Korean J Radiol.
2020 Apr;21(4):402-412. 10.3348/kjr.2019.0538.
Preoperative Prediction for Early Recurrence Can Be as Accurate as Postoperative Assessment in Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology and Center for Imaging Science, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. kmmks.jang@samsung.com
- 2Department of Mathematics, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- KMID: 2471806
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2019.0538
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the performance of predicting early recurrence using preoperative factors only in comparison with using both pre-/postoperative factors.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
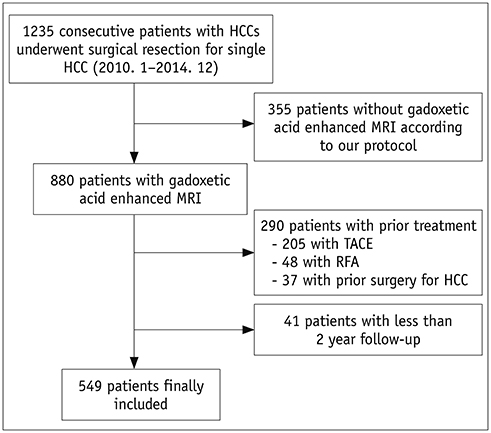
We retrospectively reviewed 549 patients who had undergone curative resection for single hepatcellular carcinoma (HCC) within Milan criteria. Multivariable analysis was performed to identify pre-/postoperative high-risk factors of early recurrence after hepatic resection for HCC. Two prediction models for early HCC recurrence determined by stepwise variable selection methods based on Akaike information criterion were built, either based on preoperative factors alone or both pre-/postoperative factors. Area under the curve (AUC) for each receiver operating characteristic curve of the two models was calculated, and the two curves were compared for non-inferiority testing. The predictive models of early HCC recurrence were internally validated by bootstrap resampling method.
RESULTS
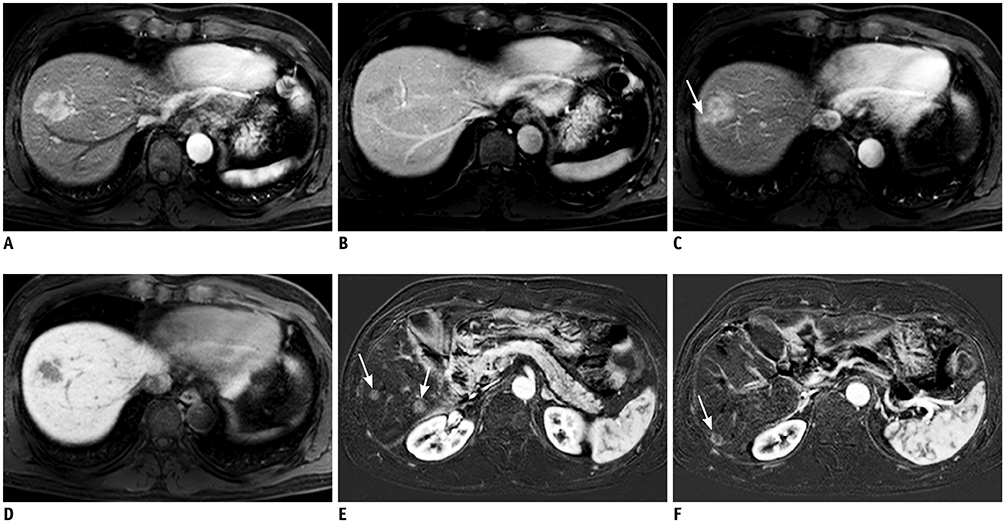
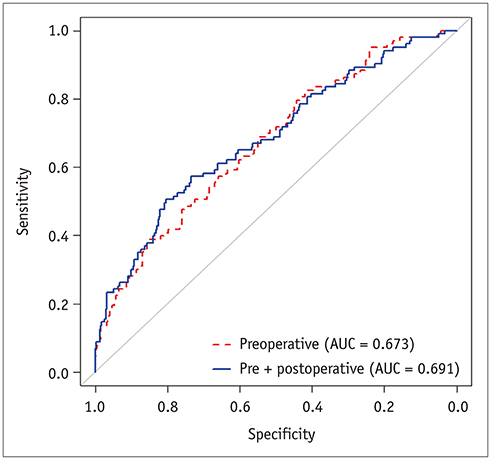
Multivariable analysis on preoperative factors alone identified aspartate aminotransferase/platelet ratio index (OR, 1.632; 95% CI, 1.056-2.522; p = 0.027), tumor size (OR, 1.025; 95% CI, 0.002-1.049; p = 0.031), arterial rim enhancement of the tumor (OR, 2.350; 95% CI, 1.297-4.260; p = 0.005), and presence of nonhypervascular hepatobiliary hypointense nodules (OR, 1.983; 95% CI, 1.049-3.750; p = 0.035) on gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging as significant factors. After adding postoperative histopathologic factors, presence of microvascular invasion (OR, 1.868; 95% CI, 1.155-3.022; p = 0.011) became an additional significant factor, while tumor size became insignificant (p = 0.119). Comparison of the AUCs of the two models showed that the prediction model built on preoperative factors alone was not inferior to that including both pre-/postoperative factors {AUC for preoperative factors only, 0.673 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.623-0.723) vs. AUC after adding postoperative factors, 0.691 (95% CI, 0.639-0.744); p = 0.0013}. Bootstrap resampling method showed that both the models were valid.
