Korean J Gastroenterol.
2019 Jun;73(6):360-364. 10.4166/kjg.2019.73.6.360.
Drug Induced Liver Injury by Prophylactic Administration of Albendazole
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University Hospital, Busan, Korea. sunglee@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2454098
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4166/kjg.2019.73.6.360
Abstract
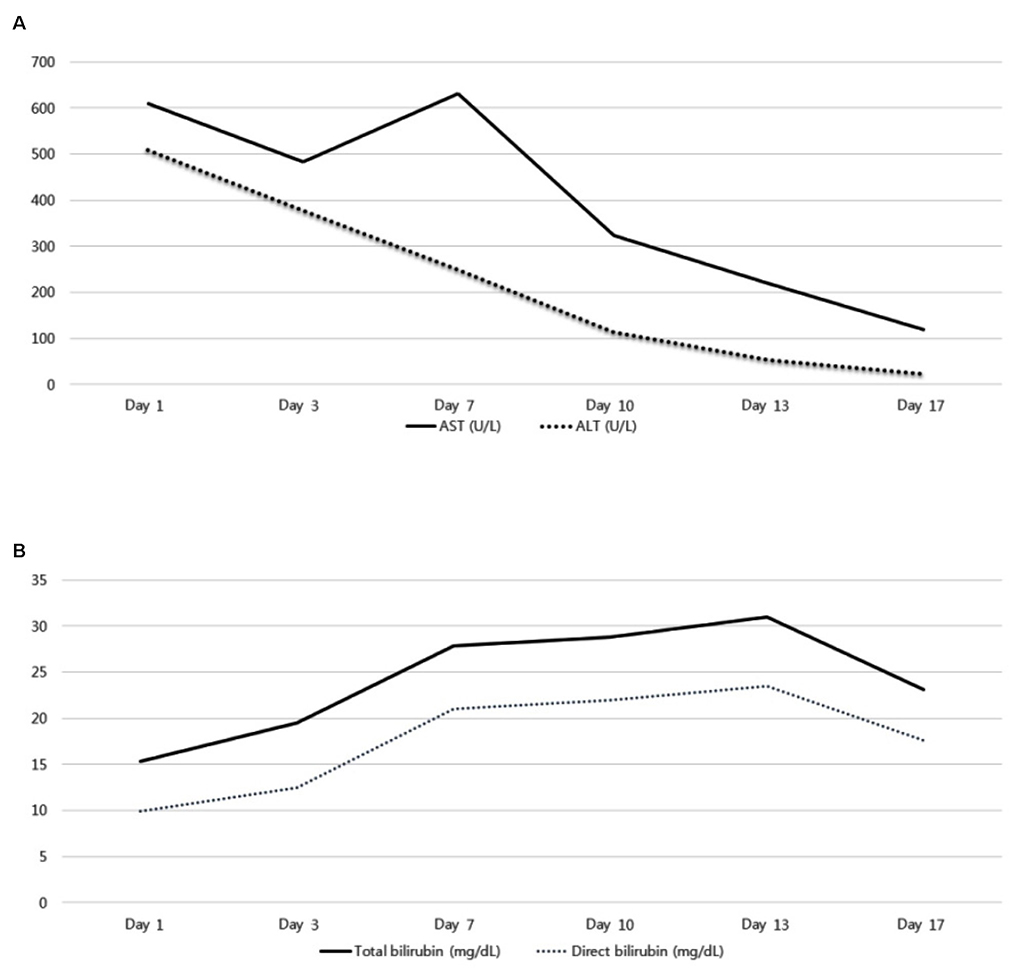
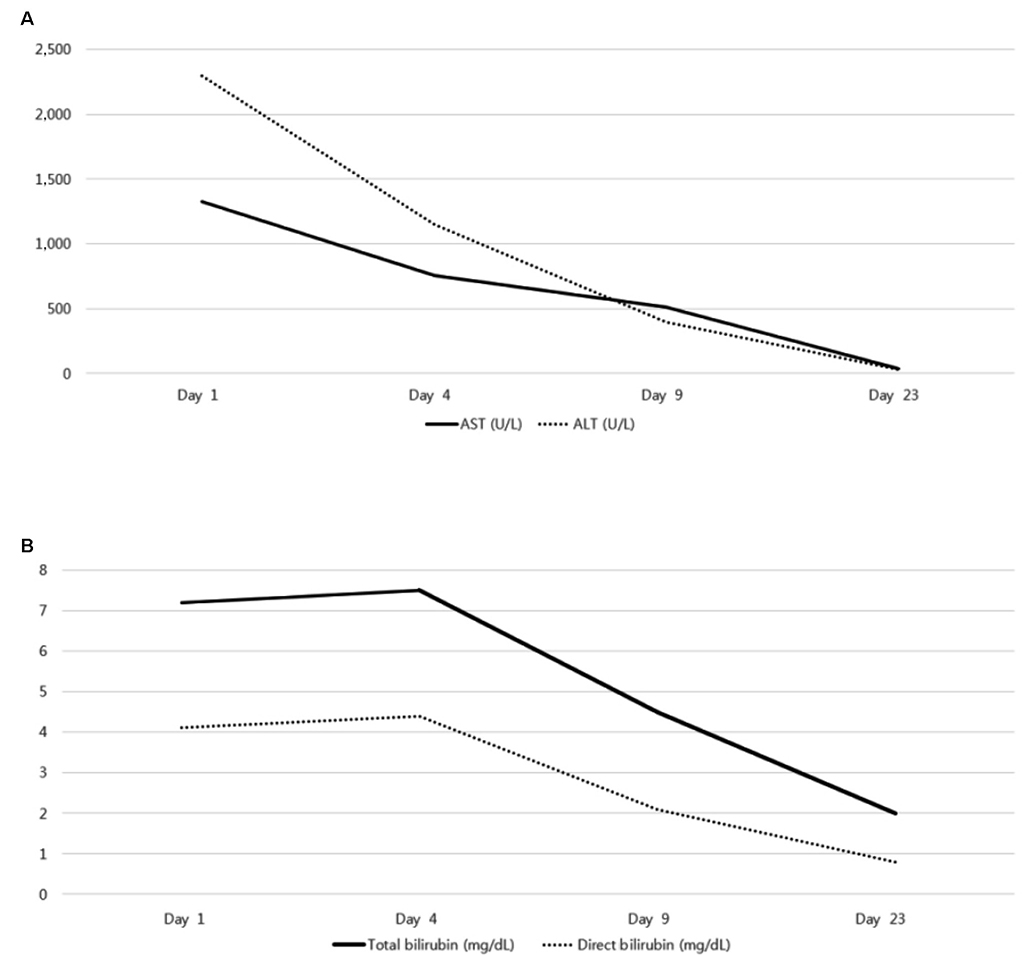
- Albendazole is used as a typical antiparasitic agent worldwide. The side effects of albendazole may include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dizziness, headache, alopecia, and increased liver enzymes. Mild elevation of the liver enzyme has been reported in more than 10% of cases, but drug induced liver injury was reported to be very rare. A 30-year-old woman visited the Dong-A University Hospital with anorexia, nausea, jaundice, and elevated liver enzyme. For diagnosis, other acute hepatitis etiologies were excluded, but the prophylactic administration of albendazole was verified. This paper introduces a case of drug-induced liver injury through the prophylactic administration of albendazole. Physicians should be aware of severe liver injury as one of the side effects of albendazole.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Albendazole. [Internet]. Seoul: Korea Pharmaceutical Information Center;c2018. cited 2018 Sep 12. Available from: http://www.health.kr/.2. Lee SH. Transition of parasitic diseases in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2007; 50:937–945.
Article3. Huh S. Chemotherapeutic drugs for common parasitic diseases in Korea. J Korean Med Assoc. 2013; 56:513–522.
Article4. Chang CY, Schiano TD. Review article: drug hepatotoxicity. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007; 25:1135–1151.
Article5. Bénichou C. Criteria of drug-induced liver disorders. Report of an international consensus meeting. J Hepatol. 1990; 11:272–276.6. Kim DJ. The assessment of toxic liver injury. Korean J Gastroenterol. 2009; 53:5–14.7. Navarro VJ, Senior JR. Drug-related hepatotoxicity. N Engl J Med. 2006; 354:731–739.
