Anesth Pain Med.
2020 Jan;15(1):53-60. 10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.53.
Systemic hemodynamic effects of norepinephrine versus phenylephrine in intermittent bolus doses during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Jeju National University Hospital, Jeju, Korea
- KMID: 2500455
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.17085/apm.2020.15.1.53
Abstract
- Background
Norepinephrine, a potent α-adrenergic agonist with β-adrenergic effects, has recently emerged as a potential alternative to phenylephrine that does not lower cardiac output (CO) and heart rate (HR) during cesarean deliveries. We examined the systemic hemodynamic effects of both agents in this setting, using intermittent bolus doses to treat spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension.
Methods
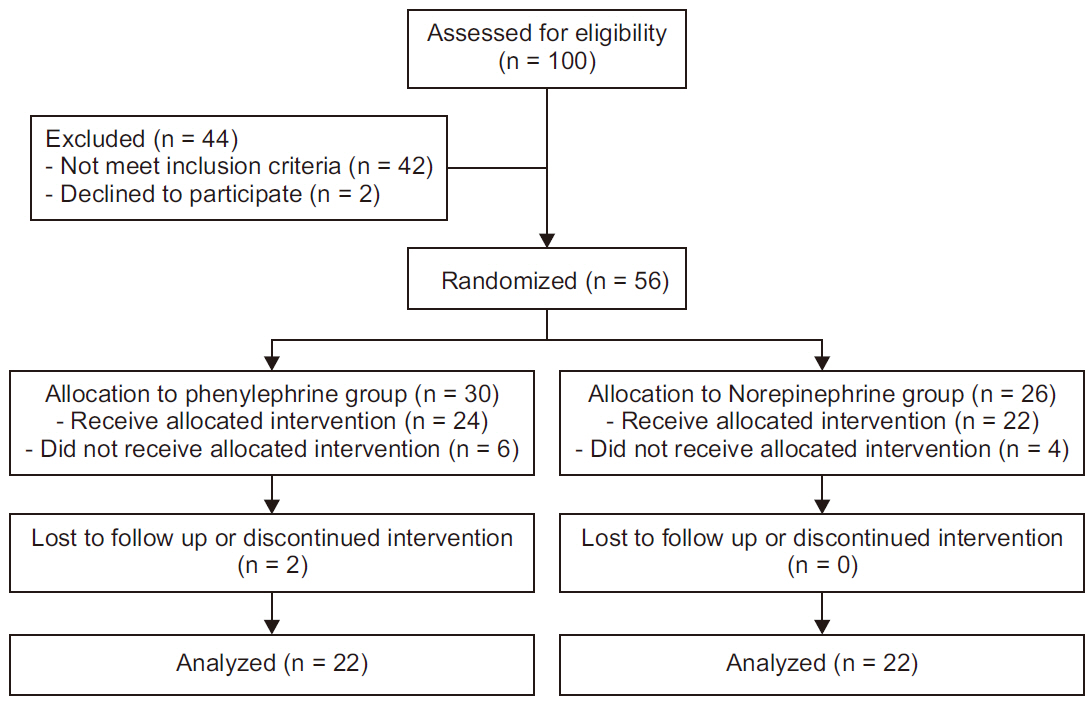
A total of 56 parturients consenting to spinal anesthesia for elective cesarean delivery were randomly assigned to phenylephrine (100 μg/ml) or norepinephrine (5 μg/ ml) intermittent bolus dosing. The primary study outcome was maternal normalized CO, examining and other hemodynamic variables, maternal side effects, and fetal outcomes secondarily.
Results
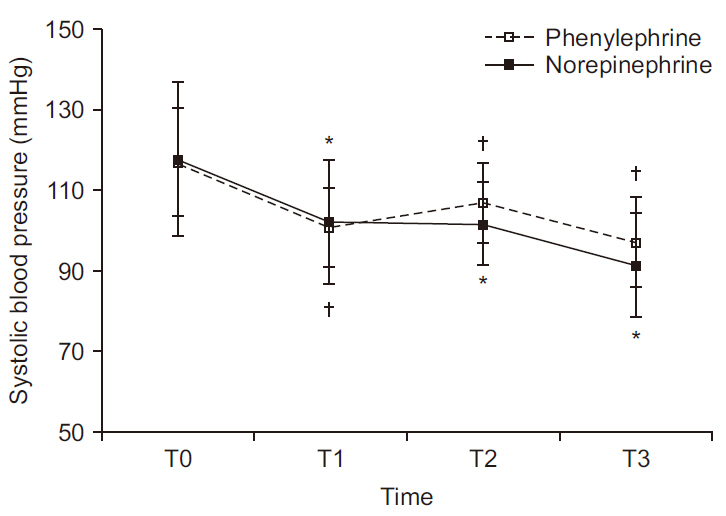
In terms of systolic blood pressure and HR, there were significant within-group differences over time (P < 0.001 and P < 0.001, respectively). Normalized CO and stroke volume (SV) also showed significant differences between groups (P < 0.001 and P = 0.002, respectively). In the phenylephrine group, normalized CO and SV declined (relative to baseline values) by as much as 13% and 9%, respectively; whereas in the norepinephrine group, normalized CO did not differ significantly from baseline, and SV increased up to 5% (relative to baseline). Normalized total peripheral resistance likewise displayed significant within-group differences over time (P < 0.001).
