7°). SVA was improved from 189.5±93.0 mm, preoperatively to 12.4±40.8 mm, postoperatively. There occurred six, eight, and 14 cases of complications at intraoperative, early (<2 weeks) postoperative, and late (≥2 weeks) postoperative period, respectively. Additional operations were needed in nine patients due to the complications.
Conclusion
: PSO could provide satisfactory results for patients with fixed sagittal imbalance regarding clinical and radiographic outcomes. Additional correction of LL could be achieved with conduction of adjunctive multi-level PCOs during PSO.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 4 articles
-
The Fate of Proximal Junctional Vertebral Fractures after Long-Segment Spinal Fixation : Are There Predictable Radiologic Characteristics for Revision surgery?
Hyun Jun Jang, Jeong Yoon Park, Sung Uk Kuh, Dong Kyu Chin, Keun Su Kim, Yong Eun Cho, Bang Sang Hahn, Kyung Hyun Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2021;64(3):437-446. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2020.0236.Systematic Review of Reciprocal Changes after Spinal Reconstruction Surgery : Do Not Miss the Forest for the Trees
Chang-Wook Kim, Seung-Jae Hyun, Ki-Jeong Kim
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2021;64(6):843-852. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2020.0234.Partial Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy for Patients with Thoracolumbar Fractures : Comparative Study between Burst Fracture and Posttraumatic Kyphosis
Ho Yong Choi, Dae Jean Jo
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2022;65(1):64-73. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2021.0069.Pediatric Spine Trauma
Sungjae An, Seung-Jae Hyun
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2022;65(3):361-369. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2021.0282.
Reference
-
References
1. Alzakri A, Boissière L, Cawley DT, Bourghli A, Pointillart V, Gille O, et al. L5 pedicle subtraction osteotomy: indication, surgical technique and specificities. Eur Spine J. 27:644–651. 2018.
Article2. Auerbach JD, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Sehn JK, Milby AH, Bumpass D, et al. Major complications and comparison between 3-column osteotomy techniques in 105 consecutive spinal deformity procedures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 37:1198–1210. 2012.
Article3. Bae J, Lee SH. Minimally invasive spinal surgery for adult spinal deformity. Neurospine. 15:18–24. 2018.
Article4. Bridwell KH. Decision making regarding Smith-Petersen vs. pedicle subtraction osteotomy vs. vertebral column resection for spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 31(19 Suppl):S171–S178. 2006.
Article5. Bridwell KH, Lewis SJ, Lenke LG, Baldus C, Blanke K. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the treatment of fixed sagittal imbalance. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 85-A:454–463. 2003.
Article6. Buchowski JM, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Kuhns CA, Lehman RA Jr, Kim YJ, et al. Neurologic complications of lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy: a 10-year assessment. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 32:2245–2252. 2007.7. Choi HY, Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, Kim HJ. Effectiveness and safety of tranexamic acid in spinal deformity surgery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 60:75–81. 2017.
Article8. Choi HY, Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, Kim HJ. Freehand S2 alar-iliac screw placement using K-wire and cannulated screw : technical case series. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 61:75–80. 2018.
Article9. Choi HY, Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, Kim HJ. Surgical and radiographic outcomes after pedicle subtraction osteotomy according to surgeon’s experience. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 42:E795–E801. 2017.
Article10. Daubs MD, Brodke DS, Annis P, Lawrence BD. Perioperative complications of pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Global spine J. 6:630–635. 2016.
Article11. Dickson DD, Lenke LG, Bridwell KH, Koester LA. Risk factors for and assessment of symptomatic pseudarthrosis after lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:1190–1195. 2014.
Article12. Eskilsson K, Sharma D, Johansson C, Hedlund R. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy: a comprehensive analysis in 104 patients. Does the cause of deformity influence the outcome? J Neurosurg Spine. 27:56–62. 2017.13. Glassman SD, Bridwell K, Dimar JR, Horton W, Berven S, Schwab F. The impact of positive sagittal balance in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 30:2024–2029. 2005.
Article14. Gum JL, Carreon LY, Buchowski JM, Lenke LG, Glassman SD. Utilization trends of pedicle subtraction osteotomies compared to posterior spinal fusion for deformity: a national database analysis between 2008-2011. Scoliosis Spinal Disord. 11:25. 2016.
Article15. Gupta MC, Ferrero E, Mundis G, Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Schwab F, et al. Pedicle subtraction osteotomy in the revision versus primary adult spinal deformity patient: is there a difference in correction and complications? Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 40:E1169–E1175. 2015.16. Han S, Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, Kim HJ, Lee BH, et al. Multilevel posterior column osteotomies are not inferior for the correction of rigid adult spinal deformity compared with pedicle subtraction osteotomy. World Neurosurg. 107:839–845. 2017.