Article8. Zimmerman HJ. Drug-induced liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2000; 4:73–96. vi
Article9. Bunchorntavakul C, Reddy KR. Review article: herbal and dietary supplement hepatotoxicity. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2013; 37:3–17.
Article10. Lewis JH. Drug-induced liver injury throughout the drug development life cycle: where we have been, where we are now, and where we are headed. Perspectives of a clinical hepatologist. Pharm Med. 2013; 27:165–191.
Article11. Larson AM, Polson J, Fontana RJ, et al. Acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure: results of a United States multicenter, prospective study. Hepatology. 2005; 42:1364–1372.
Article12. Rockey DC, Caldwell SH, Goodman ZD, Nelson RC, Smith AD, American Association. Liver biopsy. Hepatology. 2009; 49:1017–1044.
Article13. Pugh AJ, Barve AJ, Falkner K, Patel M, McClain CJ. Drug-induced hepatotoxicity or drug-induced liver injury. Clin Liver Dis. 2009; 13:277–294.
Article14. Zimmerman HJ. Hepatotoxicity: the adverse effects of drugs and other chemicals on the liver. 2nd ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;1999.15. Choi GY, Yang HW, Cho SH, et al. Acute drug-induced hepatitis caused by albendazole. J Korean Med Sci. 2008; 23:903–905.
Article16. Bilgic Y, Yilmaz C, Cagin YF, Atayan Y, Karadag N, Harputluoglu MMM. Albendazole induced recurrent acute toxic hepatitis: a case report. Acta Gastroenterol Belg. 2017; 80:309–311.17. Shah C, Mahapatra A, Shukla A, Bhatia S. Recurrent acute hepatitis caused by albendazole. Trop Gastroenterol. 2013; 34:38–39.
Article18. Kim MK, Park HW, Kim WJ, et al. A case of acute drug-induced hepatotoxicity after albendazole treatment. Korean J Med. 2008; 75:564–568.19. Huh S. Is it necessary to take anthelmintics every year in Korea? J Korean Med Assoc. 2018; 61:198–204.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A case of acute drug-induced hepatotoxicity after albendazole treatment
- Acute Drug-Induced Hepatitis Caused by Albendazole
- A Case of Primaquine-Induced Acute Liver Failure
- Albendazole and Praziquantel: Review and Safety Monitoring in Korea
- Lysophosphatidic acid protects against acetaminophen-induced acute liver injury