Clinical Significance of a High SARS-CoV-2 Viral Load in the Saliva
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Infectious Diseases, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2500852
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e195
Abstract
- Background
Patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) can unknowingly spread the virus to several people during the early subclinical period.
Methods
We evaluated the viral dynamics in various body fluid specimens, such as nasopharyngeal swab, oropharyngeal swab, saliva, sputum, and urine specimens, of two patients with COVID-19 from hospital day 1 to 9. Additional samples of the saliva were taken at 1 hour, 2 hours, and 4 hours after using a chlorhexidine mouthwash. The severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) viral load was determined by real-time reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (rRT-PCR).
Results
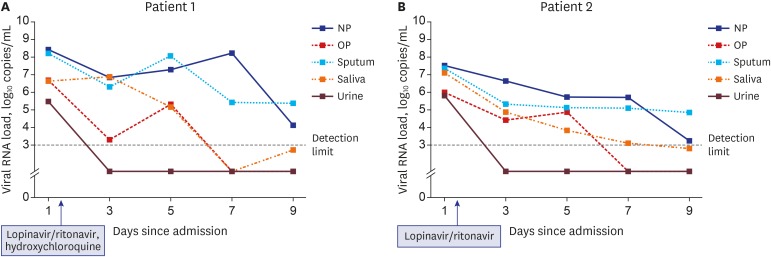
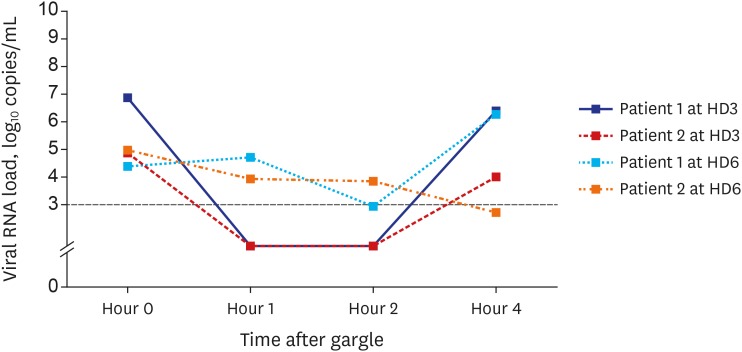
SARS-CoV-2 was detected from all the five specimens of both patients by rRT-PCR. The viral load was the highest in the nasopharynx (patient 1 = 8.41 log10 copies/mL; patient 2 = 7.49 log10 copies/mL), but it was also remarkably high in the saliva (patient 1 = 6.63 log10 copies/mL; patient 2 = 7.10 log10 copies/mL). SARS-CoV-2 was detected up to hospital day 6 (illness day 9 for patient 2) from the saliva of both patients. The viral load in the saliva decreased transiently for 2 hours after using the chlorhexidine mouthwash.
Conclusion
SARS-CoV-2 viral load was consistently high in the saliva; it was relatively higher than that in the oropharynx during the early stage of COVID-19. Chlorhexidine mouthwash was effective in reducing the SARS-CoV-2 viral load in the saliva for a short-term period.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Viral Load Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Saliva in Korean Patients: a Prospective Multi-center Comparative Study
Seong Eun Kim, Ji Yeon Lee, Ahrang Lee, Soosung Kim, Kyung-Hwa Park, Sook-In Jung, Seung-Ji Kang, Tae Hoon Oh, Uh Jin Kim, Seung Yeob Lee, Seung-Jung Kee, Hee-Chang Jang
J Korean Med Sci. 2020;35(31):e287. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2020.35.e287.Serial Screening for SARS-CoV-2 in Rectal Swabs of Symptomatic COVID-19 Patients
Sung Hoon Jung, Sei Won Kim, Heayon Lee, Jung Hwan Oh, Jihyang Lim
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(44):e301. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e301.Analysis of PubMed and KoreaMed Indexed Korean Publications on COVID-19
Jong-Min Kim, Jin-Hong Yoo, Hae Kyung Cho, Sung-Tae Hong
J Korean Med Sci. 2021;36(49):e345. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e345.
Reference
-
1. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Updates on 2019 Novel Coronavirus: for Press Release. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention;2020.2. Song JY, Yun JG, Noh JY, Cheong HJ, Kim WJ. Covid-19 in South Korea - Challenges of subclinical manifestations. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(19):1858–1859. PMID: 32251568.
Article3. Pan Y, Zhang D, Yang P, Poon LL, Wang Q. Viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in clinical samples. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020; 20(4):411–412. PMID: 32105638.
Article4. Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, et al. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020; 395(10223):497–506. PMID: 31986264.
Article5. To KK, Tsang OT, Chik-Yan Yip C, Chan KH, Wu TC, Chan JM, et al. Consistent detection of 2019 novel coronavirus in saliva. Clin Infect Dis. 2020; ciaa149. PMID: 32047895.
Article6. Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y, Liang WH, Ou CQ, He JX, et al. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020; 382(18):1708–1720. PMID: 32109013.7. Corman VM, Landt O, Kaiser M, Molenkamp R, Meijer A, Chu DK, et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. 2020; 25(3):2000045.
Article8. Duguid JP. The size and the duration of air-carriage of respiratory droplets and droplet-nuclei. J Hyg (Lond). 1946; 44(6):471–479. PMID: 20475760.
Article9. Choi WS, Kang CI, Kim Y, Choi JP, Joh JS, Shin HS, et al. Clinical presentation and outcomes of Middle East respiratory syndrome in the Republic of Korea. Infect Chemother. 2016; 48(2):118–126. PMID: 27433382.10. Lee N, Hui D, Wu A, Chan P, Cameron P, Joynt GM, et al. A major outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome in Hong Kong. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348(20):1986–1994. PMID: 12682352.
Article11. Letko M, Marzi A, Munster V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat Microbiol. 2020; 5(4):562–569. PMID: 32094589.
Article12. Widagdo W, Begeman L, Schipper D, Run PR, Cunningham AA, Kley N, et al. Tissue distribution of the MERS-Coronavirus receptor in bats. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):1193. PMID: 28446791.
Article13. Liu L, Wei Q, Alvarez X, Wang H, Du Y, Zhu H, et al. Epithelial cells lining salivary gland ducts are early target cells of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection in the upper respiratory tracts of rhesus macaques. J Virol. 2011; 85(8):4025–4030. PMID: 21289121.
Article14. To KK, Yip CC, Lai CY, Wong CK, Ho DT, Pang PK, et al. Saliva as a diagnostic specimen for testing respiratory virus by a point-of-care molecular assay: a diagnostic validity study. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2019; 25(3):372–378. PMID: 29906597.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Viral Load Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in First Two Patients in Korea
- Reinfection of SARS-CoV-2 Variants in Immunocompromised Patients with Prolonged or Relapsed Viral Shedding
- Viral Load Kinetics of SARS-CoV-2Infection in Saliva in Korean Patients:a Prospective Multi-center Comparative Study
- Understandings and Prospects of Laboratory Diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2
- Viral load and rebound in children with coronavirus disease 2019 during the first outbreak in Daegu city