CONCLUSION
Risk stratification solely based on preoperative imaging and laboratory factors was not inferior to that based on postoperative histopathologic risk factors in predicting early recurrence after curative resection in within Milan criteria single HCC patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Harada T, Shigemura T, Kodama S, Higuchi T, Ikeda S, Okazaki M. Hepatic resection is not enough for hepatocellular carcinoma. A follow-up study of 92 patients. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1992; 14:245–250.
Article2. Shah SA, Cleary SP, Wei AC, Yang I, Taylor BR, Hemming AW, et al. Recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: risk factors, treatment, and outcomes. Surgery. 2007; 141:330–339.
Article3. Tung-Ping Poon R, Fan ST, Wong J. Risk factors, prevention, and management of postoperative recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann Surg. 2000; 232:10–24.
Article4. Portolani N, Coniglio A, Ghidoni S, Giovanelli M, Benetti A, Tiberio GA, et al. Early and late recurrence after liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma: prognostic and therapeutic implications. Ann Surg. 2006; 243:229–235.5. Poon RT, Fan ST, Ng IO, Lo CM, Liu CL, Wong J. Different risk factors and prognosis for early and late intrahepatic recurrence after resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer. 2000; 89:500–507.
Article6. Imamura H, Matsuyama Y, Tanaka E, Ohkubo T, Hasegawa K, Miyagawa S, et al. Risk factors contributing to early and late phase intrahepatic recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 2003; 38:200–207.
Article7. Cucchetti A, Piscaglia F, Caturelli E, Benvegnù L, Vivarelli M, Ercolani G, et al. Comparison of recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection in patients with cirrhosis to its occurrence in a surveilled cirrhotic population. Ann Surg Oncol. 2009; 16:413–422.
Article8. Nagasue N, Uchida M, Makino Y, Takemoto Y, Yamanoi A, Hayashi T, et al. Incidence and factors associated with intrahepatic recurrence following resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1993; 105:488–494.
Article9. Shen SL, Fu SJ, Chen B, Kuang M, Li SQ, Hua YP, et al. Preoperative aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio is an independent prognostic factor for hepatitis B-induced hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatic resection. Ann Surg Oncol. 2014; 21:3802–3809.
Article10. Lee S, Kim SH, Lee JE, Sinn DH, Park CK. Preoperative gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI for predicting microvascular invasion in patients with single hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2017; 67:526–534.
Article11. An C, Kim DW, Park YN, Chung YE, Rhee H, Kim MJ. Single hepatocellular carcinoma: preoperative MR imaging to predict early recurrence after curative resection. Radiology. 2015; 276:433–443.
Article12. Lee DH, Lee JM, Lee JY, Kim SH, Kim JH, Yoon JH, et al. Non-hypervascular hepatobiliary phase hypointense nodules on gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI: risk of HCC recurrence after radiofrequency ablation. J Hepatol. 2015; 62:1122–1130.
Article13. Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, Zhu AX, Finn RS, Abecassis MM, et al. Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018; 68:723–750.
Article14. Cillo U, Giuliani T, Polacco M, Herrero Manley LM, Crivellari G, Vitale A. Prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma biological behavior in patient selection for liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol. 2016; 22:232–252.
Article15. Gomez D, Farid S, Malik HZ, Young AL, Toogood GJ, Lodge JP, et al. Preoperative neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio as a prognostic predictor after curative resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg. 2008; 32:1757–1762.
Article16. Ji F, Liang Y, Fu SJ, Guo ZY, Shu M, Shen SL, et al. A novel and accurate predictor of survival for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection: the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) combined with the aspartate aminotransferase/platelet count ratio index (APRI). BMC Cancer. 2016; 16:137.
