Intest Res.
2020 Jan;18(1):107-114. 10.5217/ir.2019.00061.
Microvascular density under magnifying narrow-band imaging endoscopy in colorectal epithelial neoplasms
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Iwate Medical University School of Medicine, Morioka, Japan
- 2Division of Molecular Diagnostic Pathology, Department of Pathology, Iwate Medical University School of Medicine, Morioka, Japan
- KMID: 2501372
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5217/ir.2019.00061
Abstract
- Background/Aims
Magnifying endoscopic classification systems, such as the Japan narrow-band imaging (NBI) Expert Team (JNET) classification, have been widely used for predicting the histologic diagnosis and invasion depth of colorectal epithelial tumors. However, disagreement exists among observers regarding magnifying endoscopic diagnosis, because these classification systems are subjective. We herein investigated the utility of endoscopic microvascular density (eMVD) calculated from magnifying NBI endoscopic images in colorectal tumors.
Methods
We reviewed magnifying NBI endoscopic images from 169 colorectal epithelial tumors (97 adenomas, 72 carcinomas/high-grade dysplasias) resected endoscopically or surgically. The eMVD on magnifying NBI endoscopic images was evaluated using image-editing software, and relationships between eMVD and clinical, endoscopic, and pathological findings were retrospectively analyzed.
Results
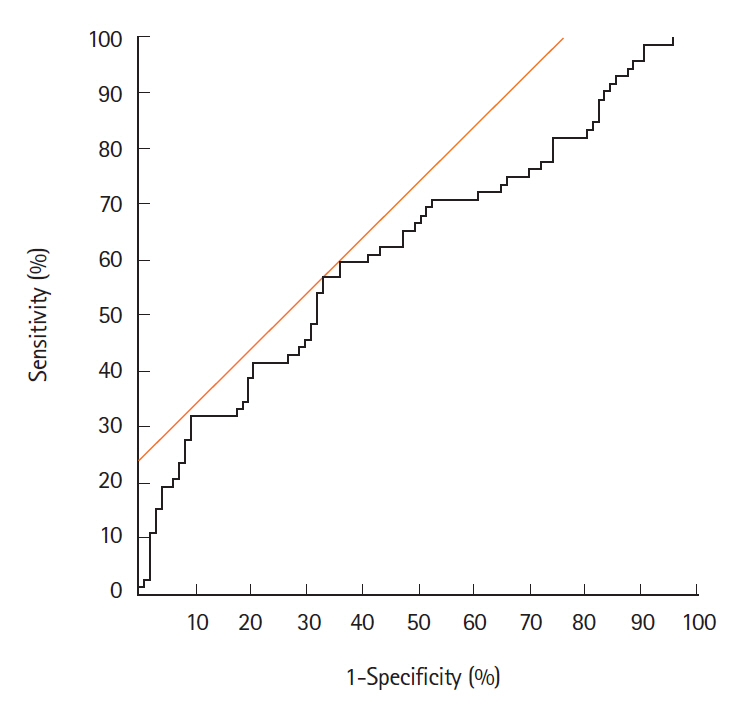
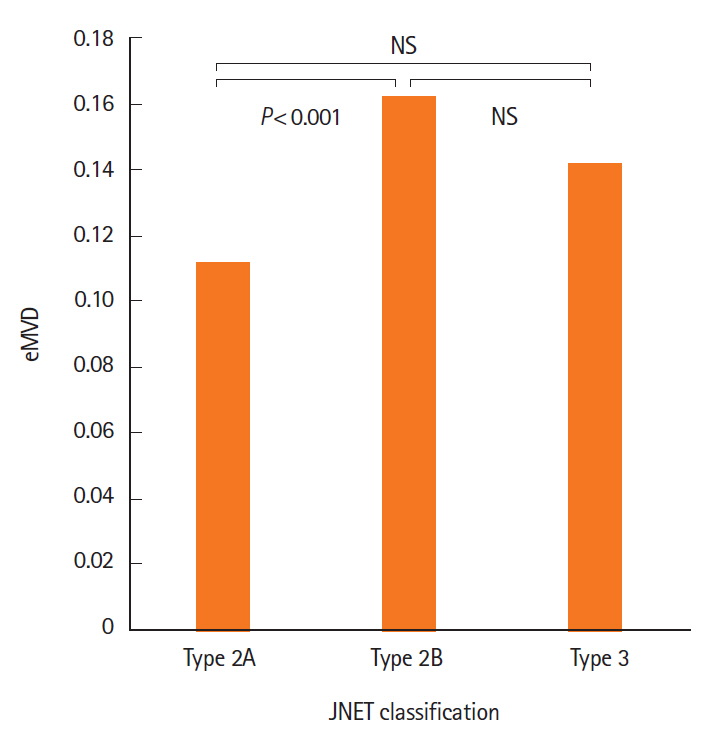
The eMVD in carcinomas (0.152 ± 0.079) was significantly higher than that in adenomas (0.119 ± 0.059, P< 0.05). The best cutoff value for distinguishing carcinoma from adenoma was 0.133. Sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy were 56.9%, 67.0%, and 62.7%, respectively. In addition, JNET type 2B tumors showed significantly higher eMVD (0.162 ± 0.079) compared to type 2A tumors (0.111 ± 0.050, P< 0.05).
