Yeungnam Univ J Med.
2020 Jan;37(1):2-12. 10.12701/yujm.2019.00297.
Drug-induced liver injury
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, Dongguk Unversity, Gyeongju, Korea
- KMID: 2501402
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.12701/yujm.2019.00297
Abstract
- Drug-induced liver injury (DILI), including herbal and dietary supplement hepatotoxicity, is often passed lightly; however, it can lead to the requirement of a liver transplant or may even cause death because of liver failure. Recently, the American College of Gastroenterology, Chinese Society of Hepatology and European Association for the Study of the Liver guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of DILI have been established, and they will be helpful for guiding clinical treatment decisions. Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method scoring is the most commonly used method to diagnose DILI; however, it has some limitations, such as poor validity and reproducibility. Recently, studies on new biomarkers have been actively carried out, which will help diagnose DILI and predict the prognosis of DILI. It is expected that the development of new therapies such as autophagy inducers and various other technologies of the fourth industrial revolution will be applicable to DILI research.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Chalasani N, Fontana RJ, Bonkovsky HL, Watkins PB, Davern T, Serrano J, et al. Causes, clinical features, and outcomes from a prospective study of drug-induced liver injury in the United States. Gastroenterology. 2008; 135:1924–34.
Article2. Hayashi PH, Bjornsson ES. Long-term outcomes after drug-induced liver injury. Curr Hepatol Rep. 2018; 17:292–9.
