Cancer Res Treat.
2020 Apr;52(2):374-387. 10.4143/crt.2019.198.
Efficacy of Brentuximab Vedotin in Relapsed or RefractoryHigh-CD30–Expressing Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas:Results of a Multicenter, Open-Labeled Phase II Trial
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 2Department of Oncology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 3Division of Hematology, Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea
- 5Center for Hematologic Malignancy, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea
- 6Department of Pathology, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 7Department of Pathology, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 8Department of Pathology, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- 9Department of Pathology, National Cancer Center, Goyang, Korea
- 10Department of Pathology, Korea Cancer Center Hospital, Korea Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Seoul, Korea
- KMID: 2500323
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2019.198
Abstract
- Purpose
The treatment outcome of brentuximab vedotin (BV) has not been related with CD30 expression in previous studies enrolling patients with a wide range of CD30 expression level. Thus, this study explored the efficacy of BV in high-CD30–expressing non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) patients most likely to benefit.
Materials and Methods
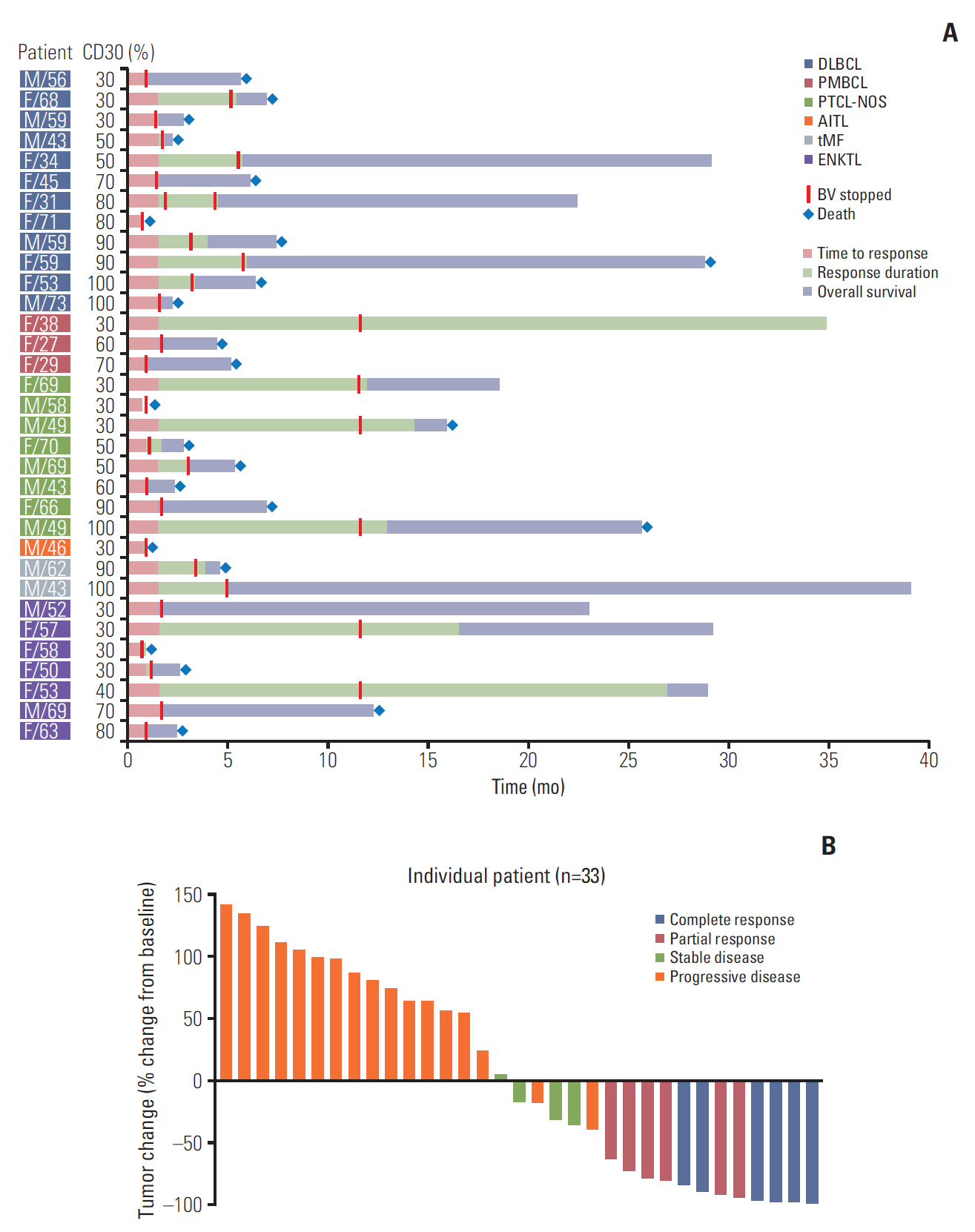
This phase II study (Clinicaltrials.gov: NCT02280785) enrolled relapsed or refractory high- CD30–expressing NHL, with BV administered intravenously at 1.8 mg/kg every 3 weeks. The primary endpoint was > 40% disease control rate, consisting of complete response (CR), partial response (PR), or stable disease. We defined high CD30 expression as ! 30% tumor cells positive for CD30 by immunohistochemistry.
