Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2020 Feb;13(1):58-63. 10.21053/ceo.2019.00556.
Development and Validation of a Low-Cost and Simple Simulator for Microlaryngeal Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery, Huashan Hospital, Fudan University, Shanghai, China
- 2Outpatient Department, Huashan Worldwide Medical Center, Shanghai, China
- KMID: 2501299
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.21053/ceo.2019.00556
Abstract
Objectives
. The simulation of microlaryngeal skills is rarely seen in surgical training, but it is particularly important in phonomicrosurgery. This study described and validated the laryngeal surgical simulator through surgical training.
Methods
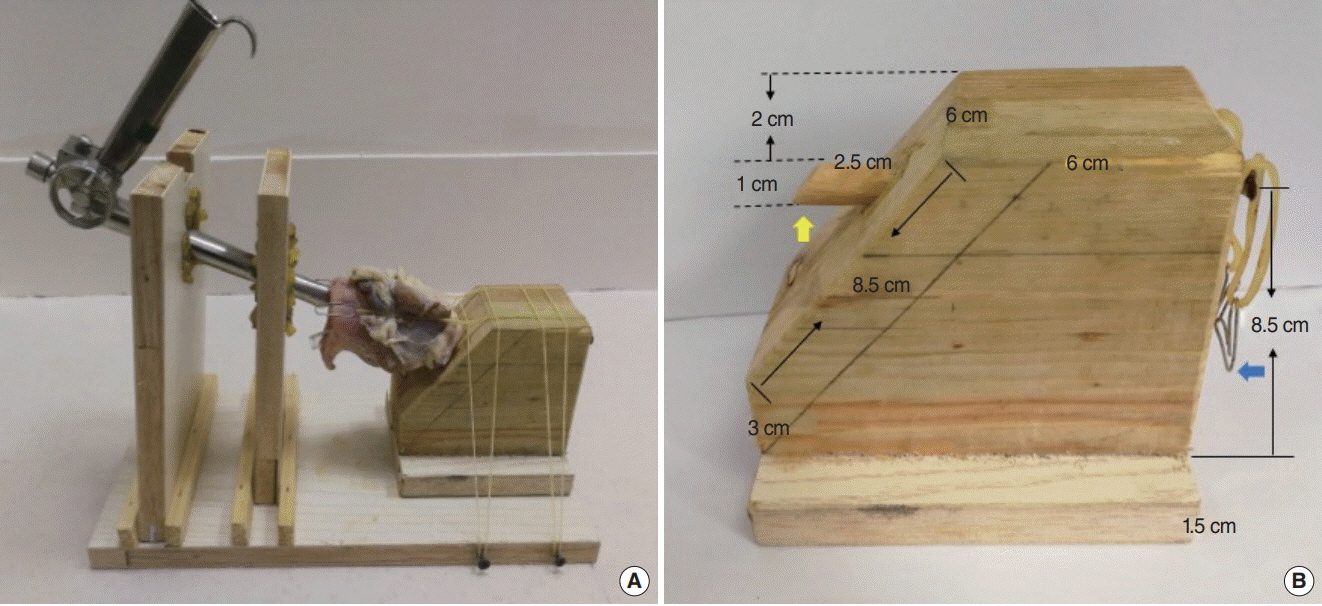
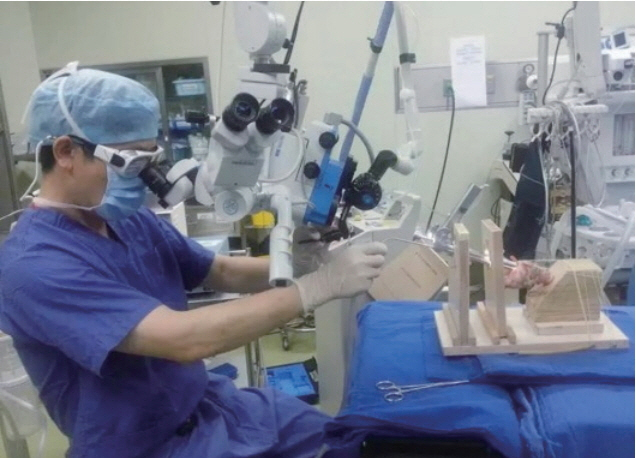