Conclusions
The eMVD as determined by magnifying NBI endoscopy is considered to be a possible objective indicator for differentiating colorectal carcinomas from adenomas.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of early colorectal cancer
Seung Wook Hong, Jeong-Sik Byeon
Intest Res. 2022;20(3):281-290. doi: 10.5217/ir.2021.00169.
Reference
-
1. Yao K, Anagnostopoulos GK, Ragunath K. Magnifying endoscopy for diagnosing and delineating early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:462–467.2. Sano Y, Tanaka S, Kudo SE, et al. Narrow-band imaging (NBI) magnifying endoscopic classification of colorectal tumors proposed by the Japan NBI Expert Team. Dig Endosc. 2016; 28:526–533.3. Tamai N, Saito Y, Sakamoto T, et al. Effectiveness of computer-aided diagnosis of colorectal lesions using novel software for magnifying narrow-band imaging: a pilot study. Endosc Int Open. 2017; 5:E690–E694.4. Hashimoto R, Matsuda T, Hamamoto H, Yamaoka H, Nakahori M, Chonan A. Usefulness of dilated blood vessels in the tumor periphery for assessing the invasion depth of small-sized depressed colorectal cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016; 95:e3913.5. Hirata M, Tanaka S, Oka S, et al. Evaluation of microvessels in colorectal tumors by narrow band imaging magnification. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:945–952.6. Konerding MA, Fait E, Gaumann A. 3D microvascular architecture of pre-cancerous lesions and invasive carcinomas of the colon. Br J Cancer. 2001; 84:1354–1362.7. Mizuno K, Kudo SE, Ohtsuka K, et al. Narrow-banding images and structures of microvessels of colonic lesions. Dig Dis Sci. 2011; 56:1811–1817.8. The Paris endoscopic classification of superficial neoplastic lesions: esophagus, stomach, and colon: November 30 to December 1, 2002. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003; 58(6 Suppl):S3–S43.9. Kawasaki K, Kurahara K, Yanai S, et al. Significance of a white opaque substance under magnifying narrow-band imaging colonoscopy for the diagnosis of colorectal epithelial neoplasms. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 82:1097–1104.
Article10. Hayashi N, Tanaka S, Hewett DG, et al. Endoscopic prediction of deep submucosal invasive carcinoma: validation of the narrow-band imaging international colorectal endoscopic (NICE) classification. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:625–632.11. Kerbel RS. Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:2039–2049.12. Takahashi Y, Ellis LM, Mai M. The angiogenic switch of human colon cancer occurs simultaneous to initiation of invasion. Oncol Rep. 2003; 10:9–13.13. Wali RK, Roy HK, Kim YL, et al. Increased microvascular blood content is an early event in colon carcinogenesis. Gut. 2005; 54:654–660.
Article14. Yonenaga Y, Mori A, Onodera H, et al. Absence of smooth muscle actin-positive pericyte coverage of tumor vessels correlates with hematogenous metastasis and prognosis of colorectal cancer patients. Oncology. 2005; 69:159–166.15. Staton CA, Chetwood AS, Cameron IC, Cross SS, Brown NJ, Reed MW. The angiogenic switch occurs at the adenoma stage of the adenoma carcinoma sequence in colorectal cancer. Gut. 2007; 56:1426–1432.16. Des Guetz G, Uzzan B, Nicolas P, et al. Microvessel density and VEGF expression are prognostic factors in colorectal cancer. Meta-analysis of the literature. Br J Cancer. 2006; 94:1823–1832.
Article17. Väyrynen SA, Väyrynen JP, Klintrup K, et al. Clinical impact and network of determinants of tumour necrosis in colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 2016; 114:1334–1342.
Article18. Shimoyama T, Fukuda Y, Kusano H, et al. Microangiographic study of colorectal polyp. J Jpn Soc Coloproctol. 1989; 42:76–86.
Article19. Hisabe T, Yao K, Imamura K, et al. White opaque substance visualized using magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging in colorectal epithelial neoplasms. Dig Dis Sci. 2014; 59:2544–2549.20. Mori Y, Kudo SE, Wakamura K, et al. Novel computer-aided diagnostic system for colorectal lesions by using endocytoscopy (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2015; 81:621–629.
Article21. Misawa M, Kudo SE, Mori Y, et al. Characterization of colorectal lesions using a computer-aided diagnostic system for narrow-band imaging endocytoscopy. Gastroenterology. 2016; 150:1531–1532.
Article22. Chen PJ, Lin MC, Lai MJ, Lin JC, Lu HH, Tseng VS. Accurate classification of diminutive colorectal polyps using computer-aided analysis. Gastroenterology. 2018; 154:568–575.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Usefulness of Magnifying Chromoendoscopy and Magnifying Narrow Band Imaging Endoscopy for Predicting the Submucosal Invasion of Early Colorectal Cancers
- Usefulness of Narrow-Band Imaging in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection of the Stomach
- The Usefulness of Magnifying Endoscopy and Narrow-Band Imaging in Measuring the Depth of Invasion before Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Clinical Role of Magnifying Endoscopy with Narrow-band Imaging in the Diagnosis of Early Gastric Cancer
- Endoscopic Assessment of Colorectal Cancer with Superficial or Deep Submucosal Invasion Using Magnifying Colonoscopy