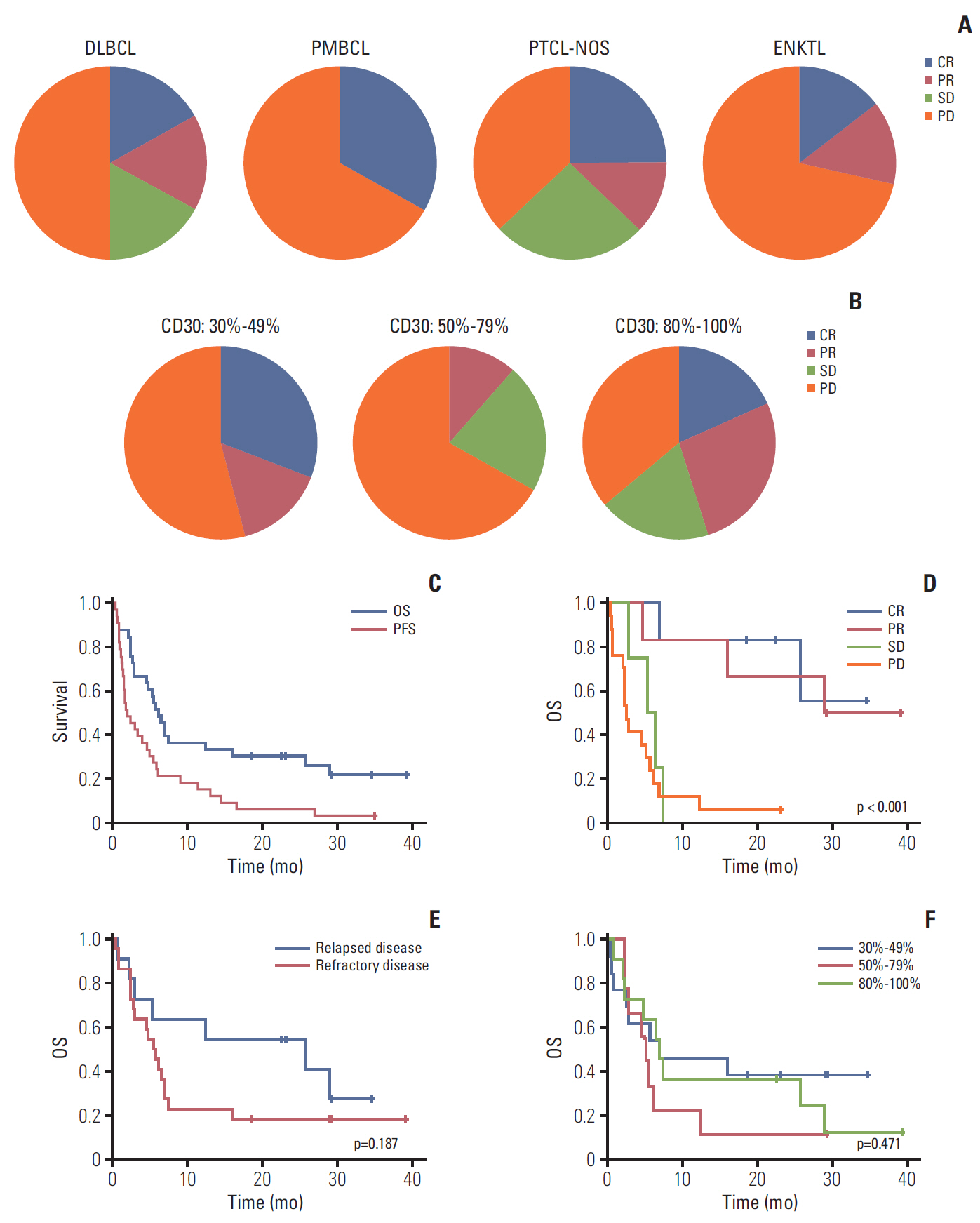
Results
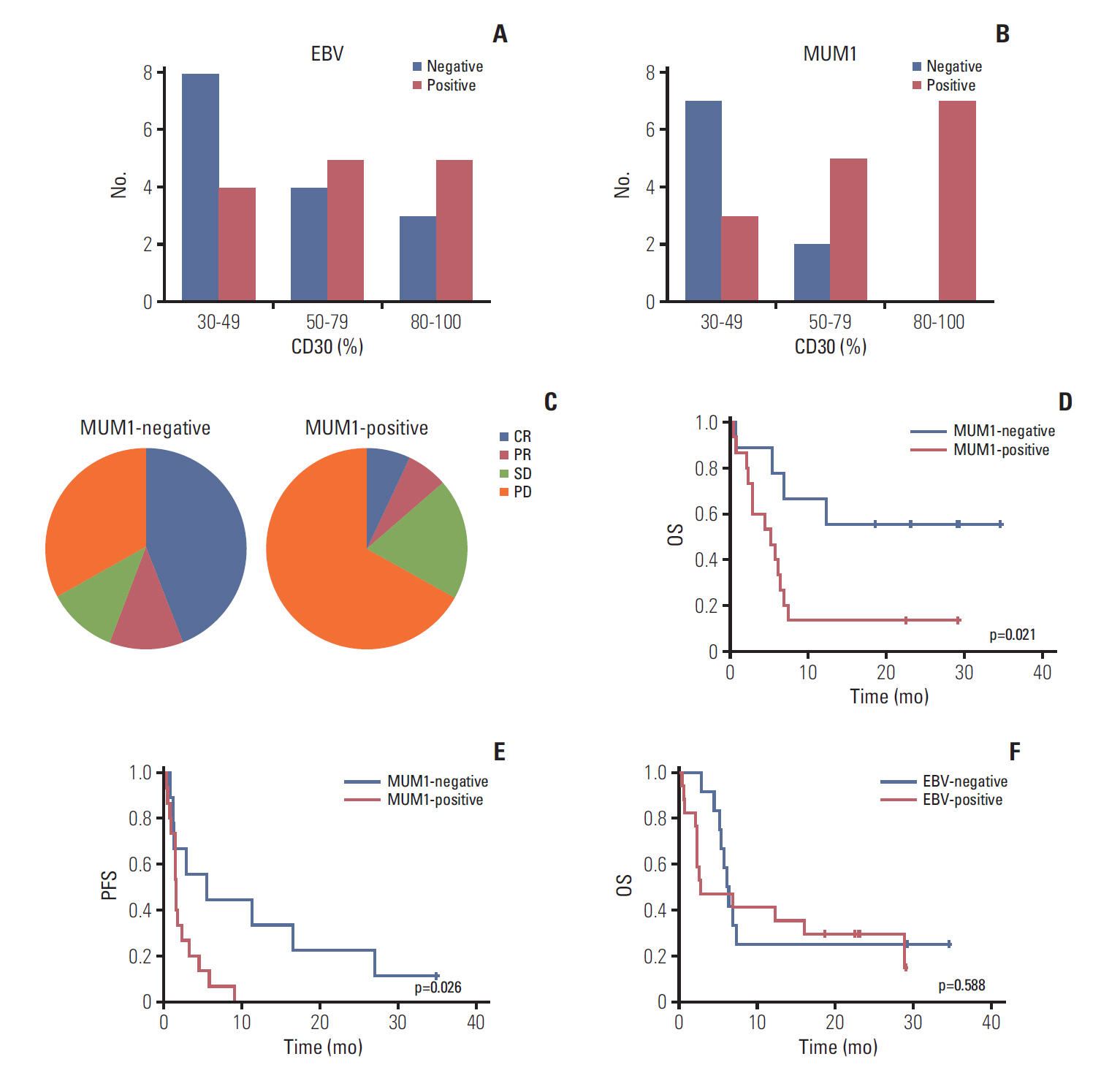
High-CD30-expressing NHL patients (n=33) were enrolled except anaplastic large cell lymphoma. The disease control rate was 48.5% (16/33) including six CR and six PR; six patients (4CR, 2PR) maintained their response over 16 completed cycles. Response to BV and survival were not associated with CD30 expression levels. Over a median of 29.2 months of follow-up, the median progression-free and overall survival rates were 1.9 months and 6.1 months, respectively. The most common adverse events were fever (39%), neutropenia (30%), fatigue (24%), and peripheral sensory neuropathy (27%). In a post-hoc analysis for the association of multiple myeloma oncogene 1 (MUM1) on treatment outcome, MUM1- negative patients showed a higher response (55.6%, 5/9) than MUM1-positive patients (13.3%, 2/15).