Article3. Zhu Y, Niu M, Chen J, Zou ZS, Ma ZJ, Liu SH, et al. Hepatobiliary and pancreatic: comparison between Chinese herbal medicine and Western medicine-induced liver injury of 1985 patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 31:1476–82.
Article4. Lee WJ, Kim HW, Lee HY, Son CG. Systematic review on herb-induced liver injury in Korea. Food Chem Toxicol. 2015; 84:47–54.
Article5. Wysowski DK, Swartz L. Adverse drug event surveillance and drug withdrawals in the United States, 1969-2002: the importance of reporting suspected reactions. Arch Intern Med. 2005; 165:1363–9.
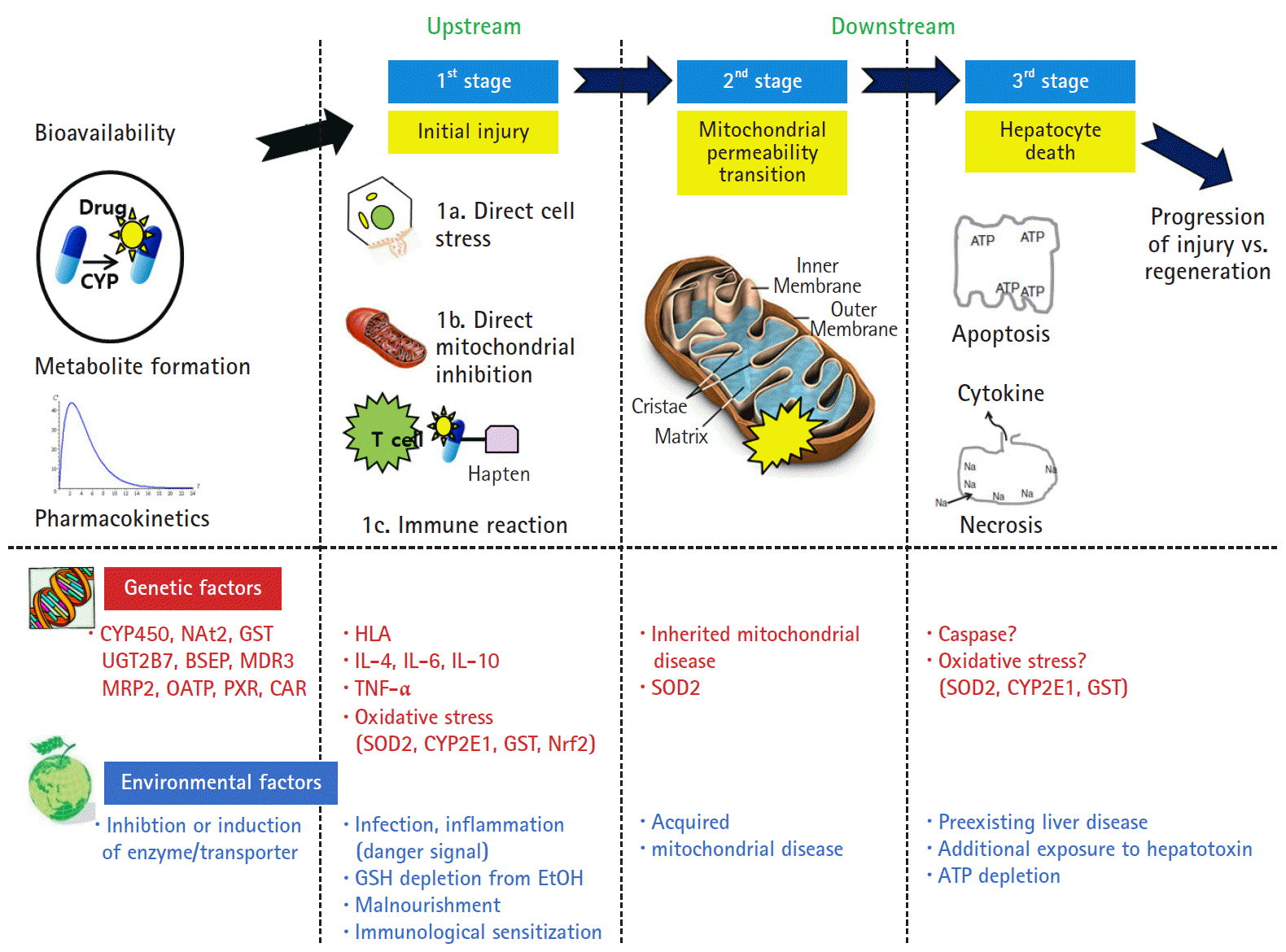
Article6. Holt MP, Ju C. Mechanisms of drug-induced liver injury. AAPS J. 2006; 8:E48–54.
Article7. Chalasani NP, Hayashi PH, Bonkovsky HL, Navarro VJ, Lee WM, Fontana RJ, et al. ACG clinical guideline: the diagnosis and management of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Am J Gastroenterol. 2014; 109:950–66.
Article8. Yu YC, Mao YM, Chen CW, Chen JJ, Chen J, Cong WM, et al. CSH guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced liver injury. Hepatol Int. 2017; 11:221–41.
Article9. European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: drug-induced liver injury. J Hepatol. 2019; 70:1222–61.10. Fontana RJ, Seeff LB, Andrade RJ, Björnsson E, Day CP, Serrano J, et al. Standardization of nomenclature and causality assessment in drug-induced liver injury: summary of a clinical research workshop. Hepatology. 2010; 52:730–42.
Article11. Devarbhavi H. An update on drug-induced liver injury. J Clin Exp Hepatol. 2012; 2:247–59.
Article12. Bénichou C. Criteria of drug-induced liver disorders. Report of an international consensus meeting. J Hepatol. 1990; 11:272–6.13. Visentin M, Lenggenhager D, Gai Z, Kullak-Ublick GA. Drug-induced bile duct injury. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2018; 1864:1498–506.
