J Breast Cancer.
2020 Feb;23(1):69-79. 10.4048/jbc.2020.23.e13.
Expression of Histo-blood Group Antigens in Tumor and Adjacent Normal Breast Tissues as Prognostic Markers of Breast Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Laboratory of Biotechnology and Experimental Medicine, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, University of Hassan II Casablanca, Casablanca, Morocco.
- 2Laboratory of Hematology, Cellular and Genetic Engineering, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, University of Hassan II Casablanca, Casablanca, Morocco.
- 3Pathology Department, University Hospital Ibn Rochd, Casablanca, Morocco.
- 4Laboratory of Medical Informatics, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, University of Hassan II Casablanca, Casablanca, Morocco.
- 5Department of Biology, Faculty of Sciences, Mohammed V University, Rabat, Morocco. younes_zaid@yahoo.ca
- 6Laboratory of Thrombosis and Hemostasis, Montreal Heart Institute, Montreal, QC, Canada.
- 7Department of Medicine, Research Center, Abulcasis University of Health Sciences, Rabat, Morocco.
- 8Pathology Laboratory, Faculty of Medicine and Pharmacy, University of Hassan II Casablanca, Casablanca, Morocco.
- KMID: 2470883
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4048/jbc.2020.23.e13
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Aberrant glycosylation of the histo-blood group antigens (including the angina bullosa haemorrhagica [ABH]) is often observed during malignant transformation in most types of carcinomas. Data concerning their ethnic distributions are diverse which explains why their biological characteristics have to be studied in different populations. Our aim was to analyze the expression of the histo-blood group (specifically the ABH) antigens in breast carcinoma.
METHODS
The expression of the histo-blood group (specifically the ABH) antigens was studied in 109 patients with breast carcinoma using immunohistochemistry. Statistical analysis was performed using χ² and Fisher analyses.
RESULTS
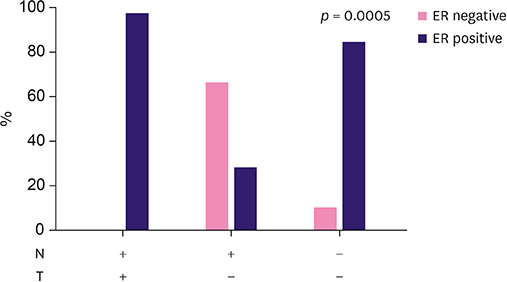
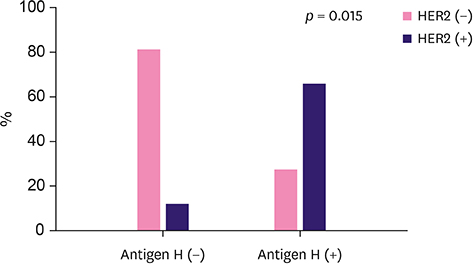
The loss of expression of histo-blood group (ABH) antigens in breast carcinoma was observed in 81.13% of patients with blood group O, 37.93% with blood group A, and 96.30% with blood group B. One key finding of this study was that the loss of expression of the ABH antigen was also observed in normal tissues adjacent to the tumor. The loss of expression was associated with higher tumor grade (p < 0.05). Expression of H antigen was observed in 50% of cases with loss of expression of B antigen and was associated with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) overexpression (p < 0.05). The loss of H antigen in patients with blood group O was associated with estrogen receptor expression (p < 0.001). Incompatible A antigen in tumor was expressed in 20.75% of patients with blood group O.
CONCLUSION
Loss of the ABH antigens correlated with the Scarff-Bloom-Richardson histologic grading. H antigen was associated with HER2 overexpression in breast cancer. However, further studies are needed to determine the role of incompatible A antigen in mammary carcinogenesis.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Storry JR, Olsson ML. The ABO blood group system revisited: a review and update. Immunohematology. 2009; 25:48–59.
Article2. Wang B, Akiyama K, Jia JT, Kimura H. Measuring H type 1 and H type 2 antigens in human saliva by immunoassay using artificial antigens as standard substances. Forensic Sci Int. 1994; 67:1–8.
Article3. Orntoft TF, Holmes EH, Johnson P, Hakomori S, Clausen H. Differential tissue expression of the Lewis blood group antigens: enzymatic, immunohistologic, and immunochemical evidence for Lewis a and b antigen expression in Le(a-b-) individuals. Blood. 1991; 77:1389–1396.
Article4. Alfaro JA, Zheng RB, Persson M, Letts JA, Polakowski R, Bai Y, et al. ABO(H) blood group A and B glycosyltransferases recognize substrate via specific conformational changes. J Biol Chem. 2008; 283:10097–10108.
Article5. Ravn V, Dabelsteen E. Tissue distribution of histo-blood group antigens. APMIS. 2000; 108:1–28.6. Eastlund T. The histo-blood group ABO system and tissue transplantation. Transfusion. 1998; 38:975–988.
Article7. Dabelsteen E, Gao S. ABO blood-group antigens in oral cancer. J Dent Res. 2005; 84:21–28.
Article8. Le Pendu J, Marionneau S, Cailleau-Thomas A, Rocher J, Le Moullac-Vaidye B, Clément M. ABH and Lewis histo-blood group antigens in cancer. APMIS. 2001; 109:9–31.
Article9. Ichikawa D, Handa K, Hakomori S. Histo-blood group A/B antigen deletion/reduction vs. continuous expression in human tumor cells as correlated with their malignancy. Int J Cancer. 1998; 76:284–289.
Article10. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90.
Article11. El Fakir S, Najdi A, Khazraji YC, Bennani M, Belakhel L, Abousselham L, et al. Breast cancer screening in Morocco: performance indicators during two years of an organized programme. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2015; 16:6285–6288.
Article12. Bloom HJ, Richardson WW. Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer; a study of 1409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer. 1957; 11:359–377.
Article13. Penault-Llorca F, Balaton A, Sabourin JC, Le Doussal V. . Immunochemistry evaluation of HER2 status in infiltration breast cancer: technical protocol and interpretation guidelines. Ann Pathol. 2002; 22:150–157.14. Davidsohn I, Kovarik S, Ni LY. Isoantigens A, B, and H in benign and malignant lesions of the cervix. Arch Pathol. 1969; 87:306–314.15. Orntoft TF, Hvid H, Clausen H, Hakomori S, Dabelsteen E. Loss of blood group ABO-related antigen expression in urothelium from patients with chronic cystitis. Lab Invest. 1989; 60:305–310.16. Nakagoe T, Fukushima K, Hirota M, Kusano H, Ayabe H, Tomita M, et al. An immunohistochemical study of the distribution of blood group substances and related antigens in primary colorectal carcinomas and metastatic lymph node and liver lesions, using monoclonal antibodies against A, B, H type 2, Le(a), and Le(x) antigens. J Gastroenterol. 1994; 29:265–275.
Article17. Kay HE, Wallace DM. A and B antigens of tumors arising from urinary epithelium. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1961; 26:1349–1365.18. Kapadia A, Feizi T, Jewell D, Keeling J, Slavin G. Immunocytochemical studies of blood group A, H, I, and i antigens in gastric mucosae of infants with normal gastric histology and of patients with gastric carcinoma and chronic benign peptic ulceration. J Clin Pathol. 1981; 34:320–337.
Article19. Ichikawa D, Handa K, Withers DA, Hakomori S. Histo-blood group A/B versus H status of human carcinoma cells as correlated with haptotactic cell motility: approach with A and B gene transfection. Cancer Res. 1997; 57:3092–3096.20. Dabelsteen E, Vedtofte P, Hakomori S, Young WW Jr. Accumulation of a blood group antigen precursor in oral premalignant lesions. Cancer Res. 1983; 43:1451–1454.21. Halloran MM, Carley WW, Polverini PJ, Haskell CJ, Phan S, Anderson BJ, et al. Ley/H: an endothelial-selective, cytokine-inducible, angiogenic mediator. J Immunol. 2000; 164:4868–4877.
Article22. Goupille C, Marionneau S, Bureau V, Hallouin F, Meichenin M, Rocher J, et al. α1,2Fucosyltransferase increases resistance to apoptosis of rat colon carcinoma cells. Glycobiology. 2000; 10:375–382.
Article23. Lin WM, Karsten U, Goletz S, Cheng RC, Cao Y. Co-expression of CD173 (H2) and CD174 (Lewis Y) with CD44 suggests that fucosylated histo-blood group antigens are markers of breast cancer-initiating cells. Virchows Arch. 2010; 456:403–409.
Article24. Ross JS, Fletcher JA. The HER-2/neu oncogene in breast cancer: prognostic factor, predictive factor, and target for therapy. Stem Cells. 1998; 16:413–428.
Article25. Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA, Dressler LG, Cowan D, Conway K, et al. Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina Breast Cancer Study. JAMA. 2006; 295:2492–2502.
Article26. Gao S, Worm J, Guldberg P, Eiberg H, Krogdahl A, Liu CJ, et al. Genetic and epigenetic alterations of the blood group ABO gene in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2004; 109:230–237.
Article27. Hirohashi S, Clausen H, Yamada T, Shimosato Y, Hakomori S. Blood group A cross-reacting epitope defined by monoclonal antibodies NCC-LU-35 and -81 expressed in cancer of blood group O or B individuals: its identification as Tn antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985; 82:7039–7043.
Article28. Kawaguchi T, Takazawa H, Imai S, Morimoto J, Watanabe T, Kanno M, et al. Expression of Vicia villosa agglutinin (VVA)-binding glycoprotein in primary breast cancer cells in relation to lymphatic metastasis: is atypical MUC1 bearing Tn antigen a receptor of VVA? Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2006; 98:31–43.
Article29. Nakagoe T, Fukushima K, Nanashima A, Sawai T, Tsuji T, Jibiki MA, et al. Comparison of the expression of ABH/Lewis-related antigens in polypoid and non-polypoid growth types of colorectal carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001; 16:176–183.
Article30. Marionneau S, Le Moullac-Vaidye B, Le Pendu J. Expression of histo-blood group A antigen increases resistance to apoptosis and facilitates escape from immune control of rat colon carcinoma cells. Glycobiology. 2002; 12:851–856.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Telomerase Activity in Human Breast Tumors
- Telomerase Activity in Human Breast Tumors
- Quantitative Measurement of Serum MicroRNA-21 Expression in Relation to Breast Cancer Metastasis in Chinese Females
- An Immunohistochemical Study for the neu and ras Oncoprotein and Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor in the Breast Carcinoma
- Prognosis of GLUT1 Expression in Human Breast Carcinoma