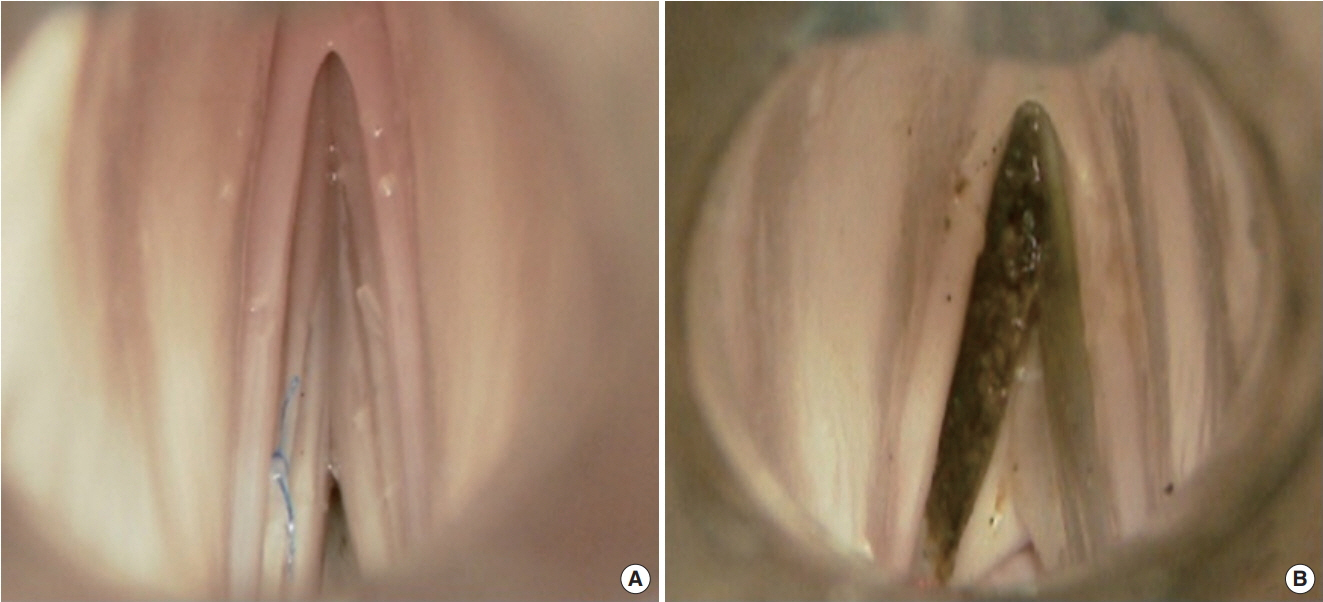
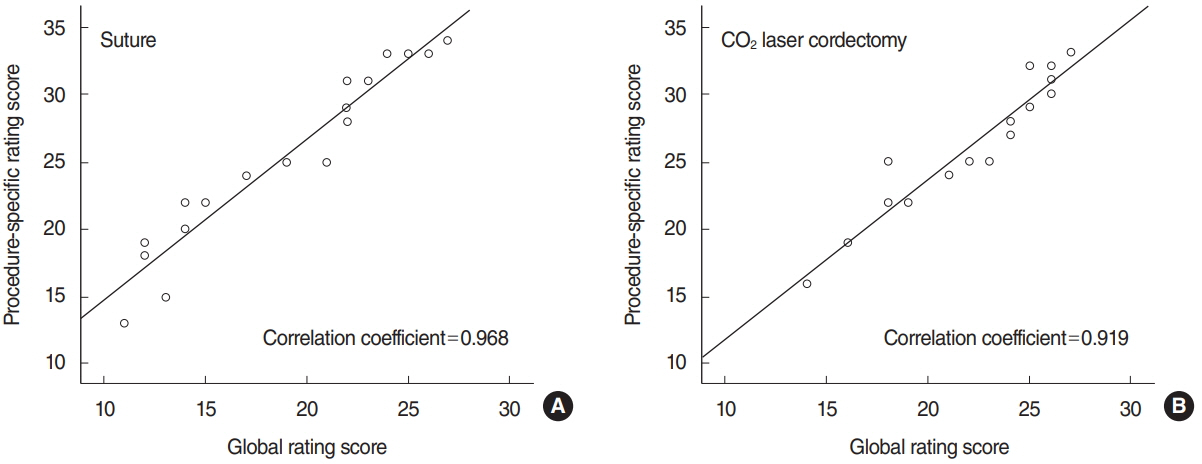
. A simple and low-cost simulator was developed for the fixation of the suspension laryngoscope and porcine larynges. Twenty participants with work skills and experience did preparation before training, and performed suture and carbon dioxide (CO2) laser cordectomy for simulator evaluation. The results were proposed by the aspects of time taken for each procedure, the global rating scale, a procedure-specific assessment, and a post-simulation questionnaire.
Results
. All participants completed the preparation within 9 minutes and reached the conclusion that the microlaryngeal surgical simulator was helpful in improving their surgical skills. The performance of experts was superior to that of novices in both suture and CO2 laser cordectomy.
