Ann Rehabil Med.
2019 Dec;43(6):625-634. 10.5535/arm.2019.43.6.625.
Changes in Language Function and Recovery-Related Prognostic Factors in First-Ever Left Hemispheric Ischemic Stroke
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Physical and Rehabilitation Medicine, Center for Prevention and Rehabilitation, Heart Vascular Stroke Institute, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yun1225.kim@samsung.com
- 2Department of Rehabilitation Medicine and Research Institute of Rehabilitation Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Pusan National University Yangsan Hospital, Pusan National University School of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 4Division of Chronic Disease Control, Center for Disease Prevention, Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Osong, Korea.
- 5Samsung Advanced Institute for Health Sciences & Technology, Sungkyunkwan University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2468689
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2019.43.6.625
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To investigate longitudinal changes in language function in left-hemispheric ischemic stroke patients as well as factors that influence language recovery until 1 year after stroke onset.
METHODS
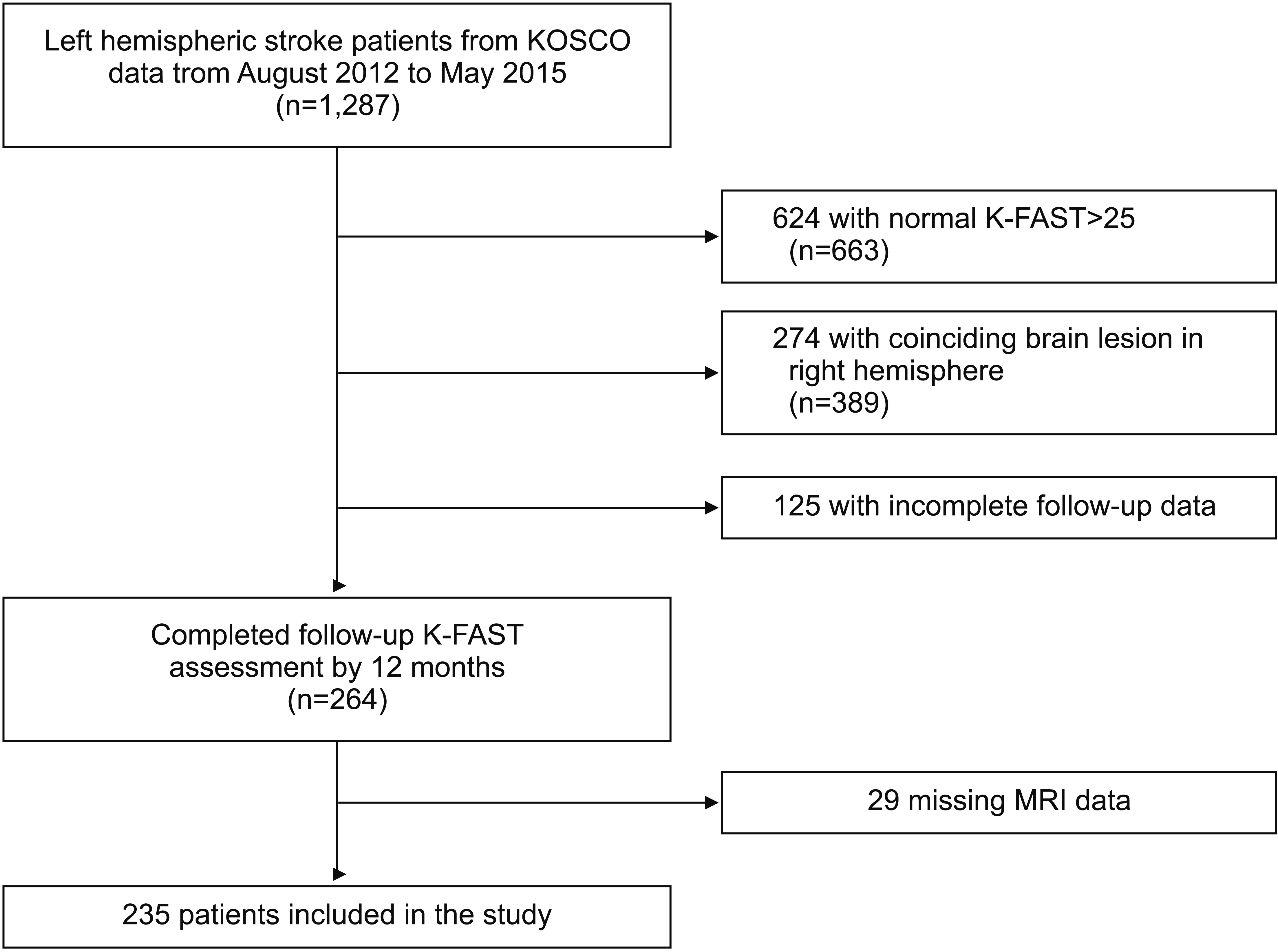
We analyzed data from 235 patients with first-ever left-hemispheric ischemic stroke. All patients completed the Korean version of the Frenchay Aphasia Screening Test (K-FAST) at 7 days (T1), 3 months (T2), 6 months (T3), and 1 year (T4) after stroke onset. Repeated measures analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to investigate changes in language function between time points. Subgroup analysis was performed according to the K-FAST scores at T1. Stroke lesion volume was assessed using diffusion tensor images, and involvement of language-related brain regions was examined. Multiple regression analysis was used to analyze factors influencing improvement of K-FAST score.