Conclusion
BV performance as a single agent was acceptable in terms of disease control rates and toxicity profiles, especially MUM1-negative patients.
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Basic immunohistochemistry for lymphoma diagnosis
Junhun Cho
Blood Res. 2022;57(S1):55-61. doi: 10.5045/br.2022.2022037.
Reference
-
References
1. Francisco JA, Cerveny CG, Meyer DL, Mixan BJ, Klussman K, Chace DF, et al. cAC10-vcMMAE, an anti-CD30-monomethyl auristatin E conjugate with potent and selective antitumor activity. Blood. 2003; 102:1458–65.
Article2. Younes A, Gopal AK, Smith SE, Ansell SM, Rosenblatt JD, Savage KJ, et al. Results of a pivotal phase II study of brentuximab vedotin for patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30:2183–9.3. Pro B, Advani R, Brice P, Bartlett NL, Rosenblatt JD, Illidge T, et al. Brentuximab vedotin (SGN-35) in patients with relapsed or refractory systemic anaplastic large-cell lymphoma: results of a phase II study. J Clin Oncol. 2012; 30:2190–6.
Article4. Duvic M, Tetzlaff MT, Gangar P, Clos AL, Sui D, Talpur R. Results of a phase II trial of brentuximab vedotin for CD30+ cutaneous T-cell lymphoma and lymphomatoid papulosis. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:3759–65.
Article5. Kim YH, Tavallaee M, Sundram U, Salva KA, Wood GS, Li S, et al. Phase II investigator-initiated study of brentuximab vedotin in mycosis fungoides and Sezary syndrome with variable CD30 expression level: a multi-institution collaborative project. J Clin Oncol. 2015; 33:3750–8.6. Jacobsen ED, Sharman JP, Oki Y, Advani RH, Winter JN, Bello CM, et al. Brentuximab vedotin demonstrates objective responses in a phase 2 study of relapsed/refractory DLBCL with variable CD30 expression. Blood. 2015; 125:1394–402.
Article7. Horwitz SM, Advani RH, Bartlett NL, Jacobsen ED, Sharman JP, O'Connor OA, et al. Objective responses in relapsed T-cell lymphomas with single-agent brentuximab vedotin. Blood. 2014; 123:3095–100.
Article8. Zinzani PL, Pellegrini C, Chiappella A, Di Rocco A, Salvi F, Cabras MG, et al. Brentuximab vedotin in relapsed primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma: results from a phase 2 clinical trial. Blood. 2017; 129:2328–30.
Article9. Hu S, Xu-Monette ZY, Balasubramanyam A, Manyam GC, Visco C, Tzankov A, et al. CD30 expression defines a novel subgroup of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with favorable prognosis and distinct gene expression signature: a report from the International DLBCL Rituximab-CHOP Consortium Program Study. Blood. 2013; 121:2715–24.
Article10. Hao X, Wei X, Huang F, Wei Y, Zeng H, Xu L, et al. The expression of CD30 based on immunohistochemistry predicts inferior outcome in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. PLoS One. 2015; 10:e0126615.
Article11. Schwartz EJ, Molina-Kirsch H, Zhao S, Marinelli RJ, Warnke RA, Natkunam Y. Immunohistochemical characterization of nasal-type extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma using a tissue microarray: an analysis of 84 cases. Am J Clin Pathol. 2008; 130:343–51.12. Li P, Jiang L, Zhang X, Liu J, Wang H. CD30 expression is a novel prognostic indicator in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:890.
Article13. Wright CW, Rumble JM, Duckett CS. CD30 activates both the canonical and alternative NF-kappaB pathways in anaplastic large cell lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 2007; 282:10252–62.14. Cao M, Wang Q, Lingel A, Zhang L. Nuclear factor κB represses the expression of latent membrane protein 1 in EpsteinBarr virus transformed cells. World J Virol. 2014; 3:22–9.
Article15. Kim WY, Nam SJ, Kim S, Kim TM, Heo DS, Kim CW, et al. Prognostic implications of CD30 expression in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma according to treatment modalities. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015; 56:1778–86.
Article16. Feng Y, Rao H, Lei Y, Huang Y, Wang F, Zhang Y, et al. CD30 expression in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type among 622 cases of mature T-cell and natural killercell lymphoma at a single institution in South China. Chin J Cancer. 2017; 36:43.
