Korean J Radiol.
2020 Mar;21(3):290-297. 10.3348/kjr.2019.0217.
Comparison of Three Magnetization Transfer Ratio Parameters for Assessment of Intestinal Fibrosis in Patients with Crohn's Disease
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China. lixuehua803@163.com
- 2Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, MO, USA.
- 3Department of Gastroenterology, The First Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-Sen University, Guangzhou, China.
- KMID: 2470752
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2019.0217
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To establish a novel standardized magnetization transfer ratio (MTR) parameter which considers the element of the normal bowel wall and to compare the efficacy of the MTR, normalized MTR, and standardized MTR in evaluating intestinal fibrosis in Crohn's disease (CD).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Abdominal magnetization transfer imaging from 20 consecutive CD patients were analyzed before performing elective operations. MTR parameters were calculated by delineating regions of interest in specified segments on MTR maps. Specimens with pathologically confirmed bowel fibrosis were classified into one of four severity grades. The correlation between MTR parameters and fibrosis score was tested by Spearman's rank correlation. Differences in MTR, normalized MTR, and standardized MTR across diverse histologic fibrosis scores were analyzed using the independent sample t test or the Mann-Whitney U test. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was computed to test the efficacies of the MTR parameters in differentiating severe intestinal fibrosis from mild-to-moderate fibrosis.
RESULTS
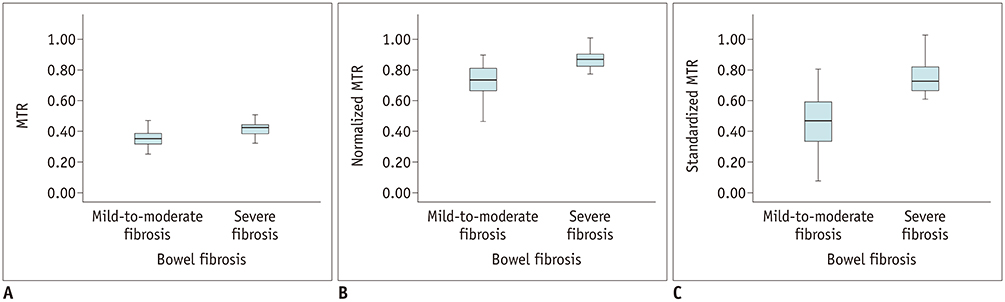
Normalized (r = 0.700; p < 0.001) and standardized MTR (r = 0.695; p < 0.001) showed a strong correlation with bowel fibrosis scores, followed by MTR (r = 0.590; p < 0.001). Significant differences in MTR (t = −4.470; p < 0.001), normalized MTR (Z = −5.003; p < 0.001), and standardized MTR (Z = −5.133; p < 0.001) were found between mild-to-moderate and severe bowel fibrosis. Standardized MTR (AUC = 0.895; p < 0.001) had the highest accuracy in differentiating severe bowel fibrosis from mild-to-moderate bowel wall fibrosis, followed by normalized MTR (AUC = 0.885; p < 0.001) and MTR (AUC = 0.798; p < 0.001).
CONCLUSION
Standardized MTR is slightly superior to MTR and normalized MTR and therefore may be an optimal parameter for evaluating the severity of intestinal fibrosis in CD.
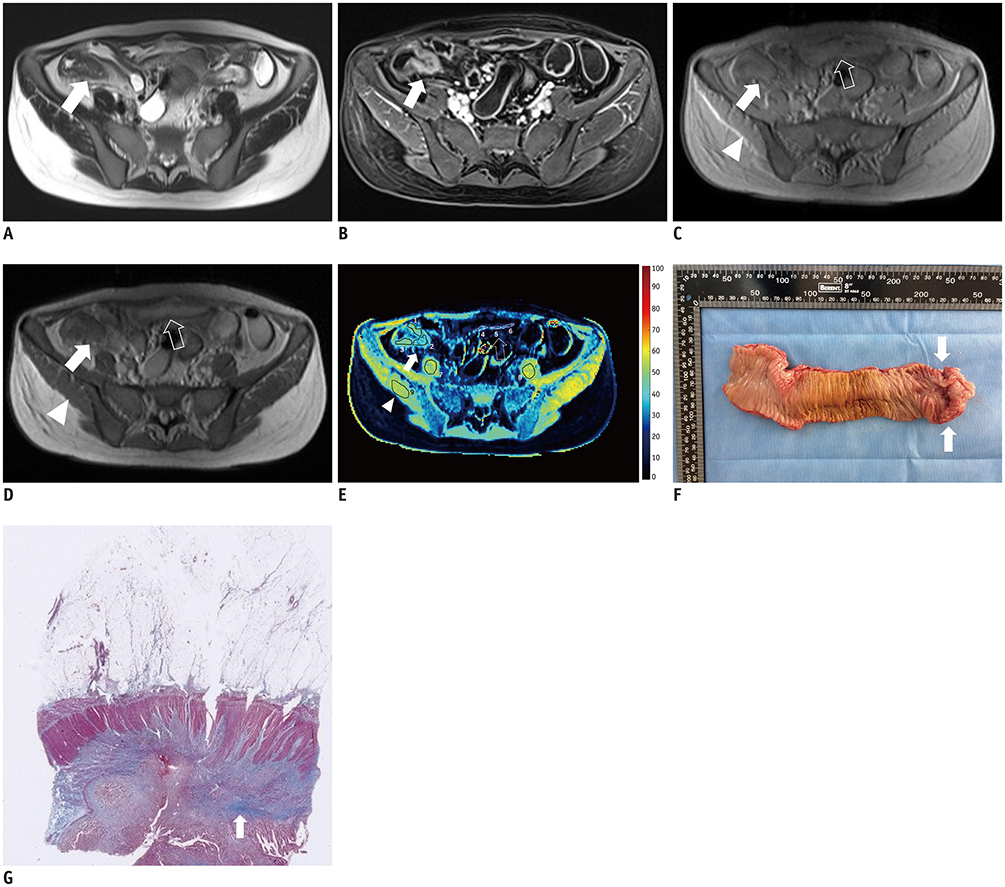
Figure
Reference
-
1. Latella G, Di Gregorio J, Flati V, Rieder F, Lawrance IC. Mechanisms of initiation and progression of intestinal fibrosis in IBD. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015; 50:53–65.