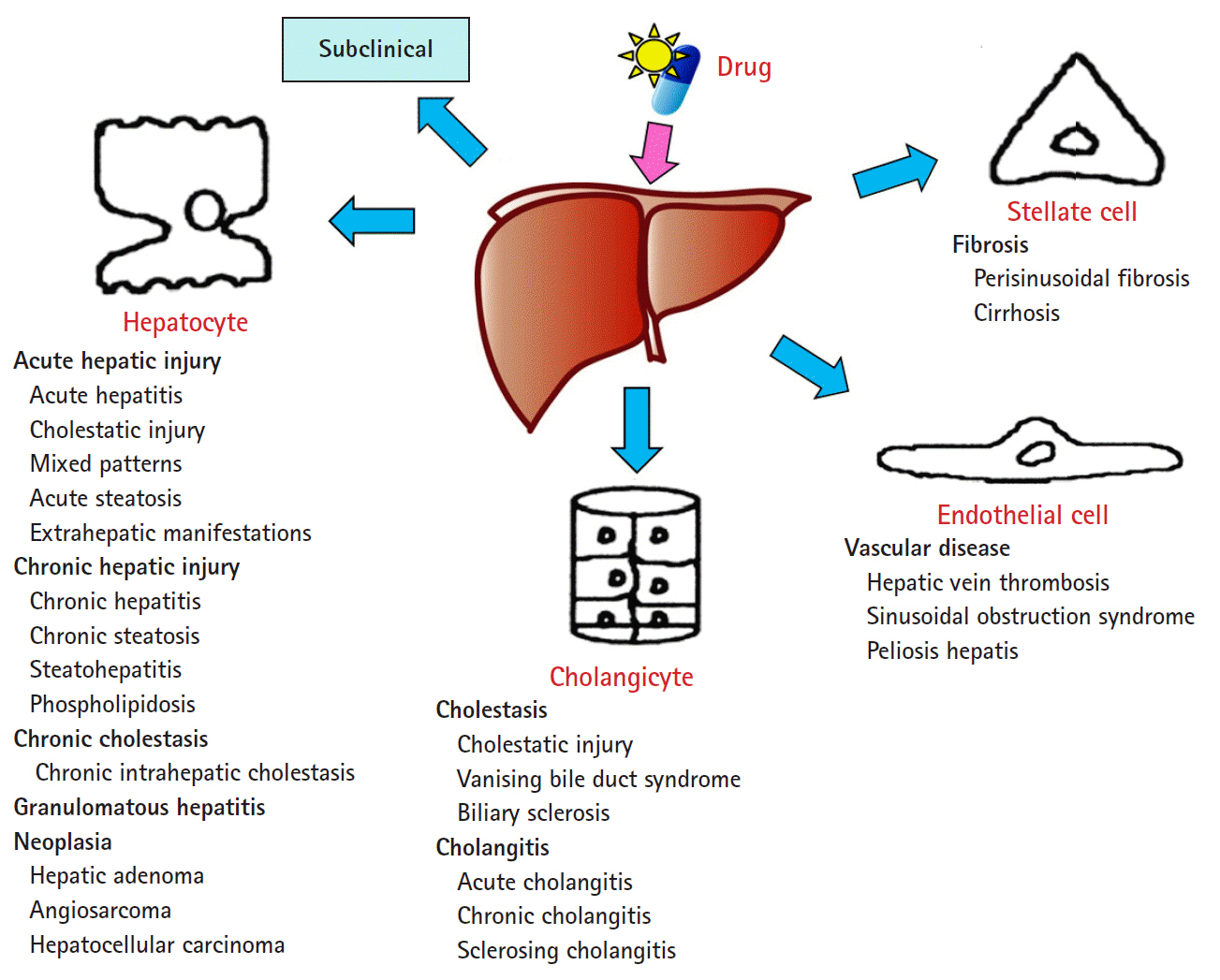
Article14. Wang T, Zhao X, Shao C, Ye L, Guo J, Peng N, et al. A proposed pathologic sub-classification of drug-induced liver injury. Hepatol Int. 2019; 13:339–51.
Article15. Ahmad J, Odin JA. Epidemiology and genetic risk factors of drug hepatotoxicity. Clin Liver Dis. 2017; 21:55–72.
Article16. Bell LN, Chalasani N. Epidemiology of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Semin Liver Dis. 2009; 29:337–47.
Article17. Suk KT, Kim DJ, Kim CH, Park SH, Yoon JH, Kim YS, et al. A prospective nationwide study of drug-induced liver injury in Korea. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:1380–7.