Article17. Boddicker RL, Kip NS, Xing X, Zeng Y, Yang ZZ, Lee JH, et al. The oncogenic transcription factor IRF4 is regulated by a novel CD30/NF-κB positive feedback loop in peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Blood. 2015; 125:3118–27.
Article18. Shaffer AL, Emre NC, Lamy L, Ngo VN, Wright G, Xiao W, et al. IRF4 addiction in multiple myeloma. Nature. 2008; 454:226–31.
Article19. Shaffer AL, Emre NC, Romesser PB, Staudt LM. IRF4: immunity. Malignancy! Therapy? Clin Cancer Res. 2009; 15:2954–61.
Article20. Park S, Kim SJ, Hong JY, Yoon DH, Kim JS, Kang HJ, et al. A phase II study of brentuximab vedotin for relapsed or refractory CD30-positive non-Hodgkin lymphomas other than anaplastic large cell lymphoma. Blood. 2017; 130:4077.21. Cheson BD, Pfistner B, Juweid ME, Gascoyne RD, Specht L, Horning SJ, et al. Revised response criteria for malignant lymphoma. J Clin Oncol. 2007; 25:579–86.
Article22. Simon R. Optimal two-stage designs for phase II clinical trials. Control Clin Trials. 1989; 10:1–10.
Article23. Schemper M, Smith TL. A note on quantifying follow-up in studies of failure time. Control Clin Trials. 1996; 17:343–6.
Article24. Prince HM, Kim YH, Horwitz SM, Dummer R, Scarisbrick J, Quaglino P, et al. Brentuximab vedotin or physician's choice in CD30-positive cutaneous T-cell lymphoma (ALCANZA): an international, open-label, randomised, phase 3, multicentre trial. Lancet. 2017; 390:555–66.25. Chen R, Hou J, Newman E, Kim Y, Donohue C, Liu X, et al. CD30 downregulation, MMAE resistance, and MDR1 upregulation are all associated with resistance to brentuximab vedotin. Mol Cancer Ther. 2015; 14:1376–84.
Article26. Chen RW, Hou J, Nair I, Wu J, Synold T, Kwak LW, et al. Inhibition of MDR1 overcomes brentuximab vedotin resistance in Hodgkin lymphoma cell line model and is synergistic with brentuximab vedotin in mouse xenograft model. Blood. 2016; 128:752.
Article27. Chen RW, Chen L, Herrera AF, Mei M, McBride K, Abary R, et al. Phase 1 study of MDR1 inhibitor plus brentuximab vedotin in relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood. 2018; 132:1636.
Article28. Yamaguchi M, Kita K, Miwa H, Nishii K, Oka K, Ohno T, et al. Frequent expression of P-glycoprotein/MDR1 by nasal T-cell lymphoma cells. Cancer. 1995; 76:2351–6.
Article29. Heo MH, Park HY, Ko YH, Kim WS, Kim SJ. IRF4/MUM1 expression is associated with poor survival outcomes in patients with peripheral T-cell lymphoma. J Cancer. 2017; 8:1018–24.
Article30. Yoshimori M, Takada H, Imadome K, Kurata M, Yamamoto K, Koyama T, et al. P-glycoprotein is expressed and causes resistance to chemotherapy in EBV-positive T-cell lymphoproliferative diseases. Cancer Med. 2015; 4:1494–504.31. Yi JH, Kim SJ, Kim WS. Brentuximab vedotin: clinical updates and practical guidance. Blood Res. 2017; 52:243–53.
Article32. Oak E, Bartlett NL. A safety evaluation of brentuximab vedotin for the treatment of Hodgkin lymphoma. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016; 15:875–82.
Article33. Horwitz S, O'Connor OA, Pro B, Illidge T, Fanale M, Advani R, et al. Brentuximab vedotin with chemotherapy for CD30-positive peripheral T-cell lymphoma (ECHELON-2): a global, double-blind, randomised, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2019; 393:229–40.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Brentuximab vedotin: clinical updates and practical guidance
- A multi-center and non-interventional registry of brentuximab vedotin in patients with relapsed or refractory CD30-positive lymphoma: the CISL1803/BRAVO study
- CD30 (Ber H2) Distribution in Hodgkin's Disease and non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
- CD30+ Large-Cell Transformation of Mycosis Fungoides Treated with Brentuximab Vedotin
- A Case of Atypical CD30+ Lymphocytic Hyperplasia Following Tick Bite