Conclusion
. This simulator could be easily assembled and was successfully validated by microlaryngeal surgical training both subjectively and objectively. It may be helpful to clinicians in microlaryngeal skills.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jackel MC, Martin A, Steiner W. Twenty-five years experience with laser surgery for head and neck tumors: report of an international symposium, Gottingen, Germany, 2005. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2007; Jun. 264(6):577–85.2. Steuer CE, El-Deiry M, Parks JR, Higgins KA, Saba NF. An update on larynx cancer. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017; Jan. 67(1):31–50.
Article3. Xidong C, Xia Z, Chenjie X, Wenhong Y, Huichang Y, Jiaqi J. Management of difficult suspension laryngoscopy using a GlideScope(R) Video Laryngoscope. Acta Otolaryngol. 2012; Dec. 132(12):1318–23.4. Latuska RF, Kuhl NO, Garrett CG, Berry JM, Gelbard A. Severe bradycardia associated with suspension laryngoscopy. Laryngoscope. 2016; Apr. 126(4):949–50.
Article5. Glassman SH, Green MS, Brodsky M. Asystole following reintubation during suspension laryngoscopy. Case Rep Anesthesiol. 2012; 2012:916306.
Article6. Dailey SH, Kobler JB, Zeitels SM. A laryngeal dissection station: educational paradigms in phonosurgery. Laryngoscope. 2004; May. 114(5):878–82.
Article7. Contag SP, Klein AM, Blount AC, Johns MM 3rd. Validation of a laryngeal dissection module for phonomicrosurgical training. Laryngoscope. 2009; Jan. 119(1):211–5.
Article8. Fleming J, Kapoor K, Sevdalis N, Harries M. Validation of an operating room immersive microlaryngoscopy simulator. Laryngoscope. 2012; May. 122(5):1099–103.
Article9. Ainsworth TA, Kobler JB, Loan GJ, Burns JA. Simulation model for transcervical laryngeal injection providing real-time feedback. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2014; Dec. 123(12):881–6.
Article10. Martin JA, Regehr G, Reznick R, MacRae H, Murnaghan J, Hutchison C, et al. Objective structured assessment of technical skill (OSATS) for surgical residents. Br J Surg. 1997; Feb. 84(2):273–8.
Article11. Moorthy K, Munz Y, Sarker SK, Darzi A. Objective assessment of technical skills in surgery. BMJ. 2003; Nov. 327(7422):1032–7.
Article12. Tsuji DH, Nita LM, Hachiya A, Imamura R, Sennes LU. T-shaped microsuture: a new suture technique for laryngeal microsurgery. J Voice. 2009; Nov. 23(6):739–42.
Article13. Remacle M, Eckel HE, Antonelli A, Brasnu D, Chevalier D, Friedrich G, et al. Endoscopic cordectomy: a proposal for a classification by the Working Committee, European Laryngological Society. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2000; 257(4):227–31.
Article14. Zambricki EA, Bergeron JL, DiRenzo EE, Sung CK. Phonomicrosurgery simulation: a low-cost teaching model using easily accessible materials. Laryngoscope. 2016; Nov. 126(11):2528–33.
Article15. Dedmon MM, Paddle PM, Phillips J, Kobayashi L, Franco RA, Song PC. Development and validation of a high-fidelity porcine laryngeal surgical simulator. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2015; Sep. 153(3):420–6.
Article16. Holliday MA, Bones VM, Malekzadeh S, Grant NN. Low-cost modular phonosurgery training station: development and validation. Laryngoscope. 2015; Jun. 125(6):1409–13.
Article17. Nixon IJ, Palmer FL, Ganly I, Patel SG. An integrated simulator for endolaryngeal surgery. Laryngoscope. 2012; Jan. 122(1):140–3.
Article18. Jiang JJ, Raviv JR, Hanson DG. Comparison of the phonation-related structures among pig, dog, white-tailed deer, and human larynges. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001; Dec. 110(12):1120–5.
Article19. Alipour F, Jaiswal S, Vigmostad S. Vocal fold elasticity in the pig, sheep, and cow larynges. J Voice. 2011; Mar. 25(2):130–6.
Article20. Isaacson G, Ianacone DC, Soliman AM. Ex vivo ovine model for suspension microlaryngoscopy training. J Laryngol Otol. 2016; Oct. 130(10):939–42.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comments on ‘Development of colonic stent simulator using three-dimensional printing technique: a simulator development study in Korea’
- Acoustic Analysis of Benign Vocal Cord Lesions: Before and after Microlaryngeal Surgery
- Vocal Dynamic Studies before and after Laryngeal Microsurgery
- Prediction of Simulator Sickness in Virtual Environments
- The Effects of Preoperative Sprayed 10% Lidocaine on the Hemodynamic Response during Suspension Microlaryngeal Surgery