Chonnam Med J.
2020 Jan;56(1):44-49. 10.4068/cmj.2020.56.1.44.
A Comparative Analysis of Clinical Screening Test and Language Specific Test in Language Delay Children
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pediatrics, Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea. sunjun@jbnu.ac.kr
- 2Research Institute of Clinical Medicine, Chonbuk National University, Jeonju, Korea.
- 3Biomedical Research Institute of Chonbuk National University Medical School, Jeonju, Korea.
- KMID: 2468145
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2020.56.1.44
Abstract
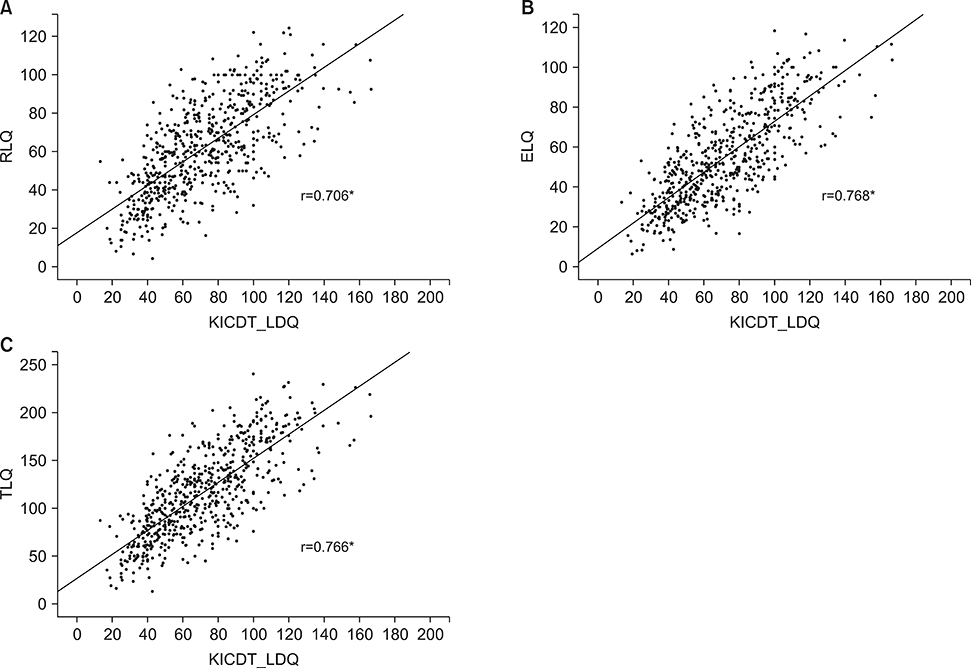
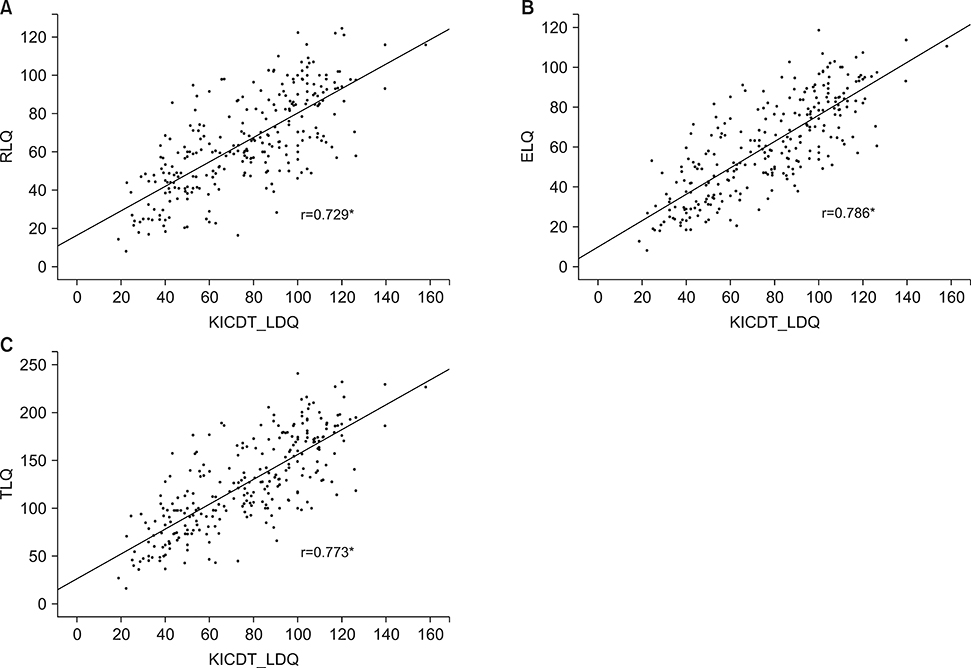
- The aim of this study was to investigate the usefulness of a clinical screening test [the Korean Infant and Child Developmental Test (KICDT)] compared to language specific tests: the sequenced language scale for infant (SELSI) and the Preschool Receptive-Expressive language Scale (PRES) in children with delayed language development. A retrospective chart review was conducted on 615 children who visited the Department of Pediatrics at Chonbuk National University Hospital from January 2013 to December 2016. All patients were evaluated with KICDT as a clinical screening test and SELSI or PRES as a language specific test. Language Developmental Quotients (LDQs) from the KICDT were compared with the Receptive Language Quotient (RLQ) and expressive language quotient (ELQ) from the SELSI or PRES. The sensitivity, specificity and predictive values of LDQ of KICDT were calculated by comparing with SELSI/PRES. Language DQs from the KICDT were significantly correlated with the RLQ (r=0.706), ELQ (r=0.768), and total language quotient (TLQ) (r=0.766) from the SELSI/PRES (p<0.05). In cross tabulation, the patients belonging to the retardation groups in both KICDT and SELSI/PRES were 417 (67.8%). Otherwise, patients belonging to the normal group in KICDT but not in SELSI/PRES were 151 (24.6%). Sensitivity and specificity of LDQ of KICDT relative to SELSI/PRES were 72.3% and 92.2% respectively (p<0.05). Our data suggests that clinical screening tests alone, not cumbersome language specific tests, can determine language developmental delays in children.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Correlation of Language Assessment Batteries of Toddlers With Developmental Language Delay
Jin A Yoon, Shin Wook An, Ye Seul Choi, Jae Sik Seo, Seon Jun Yoon, Soo-Yeon Kim, Yong Beom Shin
Ann Rehabil Med. 2022;46(5):256-262. doi: 10.5535/arm.22045.