RESULTS
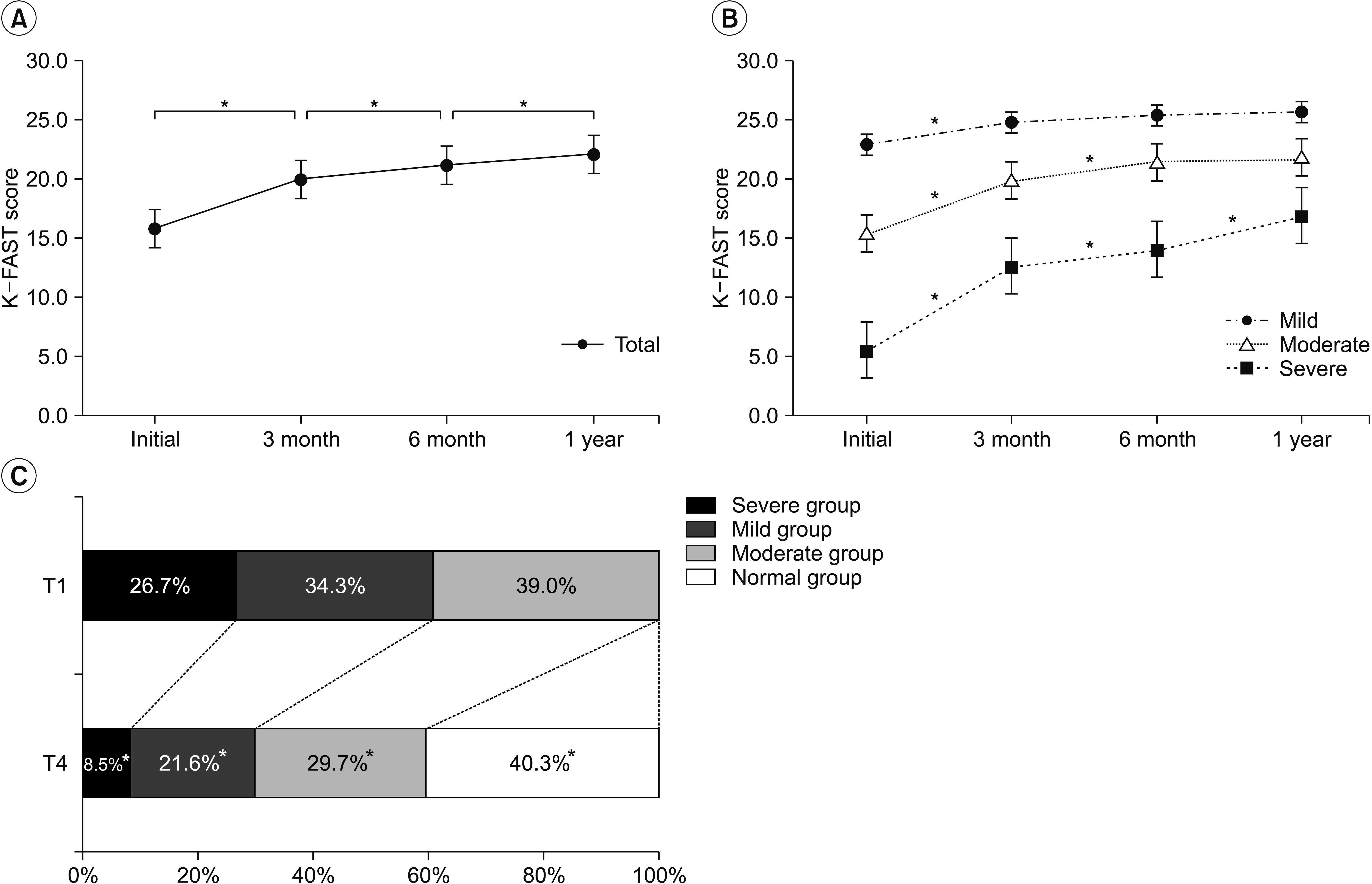
The K-FAST scores at T1, T2, T3, and T4 differed significantly (p < 0.05). In the subgroup analysis, only the severe group showed continuous significant improvement by 1 year. Factors that negatively influenced improvement of language function were the age at onset, initial National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score, and initial K-FAST score, whereas education level and stroke lesion volume positively affected recovery. Involvement of language-related brain regions did not significantly influence long-term language recovery after ischemic stroke.
CONCLUSION
Recovery of language function varied according to the severity of the initial language deficit. The age at stroke onset, education level, initial severity of aphasia, initial NIHSS score, and total stroke lesion volume were found to be important factors for recovery of language function.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Engelter ST, Gostynski M, Papa S, Frei M, Born C, Ajdacic-Gross V, et al. Epidemiology of aphasia attributable to first ischemic stroke: incidence, severity, fluency, etiology, and thrombolysis. Stroke. 2006; 37:1379–84.2. Hoffmann M, Chen R. The spectrum of aphasia subtypes and etiology in subacute stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013; 22:1385–92.
Article3. Charidimou A, Kasselimis D, Varkanitsa M, Selai C, Potagas C, Evdokimidis I. Why is it difficult to predict language impairment and outcome in patients with aphasia after stroke? J Clin Neurol. 2014; 10:75–83.
Article4. Watila MM, Balarabe SA. Factors predicting poststroke aphasia recovery. J Neurol Sci. 2015; 352:12–8.5. Sul B, Kim JS, Hong BY, Lee KB, Hwang WS, Kim YK, et al. The prognosis and recovery of aphasia related to stroke lesion. Ann Rehabil Med. 2016; 40:786–93.
Article6. Plowman E, Hentz B, Ellis C Jr. Post-stroke aphasia prognosis: a review of patient-related and strokerelated factors. J Eval Clin Pract. 2012; 18:689–94.
Article7. Hamilton RH, Chrysikou EG, Coslett B. Mechanisms of aphasia recovery after stroke and the role of noninvasive brain stimulation. Brain Lang. 2011; 118:40–50.
Article8. Chang WH, Sohn MK, Lee J, Kim DY, Lee SG, Shin YI, et al. Korean Stroke Cohort for functioning and rehabilitation (KOSCO): study rationale and protocol of a multi-centre prospective cohort study. BMC Neurol. 2015; 15:42.
Article9. Bradley WG, Daroff RB, Fenichel GM, Jankovic J. Neurology in clinical practice: principles of diagnosis and management. 4th ed. Philadelphia: Butterworth Heinemann;2004.10. Enderby P, Crow E. Frenchay Aphasia Screening Test: validity and comparability. Disabil Rehabil. 1996; 18:238–40.
Article11. Blank I, Balewski Z, Mahowald K, Fedorenko E. Syntactic processing is distributed across the language system. Neuroimage. 2016; 127:307–23.
Article12. El Hachioui H, Lingsma HF, van de Sandt-Koenderman MW, Dippel DW, Koudstaal PJ, Visch-Brink EG. Long-term prognosis of aphasia after stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2013; 84:310–5.
Article13. Maas MB, Lev MH, Ay H, Singhal AB, Greer DM, Smith WS, et al. The prognosis for aphasia in stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012; 21:350–7.
Article14. Lazar RM, Minzer B, Antoniello D, Festa JR, Krakauer JW, Marshall RS. Improvement in aphasia scores after stroke is well predicted by initial severity. Stroke. 2010; 41:1485–8.
Article15. Kertesz A. What do we learn from recovery from aphasia? Adv Neurol. 1988; 47:277–92.16. Forkel SJ, Catani M. Lesion mapping in acute stroke aphasia and its implications for recovery. Neuropsychologia. 2018; 115:88–100.
Article17. Laska AC, Hellblom A, Murray V, Kahan T, Von Arbin M. Aphasia in acute stroke and relation to outcome. J Intern Med. 2001; 249:413–22.
Article18. Pickersgill MJ, Lincoln NB. Prognostic indicators and the pattern of recovery of communication in aphasic stroke patients. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1983; 46:130–9.
Article19. Lendrem W, Lincoln NB. Spontaneous recovery of language in patients with aphasia between 4 and 34 weeks after stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1985; 48:743–8.