Article18. Danan G, Benichou C. Causality assessment of adverse reactions to drugs--I. A novel method based on the conclusions of international consensus meetings: application to drug-induced liver injuries. J Clin Epidemiol. 1993; 46:1323–30.
Article19. Hayashi PH. Overview of causality assessment in drug-induced liver injury. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2017; 9:29–33.
Article20. Hoofnagle JH. Drug-induced liver injury network (DILIN). Hepatology. 2004; 40:773.
Article21. Hayashi PH. Drug-induced liver injury network causality assessment: criteria and experience in the United States. Int J Mol Sci. 2016; 17:201.
Article22. Antoine DJ, Williams DP, Kipar A, Jenkins RE, Regan SL, Sathish JG, et al. High-mobility group box-1 protein and keratin-18, circulating serum proteins informative of acetaminophen-induced necrosis and apoptosis in vivo. Toxicol Sci. 2009; 112:521–31.
Article23. McGill MR, Jaeschke H. Biomarkers of drug-induced liver injury. Adv Pharmacol. 2019; 85:221–39.
Article24. Neuman MG. Biomarkers of drug-induced liver toxicity. Ther Drug Monit. 2019; 41:227–34.
Article25. Lammert C, Einarsson S, Saha C, Niklasson A, Bjornsson E, Chalasani N. Relationship between daily dose of oral medications and idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury: search for signals. Hepatology. 2008; 47:2003–9.
Article26. Russmann S, Kullak-Ublick GA, Grattagliano I. Current concepts of mechanisms in drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Curr Med Chem. 2009; 16:3041–53.
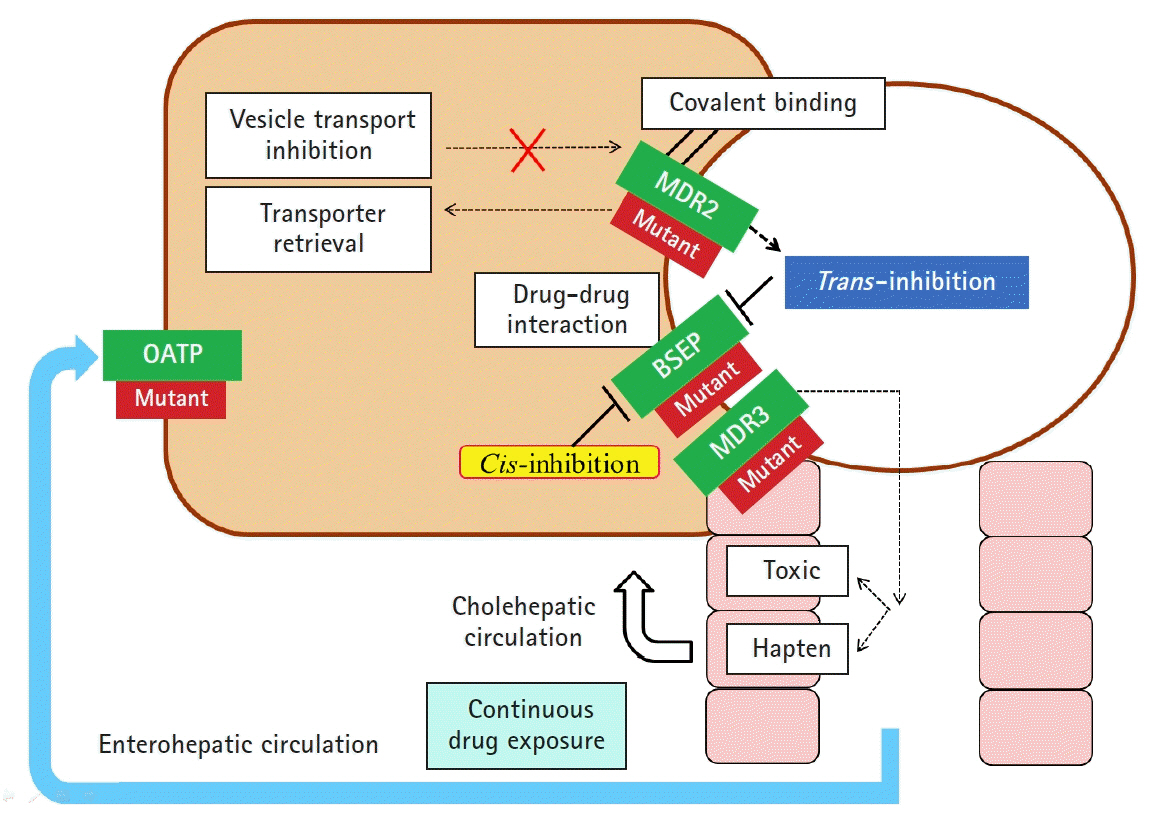
Article27. Gijbels E, Vinken M. Mechanisms of drug-induced cholestasis. Methods Mol Biol. 2019; 1981:1–14.