Conclusions
During elective cesarean delivery, intermittent bolus doses of norepinephrine proved effective for treating spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension, while maintaining CO and SV. No maternal complications or fetal effects were evident.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
Ngan Kee WD WD., Lee SW., Ng FF., Tan PE., Khaw KS. 2015. Randomized double-blinded comparison of norepinephrine and phenylephrine for maintenance of blood pressure during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery. Anesthesiology. 122:736–45. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000601. PMID: 25635593.Stewart A., Fernando R., McDonald S., Hignett R., Jones T., Columb M. 2010. The dose-dependent effects of phenylephrine for elective cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 111:1230–7. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e3181f2eae1. PMID: 20841418.Ngan Kee WD WD., Lee SWY., Ng FF., Khaw KS. 2018. Prophylactic norepinephrine infusion for preventing hypotension during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery. Anesth Analg. 126:1989–94. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000002243. PMID: 28678073.Onwochei DN., Ngan Kee WD WD., Fung L., Downey K., Ye XY., Carvalho JCA. 2017. Norepinephrine intermittent intravenous boluses to prevent hypotension during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery: a sequential allocation dose-finding study. Anesth Analg. 125:212–8. DOI: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000001846. PMID: 28248702.Ngan Kee WD WD. 2017. A random-allocation graded dose-response study of norepinephrine and phenylephrine for treating hypotension during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery. Anesthesiology. 127:934–41. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000001880. PMID: 28872480.Langesaeter E., Rosseland LA., Stubhaug A. 2008. Continuous invasive blood pressure and cardiac output monitoring during cesarean delivery: a randomized, double-blind comparison of low-dose versus high-dose spinal anesthesia with intravenous phenylephrine or placebo infusion. Anesthesiology. 109:856–63. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31818a401f. PMID: 18946298.Hamzaoui O., Jozwiak M., Geffriaud T., Sztrymf B., Prat D., Jacobs F, et al. 2018. Norepinephrine exerts an inotropic effect during the early phase of human septic shock. Br J Anaesth. 120:517–24. DOI: 10.1016/j.bja.2017.11.065. PMID: 29452808.Vallejo MC., Attaallah AF., Elzamzamy OM., Cifarelli DT., Phelps AL., Hobbs GR, et al. 2017. An open-label randomized controlled clinical trial for comparison of continuous phenylephrine versus norepinephrine infusion in prevention of spinal hypotension during cesarean delivery. Int J Obstet Anesth. 29:18–25. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2016.08.005. PMID: 27720613.Sjöberg T., Norgren L., Andersson KE., Steen S. 1989. Comparative effects of the alpha-adrenoceptor agonists noradrenaline, phenylephrine and clonidine in the human saphenous vein in vivo and in vitro. Acta Physiol Scand. 136:463–71. DOI: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1989.tb08688.x. PMID: 2568732.Keren H., Burkhoff D., Squara P. 2007. Evaluation of a noninvasive continuous cardiac output monitoring system based on thoracic bioreactance. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 293:H583–9. DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00195.2007. PMID: 17384132.Doherty A., Ohashi Y., Downey K., Carvalho JC. 2011. Non-invasive monitoring based on bioreactance reveals significant hemodynamic instability during elective cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia. Rev Bras Anestesiol. 61:320–5. DOI: 10.1016/S0034-7094(11)70038-1. PMID: 21596192.Smiley RM. 2017. More perfect? Int J Obstet Anesth. 29:1–4. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijoa.2017.01.002. PMID: 28089182.Carvalho B., Dyer RA. 2015. Norepinephrine for spinal hypotension during cesarean delivery: another paradigm shift? Anesthesiology. 122:728–30. DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0000000000000602. PMID: 25654435.Loubani OM., Green RS. 2015. A systematic review of extravasation and local tissue injury from administration of vasopressors through peripheral intravenous catheters and central venous catheters. J Crit Care. 30:653. e9-17. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcrc.2015.01.014. PMID: 25669592.Puolakka J., Kauppila A., Tuimala R., Jouppila R., Vuori J. 1983. The effect of parturition on umbilical blood plasma levels of norepinephrine. Obstet Gynecol. 61:19–21. DOI: 10.1097/00132582-198306000-00010. PMID: 6823345.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Use of vasopressors to manage spinal anesthesia-induced hypotension during cesarean delivery
- Effects of fetal position on maternal hemodynamics after spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery
- Comparison of maternal and fetal effects of ephedrine, phenylephrine, and combination infusion during spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery
- Comparison of hemodynamic changes between phenylephrine and combined phenylephrine and glycopyrrolate groups after spinal anesthesia for cesarean delivery
- Management of hypotension after spinal anesthesia administered for caesarean section