Article17. Dong ZR, Zou J, Sun D, Shi GM, Ke AW, Cai JB, et al. Preoperative albumin-bilirubin score for postoperative solitary hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria and Child-Pugh A cirrhosis. J Cancer. 2017; 8:3862–3867.
Article18. Ariizumi S, Kitagawa K, Kotera Y, Takahashi Y, Katagiri S, Kuwatsuru R, et al. A non-smooth tumor margin in the hepatobiliary phase of gadoxetic acid disodium (Gd-EOB-DTPA)-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging predicts microscopic portal vein invasion, intrahepatic metastasis, and early recurrence after hepatectomy in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2011; 18:575–585.19. Choi JY, Lee JM, Sirlin CB. CT and MR imaging diagnosis and staging of hepatocellular carcinoma: part II. Extracellular agents, hepatobiliary agents, and ancillary imaging features. Radiology. 2014; 273:30–50.
Article20. Prasad SR, Wang H, Rosas H, Menias CO, Narra VR, Middleton WD, et al. Fat-containing lesions of the liver: radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2005; 25:321–331.
Article21. Roayaie S, Blume IN, Thung SN, Guido M, Fiel MI, Hiotis S, et al. A system of classifying microvascular invasion to predict outcome after resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 2009; 137:850–855.
Article22. Fuks D, Dokmak S, Paradis V, Diouf M, Durand F, Belghiti J. Benefit of initial resection of hepatocellular carcinoma followed by transplantation in case of recurrence: an intention-to-treat analysis. Hepatology. 2012; 55:132–140.
Article23. Kim H, Park MS, Choi JY, Park YN, Kim MJ, Kim KS, et al. Can microvessel invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma be predicted by pre-operative MRI? Eur Radiol. 2009; 19:1744–1751.
Article24. Kim KA, Kim MJ, Jeon HM, Kim KS, Choi JS, Ahn SH, et al. Prediction of microvascular invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma: usefulness of peritumoral hypointensity seen on gadoxetate disodium-enhanced hepatobiliary phase images. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 35:629–634.
Article25. Toyoda H, Kumada T, Tada T, Niinomi T, Ito T, Sone Y, et al. Non-hypervascular hypointense nodules detected by Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI are a risk factor for recurrence of HCC after hepatectomy. J Hepatol. 2013; 58:1174–1180.
Article26. Okamoto D, Yoshimitsu K, Nishie A, Tajima T, Asayama Y, Ishigami K, et al. Enhancement pattern analysis of hypervascular hepatocellular carcinoma on dynamic MR imaging with histopathological correlation: validity of portal phase imaging for predicting tumor grade. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 81:1116–1121.
Article27. Liu JP, Ma MC, Wu CY, Tai JY. Tests of equivalence and non-inferiority for diagnostic accuracy based on the paired areas under ROC curves. Stat Med. 2006; 25:1219–1238.
Article28. Neter J, Wasserman W, Kutner MH. Multicollinearity diagnostics—variance inflation factor. In : Kutner MH, Nachtsheim CJ, Neter J, Li W, editors. Applied linear statistical models. 5th ed. Homewood, IL: McGraw-Hill Irwin;1990. p. 407–411.29. Efron B, Tibshirani RJ. An introduction to the bootstrap. New York, NY: Chapman and Hall;1993.30. Lim KC, Chow PK, Allen JC, Chia GS, Lim M, Cheow PC, et al. Microvascular invasion is a better predictor of tumor recurrence and overall survival following surgical resection for hepatocellular carcinoma compared to the Milan criteria. Ann Surg. 2011; 254:108–113.
Article31. Tsai TJ, Chau GY, Lui WY, Tsay SH, King KL, Loong CC, et al. Clinical significance of microscopic tumor venous invasion in patients with resectable hepatocellular carcinoma. Surgery. 2000; 127:603–608.
Article32. Sumie S, Kuromatsu R, Okuda K, Ando E, Takata A, Fukushima N, et al. Microvascular invasion in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and its predictable clinicopathological factors. Ann Surg Oncol. 2008; 15:1375–1382.
Article33. Pawlik TM, Delman KA, Vauthey JN, Nagorney DM, Ng IO, Ikai I, et al. Tumor size predicts vascular invasion and histologic grade: implications for selection of surgical treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transpl. 2005; 11:1086–1092.
Article34. Du M, Chen L, Zhao J, Tian F, Zeng H, Tan Y, et al. Microvascular invasion (MVI) is a poorer prognostic predictor for small hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2014; 14:38.