Article28. Patel SJ, Milwid JM, King KR, Bohr S, Iracheta-Vellve A, Li M, et al. Gap junction inhibition prevents drug-induced liver toxicity and fulminant hepatic failure. Nat Biotechnol. 2012; 30:179–83.
Article29. Chalasani N, Björnsson E. Risk factors for idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Gastroenterology. 2010; 138:2246–59.
Article30. Björnsson ES. Epidemiology and risk factors for idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Semin Liver Dis. 2014; 34:115–22.
Article31. Li H, He J, Jia W. The influence of gut microbiota on drug metabolism and toxicity. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2016; 12:31–40.
Article32. Teschke R, Danan G. Diagnosis and management of drug-induced liver injury (DILI) in patients with pre-existing liver disease. Drug Saf. 2016; 39:729–44.
Article33. Chalasani N, Regev A. Drug-induced liver injury in patients with preexisting chronic liver disease in drug development: how to identify and manage? Gastroenterology. 2016; 151:1046–51.
Article34. Zimmerman HJ. Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;1999.35. Reuben A. Hy's law. Hepatology. 2004; 39:574–8.
Article36. Lo Re V 3rd, Haynes K, Forde KA, Goldberg DS, Lewis JD, Carbonari DM, et al. Risk of acute liver failure in patients with drug-induced liver injury: evaluation of Hy's law and a new prognostic model. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 13:2360–8.
Article37. Robles-Diaz M, Lucena MI, Kaplowitz N, Stephens C, Medina-Cáliz I, González-Jimenez A, et al. Use of Hy's law and a new composite algorithm to predict acute liver failure in patients with drug-induced liver injury. Gastroenterology. 2014; 147:109–18.38. de Boer YS, Sherker AH. Herbal and dietary supplement-induced liver injury. Clin Liver Dis. 2017; 21:135–49.
Article39. García-Cortés M, Stephens C, Lucena MI, Fernández-Castañer A, Andrade RJ. Causality assessment methods in drug induced liver injury: strengths and weaknesses. J Hepatol. 2011; 55:683–91.
Article40. Teschke R, Wolff A, Frenzel C, Schwarzenboeck A, Schulze J, Eickhoff A. Drug and herb induced liver injury: Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences scale for causality assessment. World J Hepatol. 2014; 6:17–32.
Article41. Suh JI, Sakong JK, Lee K, Lee YK, Park JB, Kim DJ, et al. Anxiety and depression propensities in patients with acute toxic liver injury. World J Gastroenterol. 2013; 19:9069–76.
Article42. Ford R, Schwartz L, Dancey J, Dodd LE, Eisenhauer EA, Gwyther S, et al. Lessons learned from independent central review. Eur J Cancer. 2009; 45:268–74.
Article43. Lee WM, Hynan LS, Rossaro L, Fontana RJ, Stravitz RT, Larson AM, et al. Intravenous N-acetylcysteine improves transplant-free survival in early stage non-acetaminophen acute liver failure. Gastroenterology. 2009; 137:856–64.