Article20. Pedersen PM, Vinter K, Olsen TS. Aphasia after stroke: type, severity and prognosis. The Copenhagen aphasia study. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2004; 17:35–43.21. Berthier ML. Poststroke aphasia: epidemiology, pathophysiology and treatment. Drugs Aging. 2005; 22:163–82.22. Oesch L, Tatlisumak T, Arnold M, Sarikaya H. Obesity paradox in stroke: myth or reality? A systematic review. PLoS One. 2017; 12:e0171334.23. Chiquete E, Cante-Brito C, Villarreal-Careaga J, Murillo-Bonilla LM, Rangel-Guerra R, Leon-Jimenez C, et al. Obesity paradox and functional recovery in firstever acute ischemic stroke survivors: the PREMIER study. Rev Neurol. 2010; 51:705–13.24. Jang SY, Shin YI, Kim DY, Sohn MK, Lee J, Lee SG, et al. Effect of obesity on functional outcomes at 6 months post-stroke among elderly Koreans: a prospective multicentre study. BMJ Open. 2015; 5:e008712.25. Zhao L, Du W, Zhao X, Liu L, Wang C, Wang Y, et al. Favorable functional recovery in overweight ischemic stroke survivors: findings from the China National Stroke Registry. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014; 23:e201. –6.
Article26. Goldenberg G, Spatt J. Influence of size and site of cerebral lesions on spontaneous recovery of aphasia and on success of language therapy. Brain Lang. 1994; 47:684–98.
Article27. Mazzoni M, Vista M, Pardossi L, Avila L, Bianchi F, Moretti P. Spontaneous evolution of aphasia after ischaemic stroke. Aphasiology. 1992; 6:387–96.
Article28. Knopman DS, Selnes OA, Niccum N, Rubens AB, Yock D, Larson D. A longitudinal study of speech fluency in aphasia: CT correlates of recovery and persistent nonfluency. Neurology. 1983; 33:1170–8.
Article29. Naeser MA, Baker EH, Palumbo CL, Nicholas M, Alexander MP, Samaraweera R, et al. Lesion site patterns in severe, nonverbal aphasia to predict outcome with a computer-assisted treatment program. Arch Neurol. 1998; 55:1438–48.
Article30. Naeser MA, Palumbo CL. Neuroimaging and language recovery in stroke. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1994; 11:150–74.
Article31. Butler RA, Lambon Ralph MA, Woollams AM. Capturing multidimensionality in stroke aphasia: mapping principal behavioural components to neural structures. Brain. 2014; 137(Pt 12):3248–66.
Article32. Alexander MP, Naeser MA, Palumbo C. Broca’s area aphasias: aphasia after lesions including the frontal operculum. Neurology. 1990; 40:353–62.
Article33. Basso A, Capitani E, Vignolo LA. Influence of rehabilitation on language skills in aphasic patients. A controlled study. Arch Neurol. 1979; 36:190–6.34. Demeurisse G, Demol O, Coekaerts MJ, De Beuckelaer R, Derouck M, Capon A. Quantitative study of the evolution of speech disorders after a stroke (author’s transl). Rev Med Brux. 1981; 2:923–5.35. Hanlon RE, Lux WE, Dromerick AW. Global aphasia without hemiparesis: language profiles and lesion distribution. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1999; 66:365–9.
Article36. Jung IY, Lim JY, Kang EK, Sohn HM, Paik NJ. The factors associated with good responses to speech therapy combined with transcranial direct current stimulation in post-stroke aphasic patients. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:460–9.
Article37. Kertesz A, McCabe P. Recovery patterns and prognosis in aphasia. Brain. 1977; 100 Pt 1:1–18.
Article38. Kertesz A, Lau WK, Polk M. The structural determinants of recovery in Wernicke’s aphasia. Brain Lang. 1993; 44:153–64.
Article39. Naeser MA, Helm-Estabrooks N, Haas G, Auerbach S, Srinivasan M. Relationship between lesion extent in ‘Wernicke’s area’ on computed tomographic scan and predicting recovery of comprehension in Wernicke’s aphasia. Arch Neurol. 1987; 44:73–82.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Characteristics of Cognitive Impairment in Patients With Post-stroke Aphasia
- Brain Plasticity in Aphasia
- Relationship between Cognitive-perceptual Function and Functional Independence in Patients with Ischemic Stroke
- The Relationship Between Hemispheric Lesion and Autonomic Function by Using Beat-to-Beat Heart Rate Variation
- The Related Factors to Atypical Language Dominance in Patients with Epileptic Foci in the Left Hemisphere