Article35. Yamashita Y, Tsuijita E, Takeishi K, Fujiwara M, Kira S, Mori M, et al. Predictors for microinvasion of small hepatocellular carcinoma ≤ 2 cm. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012; 19:2027–2034.36. Wai CT, Greenson JK, Fontana RJ, Kalbfleisch JD, Marrero JA, Conjeevaram HS, et al. A simple noninvasive index can predict both significant fibrosis and cirrhosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology. 2003; 38:518–526.
Article37. Hung HH, Su CW, Lai CR, Chau GY, Chan CC, Huang YH, et al. Fibrosis and AST to platelet ratio index predict post-operative prognosis for solitary small hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Int. 2010; 4:691–699.
Article38. Hann HW, Wan S, Lai Y, Hann RS, Myers RE, Patel F, et al. Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index as a prospective predictor of hepatocellular carcinoma risk in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015; 30:131–138.
Article39. Nieswandt B, Hafner M, Echtenacher B, Männel DN. Lysis of tumor cells by natural killer cells in mice is impeded by platelets. Cancer Res. 1999; 59:1295–1300.40. Kamimoto Y, Horiuchi S, Tanase S, Morino Y. Plasma clearance of intravenously injected aspartate aminotransferase isozymes: evidence for preferential uptake by sinusoidal liver cells. Hepatology. 1985; 5:367–375.
Article41. Kumada T, Toyoda H, Kiriyama S, Tanikawa M, Hisanaga Y, Kanamori A, et al. Predictive value of tumor markers for hepatocarcinogenesis in patients with hepatitis C virus. J Gastroenterol. 2011; 46:536–544.
Article42. Kim HC, Nam CM, Jee SH, Han KH, Oh DK, Suh I. Normal serum aminotransferase concentration and risk of mortality from liver diseases: prospective cohort study. BMJ. 2004; 328:983.
Article43. Golfieri R, Renzulli M, Lucidi V, Corcioni B, Trevisani F, Bolondi L. Contribution of the hepatobiliary phase of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI to dynamic MRI in the detection of hypovascular small (≤ 2 cm) HCC in cirrhosis. Eur Radiol. 2011; 21:1233–1242.44. Kim YK, Lee WJ, Park MJ, Kim SH, Rhim H, Choi D. Hypovascular hypointense nodules on hepatobiliary phase gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR images in patients with cirrhosis: potential of DW imaging in predicting progression to hypervascular HCC. Radiology. 2012; 265:104–114.
Article45. Jin S, Zhang B, Zhang L, Li S, Li S, Li P. Lung nodules assessment in ultra-low-dose CT with iterative reconstruction compared to conventional dose CT. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2018; 8:480–490.
Article46. Hwang J, Kim YK, Jeong WK, Choi D, Rhim H, Lee WJ. Nonhypervascular hypointense nodules at gadoxetic acid-enhanced MR imaging in chronic liver disease: diffusion-weighted imaging for characterization. Radiology. 2015; 276:137–146.
Article47. Kim SH, Lim HK, Lee WJ, Choi D, Park CK. Scirrhous hepatocellular carcinoma: comparison with usual hepatocellular carcinoma based on CT-pathologic features and long-term results after curative resection. Eur J Radiol. 2009; 69:123–130.
Article48. Gu KW, Kim YK, Min JH, Ha SY, Jeong WK. Imaging features of hepatic sarcomatous carcinoma on computed tomography and gadoxetic acid-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017; 42:1424–1433.
Article49. Jeong HT, Kim MJ, Kim YE, Park YN, Choi GH, Choi JS. MRI features of hepatocellular carcinoma expressing progenitor cell markers. Liver Int. 2012; 32:430–440.
Article50. Uenishi T, Kubo S, Yamamoto T, Shuto T, Ogawa M, Tanaka H, et al. Cytokeratin 19 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts early postoperative recurrence. Cancer Sci. 2003; 94:851–857.
Article51. Zhang X, Li J, Shen F, Lau WY. Significance of presence of microvascular invasion in specimens obtained after surgical treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018; 33:347–354.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The risk factors of early recurrence after hepatectomy in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Difference in Early Postoperative Recurrence Rate of Hepatocellular Carcinoma According to the Imaging Modalities Used for Preoperative Staging : Comparison Between CTAP and CTHA, Lipiodol CT and Three Phase Helical CT
- Recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma after surgical resection:angiographic pattern and predictors for early recurrence
- The Risk Factors for Intrahepatic Early Recurrence after Resection for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Development of risk scores for prognosis prediction among patients with early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma