J Korean Soc Radiol.
2020 Jan;81(1):166-175. 10.3348/jksr.2020.81.1.166.
Comparative Analysis of Image Quality and Adverse Events between Iopamidol 250 and Ioversol 320 in Hepatic Angiography for Transcatheter Arterial Chemoembolization
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Radiology, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. yijh7@naver.com
- 2Department of Radiology, Daegu Catholic University Medical Center, Catholic University of Daegu College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Radiology, CHA Gumi Medical Center, CHA University, Gumi, Korea.
- KMID: 2469190
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2020.81.1.166
Abstract
- PURPOSE
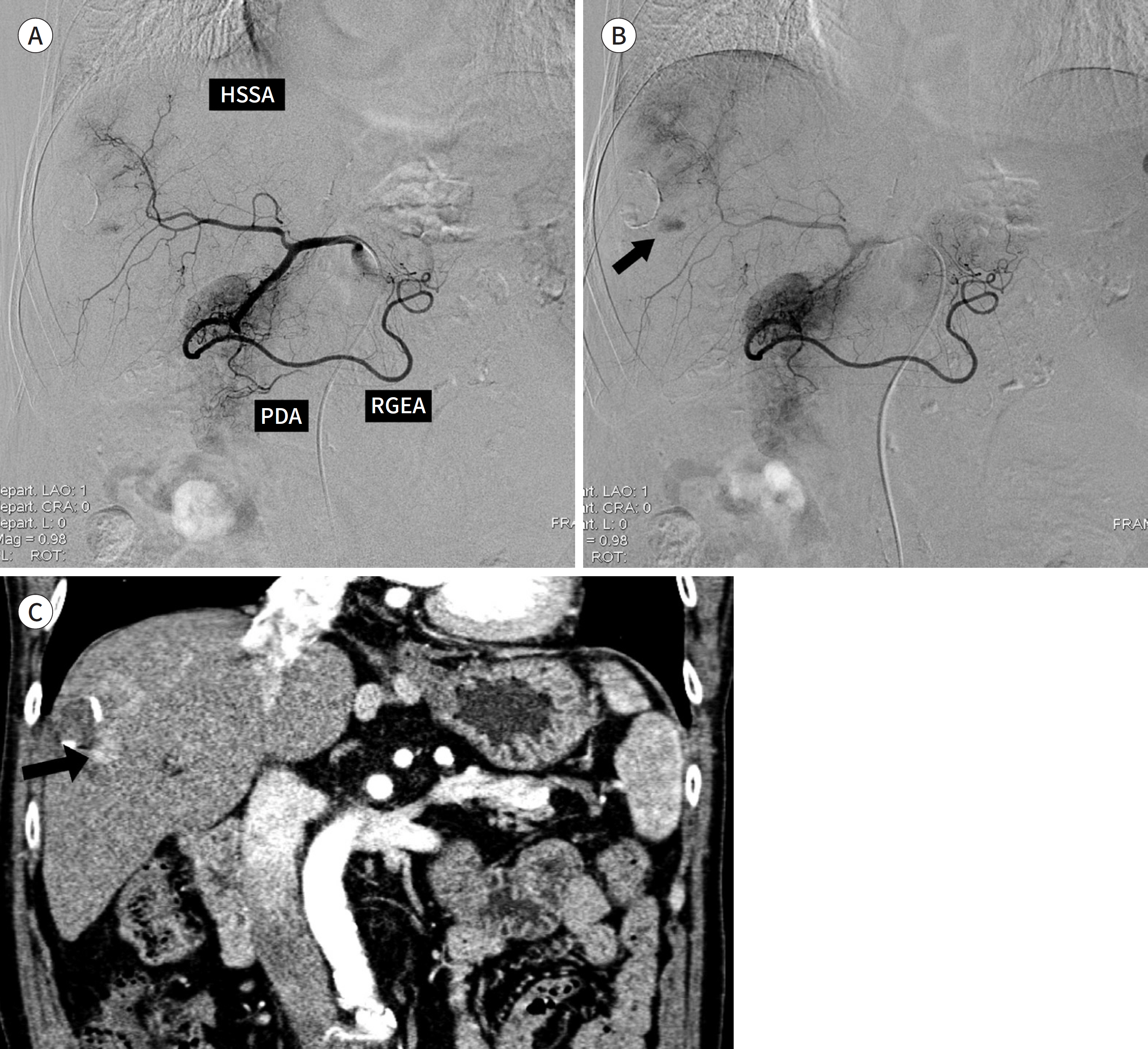
This study aimed to compare the image quality and adverse events between Iopamidol 250 and Ioversol 320 usage during transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Medical records and hepatic angiography from 113 patients who underwent TACE with Iopamidol 250 (44 patients) and Ioversol 320 (69 patients) were retrospectively reviewed. Vessel perception on hepatic angiography was graded into three categories by two radiologists for hepatic subsegmental arteries, the right gastroepiploic artery, right gastric artery, and pancreaticoduodenal artery. Imaging concordance was assessed by comparing the number of detected HCCs on hepatic angiography and CT. The adverse events before and after hepatic angiography were evaluated.
RESULTS
The mean vessel perception scores were 2.92 and 2.94 for Iopamidol 250 and Ioversol 320, respectively. The imaging concordance was 31 (70.5%) and 46 (66.7%) patients for Iopamidol 250 and Ioversol 320, respectively. There were no statistical differences in vessel perception or imaging concordance (p > 0.05). One and six patients experienced nausea for Iopamidol 250 and Ioversol 320, respectively. There was no statistical difference in adverse events (p = 0.24).
CONCLUSION
Iopamidol 250 can be used in hepatic angiography for TACE without significant difference in image quality or occurrence of adverse events from Ioversol 320.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2011; 365:1118–1127.
Article2. Korean Liver Cancer Study Group (KLCSG), National Cancer Center, Korea (NCC). 2014 Korean Liver Cancer Study Group-National Cancer Center Korea practice guideline for the management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Korean J Radiol. 2015; 16:465–522.3. Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018; 391:1301–1314.
Article4. Varela M, Real MI, Burrel M, Forner A, Sala M, Brunet M, et al. Chemoembolization of hepatocellular carcinoma with drug eluting beads: efficacy and doxorubicin pharmacokinetics. J Hepatol. 2007; 46:474–481.
Article5. Sergio A, Cristofori C, Cardin R, Pivetta G, Ragazzi R, Baldan A, et al. Transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): the role of angiogenesis and invasiveness. Am J Gastroen-terol. 2008; 103:914–921.
Article6. Grainger RG. Intravascular contrast media. Br J Radiol. 1982; 55:544.
Article7. McClennan BL, Stolberg HO. Intravascular contrast media. Ionic versus nonionic: current status. Radiol Clin North Am. 1991; 29:437–454.8. Stolberg HO, McClennan BL. Ionic versus nonionic contrast use. Curr Probl Diagn Radiol. 1991; 20:47–88.9. Wolf GL, Arenson RL, Cross AP. A prospective trial of ionic vs nonionic contrast agents in routine clinical practice: comparison of adverse effects. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1989; 152:939–944.
Article10. Saade C, Deeb IA, Mohamad M, Al-Mohiy H, El-Merhi F. Contrast medium administration and image acquisi-tion parameters in renal CT angiography: what radiologists need to know. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2016; 22:116–124.
Article11. Faggioni L, Gabelloni M. Iodine concentration and optimization in computed tomography angiography: current issues. Invest Radiol. 2016; 51:816–822.12. Imai N, Ishigami M, Ishizu Y, Kuzuya T, Honda T, Hayashi K, et al. Transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: a review of techniques. World J Hepatol. 2014; 6:844–850.
Article13. Behrendt FF, Pietsch H, Jost G, Palmowski M, Günther RW, Mahnken AH. Identification of the iodine concentration that yields the highest intravascular enhancement in MDCT angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013; 200:1151–1156.
Article14. Kim EY, Yeh DW, Choe YH, Lee WJ, Lim HK. Image quality and attenuation values of multidetector CT coronary angiography using high iodine-concentration contrast material: a comparison of the use of iopromide 370 and iomeprol 400. Acta Radiol. 2010; 51:982–989.
Article15. Awai K, Inoue M, Yagyu Y, Watanabe M, Sano T, Nin S, et al. Moderate versus high concentration of contrast material for aortic and hepatic enhancement and tumor-to-liver contrast at multidetector row CT. Radiology. 2004; 233:682–688.
Article16. Andreini D, Pontone G, Mushtaq S, Bartorelli AL, Conte E, Bertella E, et al. Coronary stent evaluation with coronary computed tomographic angiography: comparison between low-osmolar, high-iodine concentra-tion iomeprol-400 and iso-osmolar, lower-iodine concentration iodixanol-320. J Cardiovasc Comput To-mogr. 2014; 8:44–51.
Article17. Achenbach S, Paul JF, Laurent F, Becker HC, Rengo M, Caudron J, et al. Comparative assessment of image quality for coronary CT angiography with iobitridol and two contrast agents with higher iodine concentrations: iopromide and iomeprol. A multicentre randomized double-blind trial. Eur Radiol. 2017; 27:821–830.
Article18. Waser M, Kaufmann U, Luescher T, Meier B. Low or high iodine content of contrast medium for cardiac angiography?J Interv Cardiol. 1998; 11:113–116.19. Zhang JJ, Hogstrom B, Malinak J, Ikei N. Effects of viscosity on power and hand injection of iso-osmolar io-dinated contrast media through thin catheters. Acta Radiol. 2016; 57:557–564.
Article20. Morcos SK, Thomsen HS. Adverse reactions to iodinated contrast media. Eur Radiol. 2001; 11:1267–1275.
Article21. Davenport MS, Khalatbari S, Dillman JR, Cohan RH, Caoili EM, Ellis JH. Contrast material-induced nephro-toxicity and intravenous low-osmolality iodinated contrast material. Radiology. 2013; 267:94–105.
Article22. Bettmann MA. Frequently asked questions: iodinated contrast agents. Radiographics. 2004; 24(Suppl 1):S3–S10.
Article23. Namasivayam S, Kalra MK, Torres WE, Small WC. Adverse reactions to intravenous iodinated contrast media: a primer for radiologists. Emerg Radiol. 2006; 12:210–215.
Article24. Park SH, Suh SH, Kim J, Kim EY, Kim DJ, Lee SK, et al. Clinical application of iopamidol (Pamiray® 300) for ce-rebral angiography. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2007; 57:121–127.25. Kim MH, Choi S, Seon HJ, Kim YH, Kim JK, Park JG, et al. Clinical utility of iopamidol (Pamiray®370) for cardiac CT. J Korean Soc Radiol. 2011; 65:27–33.
Article26. Kopp AF, Mortele KJ, Cho YD, Palkowitsch P, Bettmann MA, Claussen CD. Prevalence of acute reactions to iopromide: postmarketing surveillance study of 74,717 patients. Acta Radiol. 2008; 49:902–911.
Article27. Palkowitsch P, Lengsfeld P, Stauch K, Heinsohn C, Kwon ST, Zhang SX, et al. Safety and diagnostic image quality of iopromide: results of a large non-interventional observational study of European and Asian patients (IMAGE). Acta Radiol. 2012; 53:179–186.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Paired Comparison of Iopamidol and Iopromide in Hepatic Arteriography
- Phase III Clinical Trial Comparing Iopamidol 250 mgI/mL and Iopamidol 300mgI/mL in Cerebral Angiography: Multicenteric, Randomized and Double Blind Study
- A Clinical Trial of Iopamidol Myelography in 27 Cases
- Usefulness of Non-ionic, Low Osmolar Contrast Agent (Reyon Iopamidol(R) 300 and Iversion(R) 320) for IVU (Intravenous Urography),Angiography and CT: An Experimental Study in Normal Rabbits
- Multidetector-row CT Angiography of Hepatic Artery: Comparison with Conventional Angiography