Clin Endosc.
2020 Mar;53(2):232-235. 10.5946/ce.2019.067.
Two-Stage Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Sigmoid-Type Achalasia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Incheon Sarang Hospital, Incheon, Korea
- 2Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Cheonggu Sungsim Hospital, Seoul, Korea
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, CHA Kumi Medical Center, Gumi, Korea
- KMID: 2500892
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2019.067
Abstract
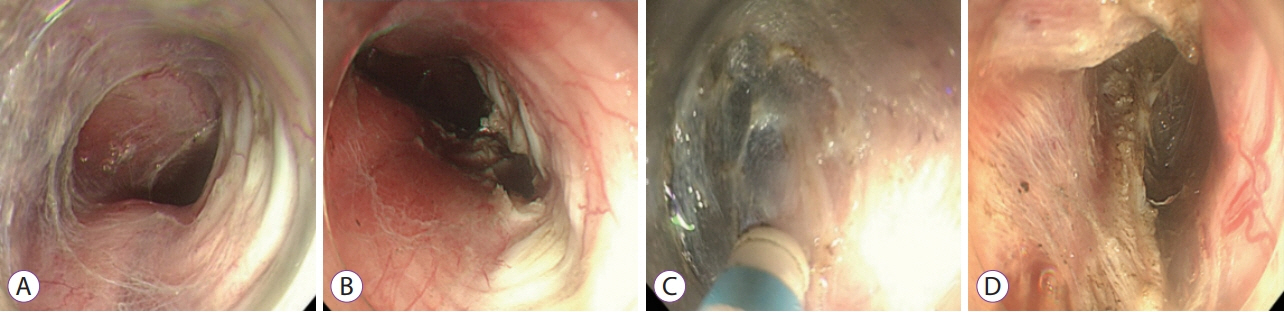
- Peroral endoscopic myotomy (POEM) has been recently considered as the first treatment option for achalasia. The standard POEM procedures are often successful in most patients, but sometimes technical challenges are encountered. We report a new technique that is divided between two tunneling sites in the esophagus for sigmoid-type achalasia. A 40-year-old male patient with dysphagia for 10 years was diagnosed with a sigmoid-shaped esophagus at our hospital. We devised a two-stage myotomy technique to treat sigmoidtype achalasia. The myotomy was first performed in the upper part of the greater flexion area and then in the lower part of the flexion. We termed this method “two-stage POEM”, which was successfully performed without any complications. This new POEM method can also be used to improve symptoms in patients with achalasia who have a structural deformity that may result in a high change of treatment failure.
Figure
Reference
-
1. von Renteln D, Inoue H, Minami H, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for the treatment of achalasia: a prospective single center study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2012; 107:411–417.
Article2. Inoue H, Minami H, Satodate H, Kudo S-E. First clinical experience of submucosal endoscopic esophageal myotomy for esophageal achalasia with no skin incision. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:AB122.
Article3. Lv L, Liu J, Tan Y, Liu D. Peroral endoscopic full-thickness myotomy for the treatment of sigmoid-type achalasia: outcomes with a minimum follow-up of 12 months. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016; 28:30–36.4. Kim WH, Cho JY, Ko WJ, et al. Comparison of the outcomes of peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia according to manometric subtype. Gut Liver. 2017; 11:642–647.
Article5. Wu QN, Xu XY, Zhang XC, et al. Submucosal fibrosis in achalasia patients is a rare cause of aborted peroral endoscopic myotomy procedures. Endoscopy. 2017; 49:736–744.
Article6. Hu JW, Li QL, Zhou PH, et al. Peroral endoscopic myotomy for advanced achalasia with sigmoid-shaped esophagus: long-term outcomes from a prospective, single-center study. Surg Endosc. 2015; 29:2841–2850.
Article7. Liu W, Liu L, Chen HL, et al. Open peroral endoscopic myotomy for achalasia with sigmoid-shaped esophagus. Endoscopy. 2017; 49:E311–E312.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Morphologic Restoration After Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy in Sigmoid-type Achalasia
- Perspective on Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Achalasia: Zhongshan Experience
- Current Status of Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy
- Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Treating Achalasia and Esophageal Motility Disorders
- Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy for Esophageal Motility Disorders