Reference
-
1. Burden V, Stott CM, Forge J, Goodyer I. The Cambridge Language and Speech Project (CLASP). I. Detection of language difficulties at 36 to 39 months. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1996; 38:613–631.
Article2. Stevenson J, Richman N. The prevalence of language delay in a population of three-year-old children and its association with general retardation. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1976; 18:431–441.
Article3. Silva PA, McGee R, Williams SM. Developmental language delay from three to seven years and its significance for low intelligence and reading difficulties at age seven. Dev Med Child Neurol. 1983; 25:783–793.
Article4. Rescorla L. The Language Development Survey: a screening tool for delayed language in toddlers. J Speech Hear Disord. 1989; 54:587–599.5. Wong V, Lee PW, Lieh-Mak F, Yeung CY, Leung PW, Luk SL, et al. Language screening in preschool Chinese children. Eur J Disord Commun. 1992; 27:247–264.
Article6. Law J, Boyle J, Harris F, Harkness A, Nye C. Prevalence and natural history of primary speech and language delay: findings from a systematic review of the literature. Int J Lang Commun Disord. 2000; 35:165–188.
Article7. Hohm E, Jennen-Steinmetz C, Schmidt MH, Laucht M. Language development at ten months. Predictive of language outcome and school achievement ten years later? Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2007; 16:149–156.8. Robertson SB, Ellis Weismer S. Effects of treatment on linguistic and social skills in toddlers with delayed language development. J Speech Lang Hear Res. 1999; 42:1234–1248.
Article9. Kim JH, Yum MS, Jeong SJ, Ko TS. Assessment of children with developmental delay: Korean infant and child development test (KICDT) and Korean Bayley scale of infant development-II (K-BSID-II). Korean J Pediatr. 2009; 52:772–777.
Article10. Kim YT. Content and reliability analyses of the Sequenced Language Scale for Infants (SELSI). Commun Sci Disord. 2002; 7:1–23.11. Kim YT. Content and reliability analyses of the Preschool Receptive - Expressive Language Scale (PRES). Commun Sci Disord. 2000; 5:1–25.12. Kamhi AG. Trying to make sense of developmental language disorders. Lang Speech Hear Serv Sch. 1998; 29:35–44.
Article13. Moreno MA. Speech and language delays in young children. JAMA Pediatr. 2015; 169:796.
Article14. Eun BL, Chung HJ, Cho S, Kim JK, Shin SM, Lee JH, et al. The appropriateness of the items of Korean Ages and Stages Questionnaires (K-ASQ) developmental screening test in Korean infants and children. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2014; 22:29–41.15. Im SH, Han EY, Song J. Clinical application of neurodevelopmental assessment for infants and toddlers. J Korean Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2012; 23:175–180.
Article16. Sung MH, Choi JM, Yoo JH, Lee YS, Hwang KG, Lee YA. Developmental quotient of very low birth weight infants assessed by Korean infant development screening test. J Korean Soc Neonatol. 2004; 11:152–159.17. Shin DH, Lee HS, Lee JY, Choi BM, Eun BL, Hong YS, et al. Usefulness of Korean infant developmental screening test in premature infants. Korean J Pediatr. 2005; 48:1337–1341.18. Choi HW, Jeong MH, Lee EH, Jeong SJ, Yum MS, Ko TS. Korean Infant and Child Developmental Test (KICDT) in children with epilepsy. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2010; 18:40–48.19. Kim SG, Kim NC, Lee IK, Oh MH, Kim YC, Lee HJ. Comparative study between Bayley scales of infant development-II and Korean infant and child developmental test in infants younger than 12 months. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2005; 13:48–56.20. Chung HJ, Eun BL, Kim HS, Kim JK, Shin SM, Lee JH, et al. The validity of Korean Ages and Stages Questionnaires (K-ASQ) in Korean infants and children. J Korean Child Neurol Soc. 2014; 22:1–11.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Developmental Delay of Language in Cerebral Palsy Children
- Speech Delay of Children with Mental Retardation
- Clinical Usefulness of Capute Developmental Test as a Screening Test for Detecting the Language Delay
- Relationship of Language, Intelligent and Social Quotients in Children with Speech and Language Disorder
- Diagnosis of Speech Disorder and Language Developmental Delay in Korean Preschoolers