Article44. Bateman DN, Dear JW, Thanacoody HK, Thomas SH, Eddleston M, Sandilands EA, et al. Reduction of adverse effects from intravenous acetylcysteine treatment for paracetamol poisoning: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2014; 383:697–704.
Article45. Singh S, Hynan LS, Lee WM; Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Improvements in hepatic serological biomarkers are associated with clinical benefit of intravenous N-acetylcysteine in early stage non-acetaminophen acute liver failure. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:1397–402.
Article46. Hu PF, Xie WF. Corticosteroid therapy in drug-induced liver injury: pros and cons. J Dig Dis. 2019; 20:122–6.
Article47. Hu PF, Wang PQ, Chen H, Hu XF, Xie QP, Shi J, et al. Beneficial effect of corticosteroids for patients with severe drug-induced liver injury. J Dig Dis. 2016; 17:618–27.
Article48. Reuben A, Koch DG, Lee WM; Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Drug-induced acute liver failure: results of a U.S. multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology. 2010; 52:2065–76.
Article49. Mindikoglu AL, Magder LS, Regev A. Outcome of liver transplantation for drug-induced acute liver failure in the United States: analysis of the United Network for Organ Sharing database. Liver Transpl. 2009; 15:719–29.
Article50. O'Grady JG, Alexander GJ, Hayllar KM, Williams R. Early indicators of prognosis in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology. 1989; 97:439–45.51. Rudraiah S, Zhang X, Wang L. Nuclear receptors as therapeutic targets in liver disease: are we there yet? Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 2016; 56:605–26.
Article52. Suh JI. Role of PXR and CAR in cholestasis. Korean J Hepatol. 2006; 12:5–15.53. Zhang J, Huang W, Chua SS, Wei P, Moore DD. Modulation of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by the xenobiotic receptor CAR. Science. 2002; 298:422–4.
Article54. Cheng J, Ma X, Krausz KW, Idle JR, Gonzalez FJ. Rifampicin-activated human pregnane X receptor and CYP3A4 induction enhance acetaminophen-induced toxicity. Drug Metab Dispos. 2009; 37:1611–21.
Article55. Ni HM, Jaeschke H, Ding WX. Targeting autophagy for drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Autophagy. 2012; 8:709–10.
Article56. Huh D, Torisawa YS, Hamilton GA, Kim HJ, Ingber DE. Microengineered physiological biomimicry: organs-on-chips. Lab Chip. 2012; 12:2156–64.
Article57. Kimura H, Sakai Y, Fujii T. Organ/body-on-a-chip based on microfluidic technology for drug discovery. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 2018; 33:43–8.
Article58. Beckwitt CH, Clark AM, Wheeler S, Taylor DL, Stolz DB, Griffith L, et al. Liver 'organ on a chip'. Exp Cell Res. 2018; 363:15–25.
Article59. Xu Y, Dai Z, Chen F, Gao S, Pei J, Lai L. Deep learning for drug-induced liver injury. J Chem Inf Model. 2015; 55:2085–93.
Article60. Fraser K, Bruckner DM, Dordick JS. Advancing predictive hepatotoxicity at the intersection of experimental, in silico, and artificial intelligence technologies. Chem Res Toxicol. 2018; 31:412–30.61. Suh JI. Establishment of tertiary hospital including southeast clinical research center in the era of the 4th industrial revolution. In : In : Choi YJ, editor. The 58th annual meeting and international symposium of Korean Society of Life Science; 2017 Aug 3-4; Gyeongju, Korea. Busan: Korean Society of Life Science;2017. p. 71.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Drug Induced Liver Injury by Prophylactic Administration of Albendazole
- Do Natural Health Products Cause Toxic Hepatitis?
- Medicinal Herbs and Toxic Hepatitis
- Ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir+dasabuvir and ribavirin associated drug-induced liver injury and syndrome of inappropriate secretion of anti-diuretic hormone: A case report
- A Case of Primaquine-Induced Acute Liver Failure