Article2. Adler J, Swanson SD, Schmiedlin-Ren P, Higgins PD, Golembeski CP, Polydorides AD, et al. Magnetization transfer helps detect intestinal fibrosis in an animal model of Crohn disease. Radiology. 2011; 259:127–135.
Article3. Dillman JR, Swanson SD, Johnson LA, Moons DS, Adler J, Stidham RW, et al. Comparison of noncontrast MRI magnetization transfer and T2-weighted signal intensity ratios for detection of bowel wall fibrosis in a Crohn's disease animal model. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2015; 42:801–810.4. Adler J, Rahal K, Swanson SD, Schmiedlin-Ren P, Rittershaus AC, Reingold LJ, et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor α prevents bowel fibrosis assessed by messenger RNA, histology, and magnetization transfer MRI in rats with Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2013; 19:683–690.
Article5. Rieder F, Fiocchi C. Mechanisms of tissue remodeling in inflammatory bowel disease. Dig Dis. 2013; 31:186–193.
Article6. Henkelman RM, Stanisz GJ, Graham SJ. Magnetization transfer in MRI: a review. NMR Biomed. 2001; 14:57–64.
Article7. Pazahr S, Blume I, Frei P, Chuck N, Nanz D, Rogler G, et al. Magnetization transfer for the assessment of bowel fibrosis in patients with Crohn's disease: initial experience. MAGMA. 2013; 26:291–301.
Article8. Aisen AM. Science to practice: can the diagnosis of fibrosis with magnetization contrast MR aid in the evaluation of patients with Crohn disease? Radiology. 2011; 259:1–3.
Article9. Li XH, Mao R, Huang SY, Sun CH, Cao QH, Fang ZN, et al. Characterization of degree of intestinal fibrosis in patients with Crohn disease by using magnetization transfer MR imaging. Radiology. 2018; 287:494–503.
Article10. Li XH, Sun CH, Mao R, Zhang ZW, Jiang XS, Pui MH, et al. Assessment of activity of Crohn disease by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015; 94:e1819.
Article11. Li XH, Sun CH, Mao R, Huang SY, Zhang ZW, Yang XF, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI enables to accurately grade inflammatory activity in patients of ileocolonic Crohn's disease: results from an observational study. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2017; 23:244–253.12. Huh J, Kim KJ, Park SH, Park SH, Yang SK, Ye BD, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR enterography to monitor bowel inflammation after medical therapy in Crohn's disease: a prospective longitudinal study. Korean J Radiol. 2017; 18:162–172.
Article13. Rimola J, Planell N, Rodríguez S, Delgado S, Ordás I, Ramírez-Morros A, et al. Characterization of inflammation and fibrosis in Crohn's disease lesions by magnetic resonance imaging. Am J Gastroenterol. 2015; 110:432–440.
Article14. Catalano OA, Gee MS, Nicolai E, Selvaggi F, Pellino G, Cuocolo A, et al. Evaluation of quantitative PET/MR enterography biomarkers for discrimination of inflammatory strictures from fibrotic strictures in Crohn disease. Radiology. 2016; 278:792–800.
Article15. Huang SY, Li XH, Huang L, Sun CH, Fang ZN, Zhang MC, et al. T2* mapping to characterize intestinal fibrosis in crohn's disease. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018; 48:829–836.
Article16. Li XH, Mao R, Huang SY, Fang ZN, Lu BL, Lin JJ, et al. Ability of DWI to characterize bowel fibrosis depends on the degree of bowel inflammation. Eur Radiol. 2019; 29:2465–2473.
Article17. Zhang MC, Li XH, Huang SY, Mao R, Fang ZN, Cao QH, et al. IVIM with fractional perfusion as a novel biomarker for detecting and grading intestinal fibrosis in Crohn's disease. Eur Radiol. 2019; 29:3069–3078.
Article18. Chen YJ, Mao R, Li XH, Cao QH, Chen ZH, Liu BX, et al. Real-time shear wave ultrasound elastography differentiates fibrotic from inflammatory strictures in patients with Crohn's disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018; 24:2183–2190.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Role of Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer andMagnetization Transfer MRI in Detecting Metabolicand Structural Changes of Renal Fibrosis in an AnimalModel at 3T
- Imaging with Magnetization Transfer Technique on the Intracranial Tumors
- Inflammatory bowel disease–associated intestinal fibrosis
- Intestinal tuberculosis or Crohn’s disease: a review of the diagnostic models designed to differentiate between these two gastrointestinal diseases
- Treatment of Rectal Stricture with Crohn's Disease Using Local Steroid Injection Following Dilation by Bougienation