Article17. Hyun SJ, Lee BH, Park JH, Kim KJ, Jahng TA, Kim HJ. Proximal junctional kyphosis and proximal junctional failure following adult spinal deformity surgery. Korean J Spine. 14:126–132. 2017.
Article18. Hyun SJ, Lenke LG, Kim YC, Koester LA, Blanke KM. Comparison of standard 2-rod constructs to multiple-rod constructs for fixation across 3-column spinal osteotomies. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:1899–1904. 2014.
Article19. Hyun SJ, Rhim SC. Clinical outcomes and complications after pedicle subtraction osteotomy for fixed sagittal imbalance patients : a long-term follow-up data. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 47:95–101. 2010.
Article20. Kim HJ, Boachie-Adjei O, Shaffrey CI, Schwab F, Lafage V, Bess S, et al. Upper thoracic versus lower thoracic upper instrumented vertebrae endpoints have similar outcomes and complications in adult scoliosis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 39:E795–E799. 2014.
Article21. Kim HJ, Iyer S. Proximal junctional kyphosis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 24:318–326. 2016.
Article22. Kim JS, Kim SM. Surgical outcomes of post-fusion lumbar flatback deformity with sagittal imbalance. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 59:615–621. 2016.
Article23. Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Cheh G, Baldus C. Results of lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomies for fixed sagittal imbalance: a minimum 5-year follow-up study. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 32:2189–2197. 2007.
Article24. Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, Glattes CR, Rhim S, Cheh G. Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity after segmental posterior spinal instrumentation and fusion: minimum five-year follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 33:2179–2184. 2008.
Article25. Makhni MC, Shillingford JN, Laratta JL, Hyun SJ, Kim YJ. Restoration of sagittal balance in spinal deformity surgery. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 61:167–179. 2018.
Article26. Moon JW, Shinn JK, Ryu D, Oh SY, Shim YS, Yoon SH. Pelvic incidence can be changed not only by age and sex, but also by posture used during imaging. Korean J Spine. 14:77–83. 2017.
Article27. Ohrt-Nissen S, Dahl B, Gehrchen M. Choice of rods in surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis: what are the clinical implications of biomechanical properties? - a review of the literature. Neurospine. 15:123–130. 2018.
Article28. Popa I, Oprea M, Andrei D, Mercedesz P, Mardare M, Poenaru DV. Utility of the pedicle subtraction osteotomy for the correction of sagittal spine imbalance. Int Orthop. 40:1219–1225. 2016.
Article29. Scheer JK, Lafage V, Smith JS, Deviren V, Hostin R, McCarthy IM, et al. Maintenance of radiographic correction at 2 years following lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy is superior with upper thoracic compared with thoracolumbar junction upper instrumented vertebra. Eur Spine J 24 Suppl. 1:S121–S130. 2015.30. Smith JS, Shaffrey CI, Klineberg E, Lafage V, Schwab F, Lafage R, et al. Complication rates associated with 3-column osteotomy in 82 adult spinal deformity patients: retrospective review of a prospectively collected multicenter consecutive series with 2-year follow-up. J Neurosurg Spine. 27:444–457. 2017.
Article31. Wang MY, Berven SH. Lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy. Neurosurgery. 60(2 Suppl 1):ONS140-ONS146; discussion ONS146, 2007.
Article32. Yagi M, King AB, Boachie-Adjei O. Incidence, risk factors, and natural course of proximal junctional kyphosis: surgical outcomes review of adult idiopathic scoliosis. Minimum 5 years of follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 37:1479–1489. 2012.
Article33. Yang BP, Ondra SL, Chen LA, Jung HS, Koski TR, Salehi SA. Clinical and radiographic outcomes of thoracic and lumbar pedicle subtraction osteotomy for fixed sagittal imbalance. J Neurosurg Spine. 5:9–17. 2006.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Outcomes of Non-Operative Management for Pseudarthrosis after Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomies at Minimum 5 Years Follow-Up
- Clinical Outcomes and Complications after Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy for Fixed Sagittal Imbalance Patients : A Long-Term Follow-Up Data
- Pedicle Subtraction and Extension Wedge Osteotomy for the Correction of Fixed Kyphotic Deformity of the Lumbar Spine: Technical Note
- A Review of Complications and Outcomes following Vertebral Column Resection in Adults
- Osteotomy of the Spine to Correct the Spinal Deformity