Ann Surg Treat Res.
2020 Apr;98(4):206-213. 10.4174/astr.2020.98.4.206.
Risk factors affecting postoperative pulmonary function in congenital diaphragmatic hernia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatric Surgery, Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- 2Department of Pediatric Surgery, Jiaxing Maternity and Child Health Care Hospital, Jiaxing, China
- 3Department of Pediatric Respiration, Xinhua Hospital Affiliated to Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
- KMID: 2500821
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4174/astr.2020.98.4.206
Abstract
- Purpose
It is well known that congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH) in infants impacts pulmonary function rehabilitation after surgery. However, the risk factors of postoperative pulmonary function are still unclear. In this research, we analyzed the potential risk factors of postoperative pulmonary function in CDH patients in order to improve the clinical management of CDH patients.
Methods
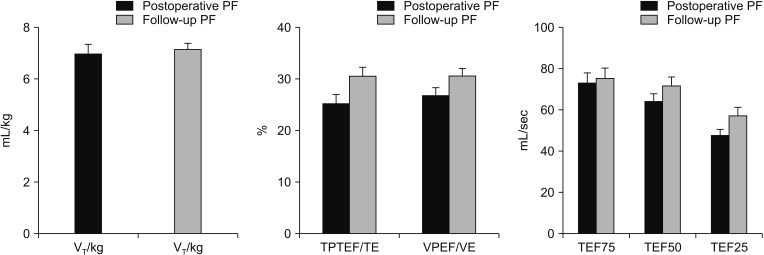
Thirty-three cases CDH infants followed were enrolled from November 2016 to September 2018. Clinical data were reviewed. Tidal breathing pulmonary function testing was performed after surgery. Correlation between pulmonary function and clinical characteristics was evaluated using multivariate analysis of variance.
Results
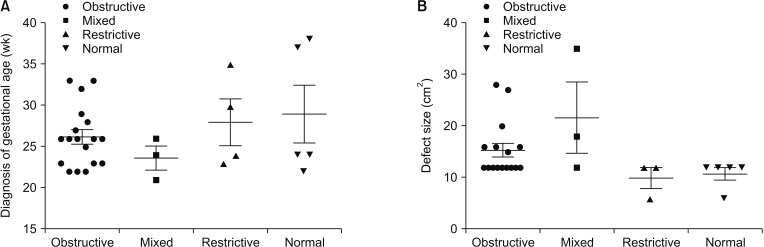
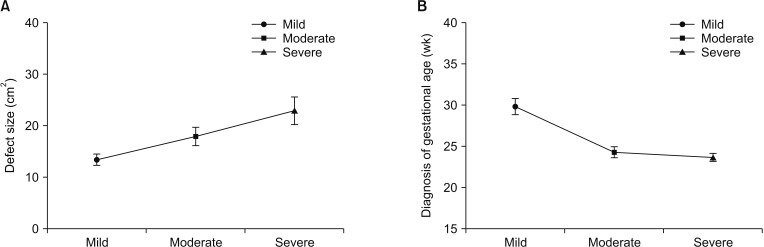
Pulmonary dysfunction was detected in 87.9% patients (29 of 33). The defect size was found to be significantly larger in patients with obstructed and mixed ventilatory disorders (P = 0.001). Diagnosis of gestational age (GA) was also significantly earlier compared to restrictive ventilatory disorders (P = 0.001). Larger defect size, and earlier prenatal diagnosis of GA were detected in severe obstructive ventilatory disorders (P = 0.007, P = 0.001, retrospectively).
Conclusion
Most patients had various degrees of pulmonary dysfunction after surgery. Patients with larger defect size and earlier diagnosis time might be vulnerable to severe obstructive and mixed ventilatory disorders.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ameis D, Khoshgoo N, Keijzer R. Abnormal lung development in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2017; 26:123–128. PMID: 28641748.
Article2. Panitch HB, Weiner DJ, Feng R, Perez MR, Healy F, McDonough JM, et al. Lung function over the first 3 years of life in children with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2015; 50:896–907. PMID: 25045135.
Article3. Spoel M, van der Cammen-van Zijp MH, Hop WC, Tibboel D, de Jongste JC, Ijsselstijn H. Lung function in young adults with congenital diaphragmatic hernia; a longitudinal evaluation. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2013; 48:130–137. PMID: 22451263.
Article4. American Thoracic Society. European Respiratory Society. ATS/ERS statement: raised volume forced expirations in infants: guidelines for current practice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2005; 172:1463–1471. PMID: 16301301.5. Spoel M, van den Hout L, Gischler SJ, Hop WC, Reiss I, Tibboel D, et al. Prospective longitudinal evaluation of lung function during the first year of life after repair of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2012; 13:e133–e139. PMID: 21666527.
Article6. Bates JH, Schmalisch G, Filbrun D, Stocks J. Tidal breath analysis for infant pulmonary function testing. ERS/ATS Task Force on Standards for Infant Respiratory Function Testing. European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society. Eur Respir J. 2000; 16:1180–1192. PMID: 11292125.7. Frey U, Stocks J, Coates A, Sly P, Bates J. Specifications for equipment used for infant pulmonary function testing. ERS/ATS Task Force on Standards for Infant Respiratory Function Testing. European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society. Eur Respir J. 2000; 16:731–740. PMID: 11106221.8. Putnam LR, Gupta V, Tsao K, Davis CF, Lally PA, Lally KP, et al. Factors associated with early recurrence after congenital diaphragmatic hernia repair. J Pediatr Surg. 2017; 52:928–932. PMID: 28359590.
Article9. Brindle ME, Cook EF, Tibboel D, Lally PA, Lally KP. Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia Study Group. A clinical prediction rule for the severity of congenital diaphragmatic hernias in newborns. Pediatrics. 2014; 134:e413–e419. PMID: 25022745.
Article10. Long AM, Bunch KJ, Knight M, Kurinczuk JJ, Losty PD. BAPS-CASS. Early population-based outcomes of infants born with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2018; 103:F517–F522. PMID: 29305406.
Article11. Keijzer R, Liu J, Deimling J, Tibboel D, Post M. Dual-hit hypothesis explains pulmonary hypoplasia in the nitrofen model of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Pathol. 2000; 156:1299–1306. PMID: 10751355.
Article12. Guilbert TW, Gebb SA, Shannon JM. Lung hypoplasia in the nitrofen model of congenital diaphragmatic hernia occurs early in development. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000; 279:L1159–L1171. PMID: 11076806.
Article13. Kitagawa M, Hislop A, Boyden EA, Reid L. Lung hypoplasia in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. A quantitative study of airway, artery, and alveolar development. Br J Surg. 1971; 58:342–346. PMID: 5574718.
Article14. Stefanutti G, Filippone M, Tommasoni N, Midrio P, Zucchetta P, Moreolo GS, et al. Cardiopulmonary anatomy and function in long-term survivors of mild to moderate congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg. 2004; 39:526–531. PMID: 15065021.
Article15. Choi SY, Lee HW, Hong J. Late lung function in the repaired congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Korean Surg Soc. 2010; 79:143–148.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Unilateral Congenital Diaphragmatic Eventration Mimicking Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
- Anesthetic Consideration Concerning a Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia in a Patient with a Single Ventricle: A case report
- Late Lung Function in the Repaired Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia
- Congenital diaphragmatic Hernia Associated with Hypoplasia of the Lung
- A Case of Sliding Hiatal Hernia associated with Bochdalek Hernia Repair