Ann Lab Med.
2020 Jul;40(4):326-330. 10.3343/alm.2020.40.4.326.
Carrier Frequency of Spinal Muscular Atrophy in a Large-scale Korean Population
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Hanyang University Guri Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Guri, Korea.
- 2Center for Clinical Medicine, Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Laboratory Medicine, Boramae Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jeannie@snu.ac.kr
- 4GC Genome, Yongin, Korea. changski.md@gmail.com
- KMID: 2470330
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2020.40.4.326
Abstract
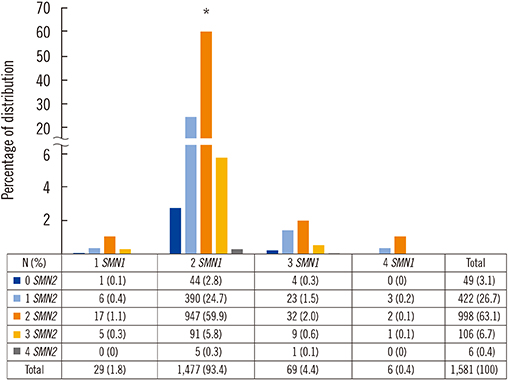
- Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is an autosomal recessive disease characterized by progressive proximal muscle weakness and atrophy. Given the recent introduction of gene therapies, knowledge of the SMA carrier frequency in various populations has become important for developing screening programs for this disease. In total, 1,581 anonymous DNA samples from an umbilical cord blood bank were tested for SMN1 and SMN2 gene copies using a multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification assay. Twenty-nine of the 1,581 newborns [1.83%; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.25-2.66%] were SMA carriers with one copy of SMN1, and no homozygous SMN1 deletion was detected. The carrier frequency in this population was estimated to be 1,834 per 100,000 (95% CI, 1,254-2,659) or 1 in 55 (95% CI, 1/79-1/38). Our data indicate that SMA carriers are not uncommon in the Korean population and may serve as a reference for designing a population screening program in Korea.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Detection of Spinal Muscular Atrophy Using a Duplexed Real-Time PCR Approach With Locked Nucleic Acid-Modified Primers
Jianyan Pan, Chunhua Zhang, Yanling Teng, Sijing Zeng, Siyi Chen, Desheng Liang, Zhuo Li, Lingqian Wu
Ann Lab Med. 2021;41(1):101-107. doi: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.1.101.
Reference
-
1. Prior TW, Leach ME, Finanger E. Spinal Muscular Atrophy. 2000. In : Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, editors. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle;1993–2020. Updated on Nov 2019. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1352/.2. Lunn MR, Wang CH. Spinal muscular atrophy. Lancet. 2008; 371:2120–2133.
Article3. Finkel RS, Mercuri E, Darras BT, Connolly AM, Kuntz NL, Kirschner J, et al. Nusinersen versus sham control in infantile-onset spinal muscular atrophy. N Engl J Med. 2017; 377:1723–1732.
Article4. Little SE, Janakiraman V, Kaimal A, Musci T, Ecker J, Caughey AB. The cost-effectiveness of prenatal screening for spinal muscular atrophy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2010; 202:253.e1–253.e7.
Article5. Zhang L, Bao Y, Riaz M, Tiller J, Liew D, Zhuang X, et al. Population genomic screening of all young adults in a health-care system: a cost-effectiveness analysis. Genet Med. 2019; 21:1958–1968.
Article6. Yoon S, Lee CH, Lee KA. Determination of SMN1 and SMN2 copy numbers in a Korean population using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Korean J Lab Med. 2010; 30:93–96.7. Lee TM, Kim SW, Lee KS, Jin HS, Koo SK, Jo I, et al. Quantitative analysis of SMN1 gene and estimation of SMN1 deletion carrier frequency in Korean population based on real-time PCR. J Korean Med Sci. 2004; 19:870–873.8. Luo M, Liu L, Peter I, Zhu J, Scott SA, Zhao G, et al. An Ashkenazi Jewish SMN1 haplotype specific to duplication alleles improves pan-ethnic carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy. Genet Med. 2014; 16:149–156.9. Verhaart IEC, Robertson A, Wilson IJ, Aartsma-Rus A, Cameron S, Jones CC, et al. Prevalence, incidence and carrier frequency of 5q-linked spinal muscular atrophy–a literature review. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2017; 12:124.
Article10. Chan V, Yip B, Yam I, Au P, Lin CK, Wong V, et al. Carrier incidence for spinal muscular atrophy in southern Chinese. J Neurol. 2004; 251:1089–1093.
Article11. Sheng-Yuan Z, Xiong F, Chen YJ, Yan TZ, Zeng J, Li L, et al. Molecular characterization of SMN copy number derived from carrier screening and from core families with SMA in a Chinese population. Eur J Hum Genet. 2010; 18:978–984.
Article12. Qu XX, Xiao B, Ji X, Jiang WT, Yang ZJ, Tao J. A pilot study on spinal muscular atrophy carrier screening in Shanghai region using real-time PCR. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2013; 30:1–4.13. Gong B, Zhang L, Hou YP, Hu HY, Li HC, Tan MY, et al. Carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy in 4719 pregnant women in Shanghai region. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2013; 30:670–672.14. Tan J, Zhang X, Wang Y, Luo S, Yang F, Liu B, et al. Screening for spinal muscular atrophy mutation carriers among 4931 pregnant women from Liuzhou region of Guangxi. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 2018; 35:467–470.15. Huang CH, Chang YY, Chen CH, Kuo YS, Hwu WL, Gerdes T, et al. Copy number analysis of survival motor neuron genes by multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification. Genet Med. 2007; 9:241–248.
Article16. Chen TH, Tzeng CC, Wang CC, Wu SM, Chang JG, Yang SN, et al. Identification of bidirectional gene conversion between SMN1 and SMN2 by simultaneous analysis of SMN dosage and hybrid genes in a Chinese population. J Neurol Sci. 2011; 308:83–87.17. Su YN, Hung CC, Lin SY, Chen FY, Chern JP, Tsai C, et al. Carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) in 107,611 pregnant women during the period 2005-2009: a prospective population-based cohort study. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e17067.
Article18. Wang KC, Chang CC, Chang YF, Wang SH, Chiang CK, Tsai CP. Evaluation and characterization of a high-resolution melting analysis kit for rapid carrier-screening test of spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurogenet. 2015; 29:113–116.
Article19. Prior TW. Professional Practice and Guidelines Committee. Carrier screening for spinal muscular atrophy. Genet Med. 2008; 10:840–842.
Article20. Committee Opinion No. 691. Committee Opinion No. 691: Carrier screening for genetic conditions. Obstet Gynecol. 2017; 129:e41–e55.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Camptocormia Due to Selective Paraspinal Muscle Atrophy
- A Case of Spinal Muscular Atrophy with Hypertrophy of Calf-Muscles
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 2 in Siblings
- Bilateral Corneal Opacities with Galactokinase Deficiency and Spinal Muscular Atrophy
- Determination of SMN1 and SMN2 Copy Numbers in a Korean Population using Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification